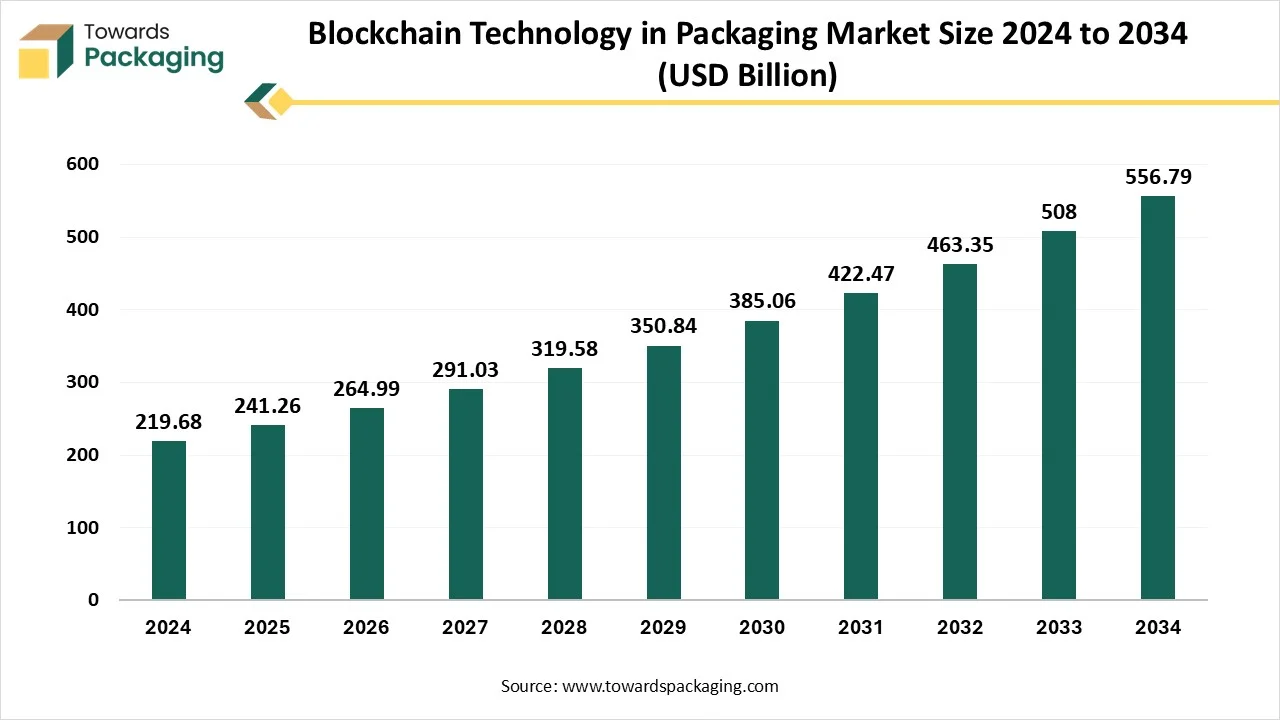
The blockchain technology in packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 265.04 billion in 2026 to USD 616.82 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 9.84% from 2026 to 2035. This report covers complete segmentation by component, blockchain type, provider, technology integration, and application highlighting dominant segments such as platform components, private blockchain, infrastructure providers, track and trace, and food & beverage end use.
It includes detailed regional data across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa, along with trade data, value chain analysis, competitive mapping, and profiles of leading companies such as Block, IBM, Coinbase, Suffescom Solutions, and Chainalysis.
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger system that records transactions across different computers in a way that protects against altering or tampering with data. Every"block" in the chain includes transaction data, and once it is added to the chain, it cannot be changed. This decentralized nature of blockchain makes it heavily secured and transparent, too, which enables all parties, including the transaction, to access the information in real-time. In addition to developing compliance, blockchain serves several other significant advantages to the industry with respect to simplifying and optimizing the sales and procurement procedure.
Blockchain in procure-to-pay can assist in buying orders and linked parties with an intelligent contract that fully automates the transaction all the way through to payment. In the Order to Cash (O2C) cycle, a smart contract provides the capability to choose a payment option to streamline the usage of dynamic factoring and discounting. As the packaging industry moves in front of more sustainable and responsible operations sustained by a transparent supply chain, blockchain will pave the way for uniting the company with a single source of truth, assisting businesses in achieving the trust of consumers while making sure of rigorous compliance.
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 241.30 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 616.82 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 9.84% |
| Market Segmentation | By Component, By Blockchain Type, By Provider, By Technology Integration and By Application |
| Top Key Players | Block, IBM, CoinBase, Suffescom Solutions, Chainalysis |
In terms of packaging, AI and blockchain technologies are creating a huge impact as they develop the sustainability, efficiency, and transparency of packaging. AI can serve predictive assistance and data analytics to grow packaging designs and material usage, reduce waste, and finally increase product lifespan. At the same time, blockchain ensures traceability, product integrity, and security throughout the supply chain to ensure consumers' and stakeholders’ trust. The merger of blockchain and AI can serve the main benefits as it is linked to packaging. AI's data processing will serve useful insights that they can utilize to perfectly update their packaging, and when combined with blockchain, they can make sure that their actionable insights are being tracked and are transparent.
Blockchain is transforming the food supply chain, and Holographs is at the front of this change. Regular supply chains are riddled with inefficiencies, where tracking the origin and journey of food products is time-consuming and prone to issues. Holograms, which are a blockchain-based solution, solve this by serving as an immutable, decentralized ledger that monitors every step of the procedure. From the farm to the user, each movement is logged with accuracy, making sure of food safety, transparency, and authenticity. Blockchain technology has already been applied across various food chains and is expected to grow further. It reduces costs for manufacturers and retailers by lowering delays and improving reliability. The transparency served by blockchain makes food recall steps more efficient. Furthermore, blockchain makes sure that consumers receive their money's worth and that their funds are also not assisting unethical practices such as slavery and child labor, which is important to ensure that the data stored on the blockchain is of good quality to maintain accessibility and consistency of information whenever needed.
One of the main challenges to using blockchain in packaging is scalability. While blockchain serves promising potential, its decentralized nature can cause transaction speed to lower significantly as network size and data volume grow. Public blockchains like Ethereum, which require all participating nodes that validate every transaction, are especially prone to these waits. This can be the main challenge for worldwide supply chains, in which high transaction volumes are the norm. Efforts to grow blockchain scalability are in progress, with solutions like sharding and off-chain transactions displaying potential.
Sensors in packaging can manage variables like humidity, temperature, pressure, and gas levels, alerting stakeholders if the product's integrity is at risk. This is complicated in food safety and pharmaceutical assistance. From NFC and RFID Tags to scannable QR codes, smart labels can improve consumer trust and traceability. Shoppers can check authenticity, recheck ingredients, and even verify the product's journey from source to shelf. Technologies like antimicrobial layers, oxygen scavengers, and moisture absorbers assist in expanding shelf life, especially in sensitive and high-value medical products. Current smart packaging mixes biodegradable materials and markets circular economy practices. Combined with artificial intelligence, businesses can manage usage and assist smart reordering or recycling initiatives, too.
Platform dominated the market with a 65.4% share in 2024. Established in the year 2013, Ethereum is one of the oldest and most found blockchain platforms. It serves as a truly decentralized blockchain and includes rigid support for intelligent contracts. , a kind of self-executing program that is considered a capable blockchain killer app. Besides this role as a blockchain platform that underpins enterprise uses, Ethereum has its self cryptocurrency called ether. The Ethereum platform has seen widespread acceptance by technologists who constructed decentralized applications (dApps) that run on the Ethereum network. For instance, there are various platforms and exchanges for non-fungible tokens, a kind of digital asset that can be exchanged on a blockchain. Ethereum has a matured ecosystem of tools for writing intelligent contracts utilizing the Solidity programming surrounding, which runs on the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
Blockchain technology serves inventive solutions to some of the packaging industry's most pressing challenges, especially around traceability, transparency, and trust. By making secure, tamper-proof digital records, blockchain can manage every step of a package lifecycle- from raw material sourcing to production, delivery, and distribution. This end-to-end visibility assists companies in combating counterfeiting, ensuring regulatory compliance, and verifying sustainability claims, as consumers increasingly demand proof of ethical and eco-friendly practices. Intelligent contracts on blockchain networks can automate transactions and quality checks between manufacturers, suppliers, and retailers, which lowers paperwork and the risk of errors or fraud.
Private blockchain dominated the market with a 55.32% share in 2024. Private blockchains have gained attention in the year 2025 because they allow companies to have complete control over network access, data visibility, and decision-making authority. As compared to public blockchains, they serve much higher throughput, provide privacy, and reduce latency too. They are specifically perfectly suited for sectors bound by regulatory requirements. Enterprises also benefit from the audibility and automation that intelligent packaging brings. Once classified, these self-executing agreements lower the demand for intermediaries and streamline operations. Compliance is solved since the company can enforce fine-grained access controls, make verifiable logs, and make sure only verified parties communicate with sensitive data.
Public blockchains are "permissionless" and distribute the data system's potential to record transactions and data, and are accessible to any member of the public. Centralized entities or particulars do not completely control these blockchain networks. This shows that any interested parties can watch the transactions and participate in any blockchain procedure. Some of these processes include validation, transaction execution, and even mere reading of the blockchain's transactions or data. In simpler terms, a public blockchain has no restrictions. Hence, anyone with a suitable device and internet connection can easily access it and start executing, validating, viewing, or transacting in it.
Infrastructure providers dominated the market with a 61.12% share in 2024. Blockchain as infrastructure in packaging serves as a foundational digital backbone that securely connects all stakeholders across the supply chain. Instead of acting as just another software layer, blockchain functions as a decentralized ledger that records and checks every transaction and data point in real time. This infrastructure allows packaging manufacturers, logistics, suppliers, retailers, providers, and even end consumers to access a tamper-proof source of truth. This decentralized architecture lowers the risk of data manipulation, which strengthens and traces compliance with growing regulations around sustainability and product safety.
Blockchain technology as a protocol provider in packaging develops the standardized rules and frameworks that allow secure, checked data exchange across the complete value chain. Acting as a protocol layer, blockchain defines how information is shared, recorded, and validated among participants without depending on a central authority.
For the packaging sector, this means that each stakeholder, from raw material suppliers to transformers, logistics providers, and brand owners, can operate on a prevalent set of cryptographic protocols that ensure data integrity and authenticity. By operating as a protocol, blockchain empowers packaging companies to develop, reduce fraud, and operational efficiency, and meet growing consumer and regulatory demands for accountability.
Track and Trace dominated the market with a 38.23 % share in 2024. Blockchain technology enables packaging companies to track the complete journey of products in a secure, transparent way. Every step- from sourcing raw materials to distribution, production, and delivery -is recorded as a time-stamped transaction on an immutable ledger. This makes sure that each movement and handling detail is verifiable and cannot be altered or deleted. This capability not only assists in preventing counterfeiting and tampering but also constructs greater trust in supply chains by serving product authenticity and compliance at every stage.
Smart contracts and automated transactions are self-executing agreements depending on blockchain technology. They ensure the enforcement of contract terms through deconcentrated networks without depending on regular intermediaries such as banks, lawyers, and government entities. At their main, smart contracts shift contract terms into computer code that is categorized into the blockchain. Once the predefined conditions are aligned, the contract is automatically activated, executing the related actions and ensuring efficiency, transparency, and security. This mechanism not only vanishes the demand for intermediaries but also mainly reduces transaction costs while developing the reliability and accuracy of contract execution.
Blockchain technology is gaining attention in the food and beverage industry, specifically for intensifying traceability and ensuring food safety compliance. By utilizing blockchain, producers can make immutable records of a product's journey with the help of a supply chain, from farm to table. This will not only develop transparency but also assist in responding quickly to food safety incidents. With the assistance of Blockchain technology, it is possible to record each transaction linked to food products, from farm to consumer. That can enable suppliers to track product movement, along with other activities. Doing so can improve food safety and transparency between those at different parts of the food chain, and track inventory management.
Blockchain technology in the pharmaceutical supply chain can assist in solving many of these problems by providing secure, transparent tracking and verifying at every stage. One of the critical functions of blockchain in the supply chain is to protect against counterfeiting and make sure that counterfeited drugs do not reach the end user. Blockchain develops control over the supply chain. Actual time tracking allows producers and distributors to track and manage supply chain procedures. This improves several components, including delivery time and inventory management, and different bottlenecks, too. In the pharmaceutical supply chain blockchain, user refunds can be started automatically.
QR Codes and smart labels integrated with blockchain technology serve real-time access to transparent and checked product information. Whenever scanned, these labels connect directly to blockchain records, enabling consumers and supply chain partners to view the product's starting, carrying history, and authenticity. This absorption grows traceability, combats counterfeiting, and assists sustainability claims by serving a secure,tamper-proof digital trail. It also allows interactive packaging experiences, in which brands can share certifications, usage tips, or promotional content directly through the label, all backed by trustworthy blockchain data.
NFC (Near Field Communication) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) integration with blockchain technology makes a powerful solution for secure, automated tracking and authentication in terms of packaging. These smart tags store unique digital identifiers that are linked to immutable blockchain records, allowing products to be checked instantly at any point in the supply chain.
As items move through production, warehousing, and distribution, RFID readers or NFC-allowed devices automatically update the blockchain ledger with actual time location and condition data. This seamless connectivity grows inventory precision, protects against tampering and counterfeiting, and gives brands and consumers trusted visibility into a product's complete lifecycle.
The urge for blockchain technology in packaging is growing fast across North America and Canada, driven by rising consumer expectations for traceability, transparency, and sustainability in the United States. Industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and e-commerce are accepting blockchain to develop supply chain security, protect against counterfeiting, and ensure compliance with strict regulations.
Brands are mixing blockchain with smart packaging solutions such as QR codes and RFID to serve consumers with actual-time, verifiable product information. In Canada, growing interest in eco-friendly practices and a regulatory push for sustainable sourcing are further fueling blockchain adoption in packaging. Government-backed invention programs and partnerships between tech firms and packaging companies are also assisting this development, making North America a main player in blockchain-driven packaging advancements.
In Asian countries, the urge for blockchain technology in packaging is gaining strong attention as manufacturers, governments, and consumers give importance to transparency and supply chain security. Countries like Japan, China, South Korea, and India are finding increased acceptance of blockchain to combat counterfeiting, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, food safety, and premium consumer goods.
Growing e-commerce volumes and stricter regulations around product authenticity and sustainability are further increasing this trend. Companies are mixing blockchain with QR codes and RFID smart labels to serve end-to-end traceability and construct trust with tech-savvy consumers who expect instant access to check product information.

By Component
By Blockchain Type
By Provider
By Technology Integration
By Application
By End User Industry


February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026