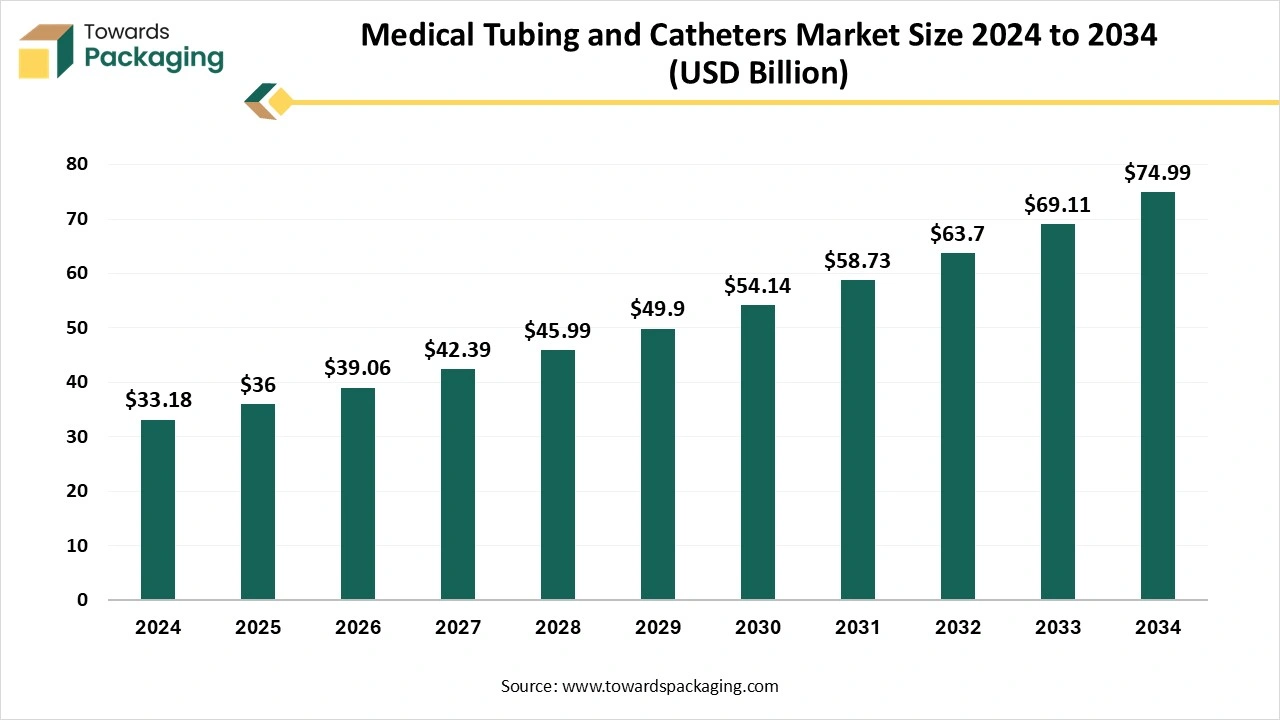
The medical tubing and catheters market is forecasted to expand from USD 39.06 billion in 2026 to USD 81.40 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2026 to 2035. Additionally, the market is driven by the rise in surgical procedures and innovations like smart catheters and sensor-embedded tubing. The key players in the market include Teleflex Incorporated, L. Gore & Associates, and Medtronic, with North America leading in market share, followed by strong growth in the Asia Pacific region.
Medical tubing refers to flexible, hollow cylinders or pipes used in medical and laboratory settings to transport fluids or gases. These tubes are made from biocompatible materials and are essential components in many medical devices and procedures. On the other hand, medical catheters are thin, flexible tubes made of medical-grade materials (like silicone, latex, or plastic) that are inserted into the body to treat diseases or perform a medical procedure. They are used to: drain fluids (like urine or blood), deliver medications or nutrients, access the bloodstream (e.g., for dialysis or intravenous treatments), and open up blocked passages (e.g., in the heart or blood vessels), etc.
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 36.00 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 81.40 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 8.5% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Market Segmentation | By Material, By Application, By End-User and By Region |
| Top Key Players | Teleflex Incorporated, L. Gore & Associates, The Lubrizol Corporation, Saint-Gobain Performance Plastics, Zeus Industrial Products, Inc., Freudenberg Medical, Tekni-Plex, Raumedic AG, The Dow Chemical Company, Nordson Corporation |
Smart Catheters and Sensor-Embedded Tubing
Modern catheters are increasingly integrated with sensors that monitor real-time physiological parameters such as pressure, temperature, and fluid flow. These smart devices enhance patient monitoring, enable early detection of complications, and reduce the need for invasive procedures. For instance, hospitals in South Korea have implemented sensor-embedded urinary and enteral feeding tubes, leading to a 22% reduction in intervention delays.
Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Materials
The industry is shifting towards sustainable materials, with a focus on biodegradable polymers like polylactic acid. These materials reduce medical waste and eliminate the need for device removal surgeries, particularly benefiting pediatric and geriatric care. Additionally, manufacturers are adopting DEHP-free and latex-free materials to meet regulatory standards and enhance patient safety.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Innovations in manufacturing are enabling the production of complex and customized tubing: 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and creation of intricate tip geometries, facilitating personalized catheter designs. While multi-lumen and co-extruded tubing designs incorporate multiple channels within a single tube, enabling simultaneous functions like infusion, aspiration, and sensing, thereby simplifying medical equipment. Micro-extrusion technology enables the production of ultra-thin tubing for applications in neonatal and neurovascular care.
Antimicrobial and Drug-Eluting Coatings
To combat infections associated with catheter use, manufacturers are developing tubing with antimicrobial coatings or drug-eluting capabilities. For example, antimicrobial-coated PVC tubing has demonstrated a 91% reduction in bacterial colonization in clinical trials involving ICU patients.
Robotic and Magnetic Navigation
Robotic magnetic navigation (RMN) systems are being employed to guide magnetic-tipped catheters through complex vascular pathways. This technology enhances catheter stability and precision during procedures like cardiac ablations, reducing reliance on fluoroscopy and associated radiation exposure.
AI can process real-time data from sensor-enabled catheters to detect early signs of infection, blockage, or dislodgement. Artificial intelligence integration alert healthcare staff automatically, reducing response time. It helps to predict complications before they become critical. For instance, AI-based algorithms can analyze temperature, flow rate, and pressure in urinary catheters to detect urinary tract infections early. AI tools like generative design and machine learning can create customized catheter geometries based on patient anatomy. It simulates performance (fluid dynamics, flexibility) to reduce trial-and-error in development. It identifies optimal materials and coatings for durability and biocompatibility.
Statistical AI models can detect production anomalies that lead to device failure. AI can help select the right type of catheter for individual patients by analysing: medical history, imaging, and lab reports. Risk of infection, mobility issues, or chronic conditions. For instance, in home dialysis, AI tools can tailor catheter care protocols based on a patient’s lifestyle and daily metrics. In catheter and tubing production, AI-powered vision systems can inspect micro-defects in real-time. AI integration helps in predictive analytics can forecast machine maintenance needs, reducing downtime.
When catheters are paired with IoT devices, AI systems can: monitor patients remotely (especially in elderly or post-op care), trigger alerts to caregivers or physicians, and adjust infusion or drainage rates based on AI-driven decisions. It can help regulate drug-eluting catheters, ensuring precise dosage delivery based on real-time feedback and personalized dosing schedules depending on patient response. AI integrated with robotic magnetic navigation systems can: guide catheters through complex pathways (e.g., cardiac, neuro), minimize operator error, and reduce radiation exposure during procedures.
Increase in Surgical Procedures
A rise in surgeries and hospital admissions due to trauma, chronic illnesses, and elective surgeries means more use of catheters for fluid management, anesthesia, and monitoring. During and after surgery, patients require intravenous (IV) lines, catheters, and drainage tubing for: Administering anesthesia, medications, or fluids, managing blood loss, and removing excess fluids. This creates consistent demand for IV tubing, epidural catheters, and suction catheters. The rise in minimally invasive surgeries relies heavily on catheter-based tools for diagnostics and treatment. Examples include balloon catheters for angioplasty or guide catheters for stent placement. Most surgeries require urinary catheterization to manage bladder function during and post-surgery. Post-operative patients, especially in orthopedic, neurological, or cardiac care, often require prolonged urinary catheter use.
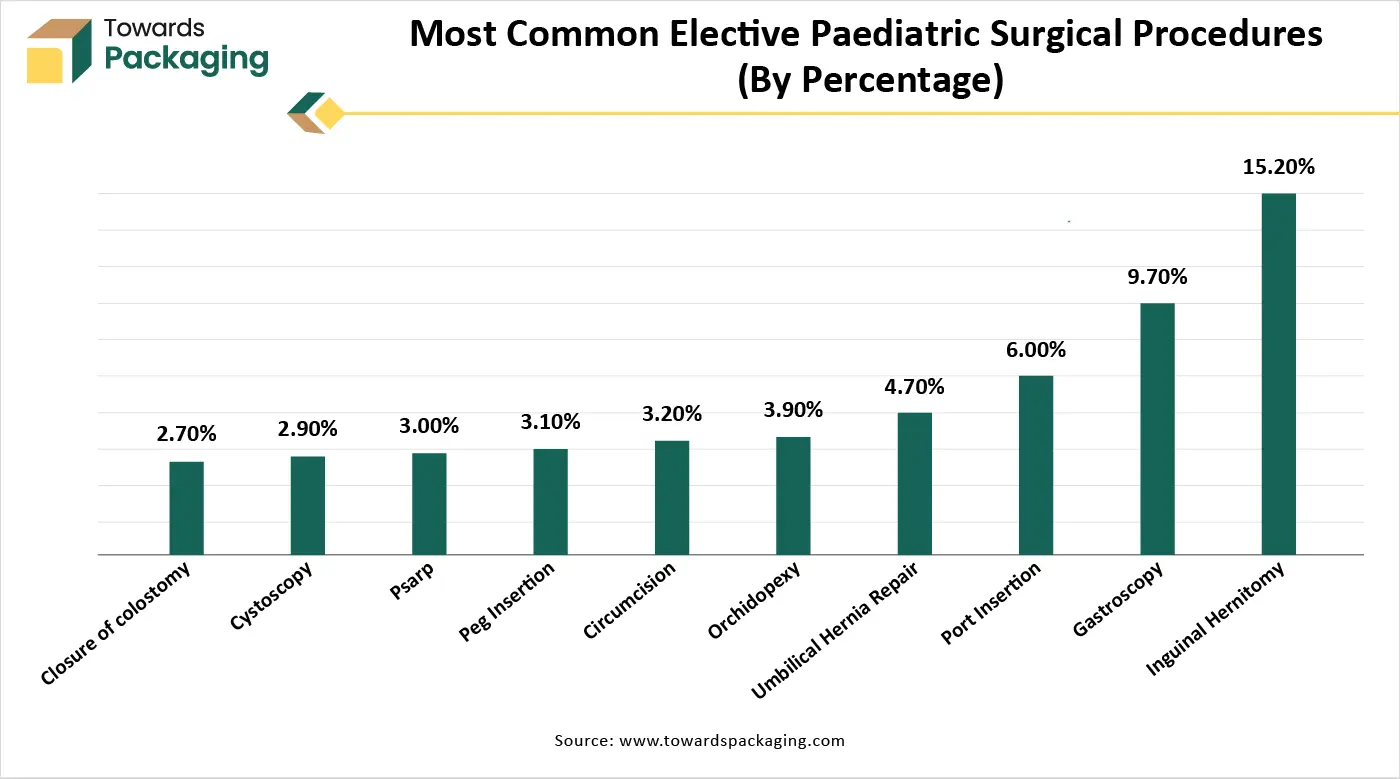
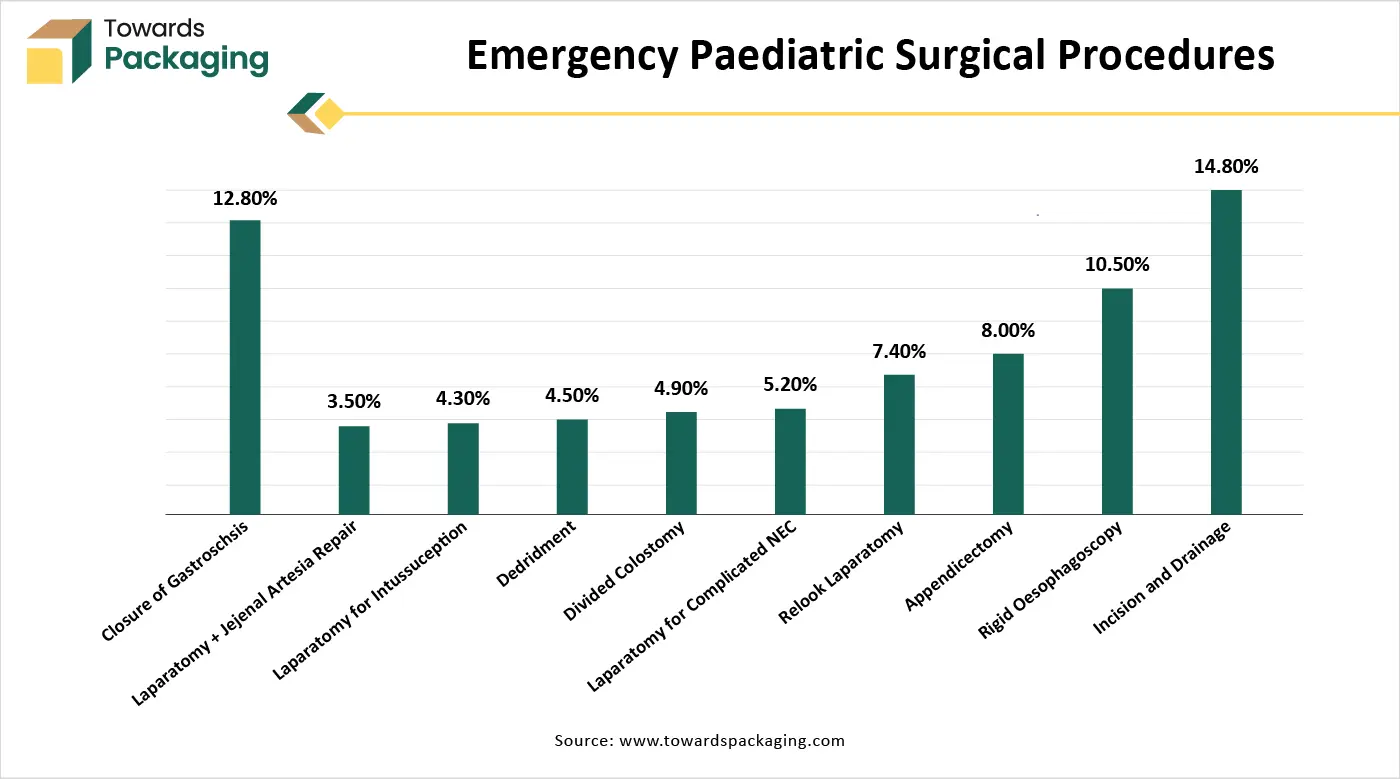
Shortage of Skilled Professionals and Stringent Regulatory Approvals
The key players operating in the medical tubing and catheters market are facing issues due to a shortage of skilled professionals and stringent regulatory approvals in the market. Advanced catheter-based procedures (like cardiac ablation or neurointerventions) require highly trained professionals. In many countries, the lack of skilled surgeons, interventional radiologists, and technicians hinders adoption. Catheters and medical tubing are Class II or III medical devices (depending on the country), requiring thorough testing for biocompatibility, safety, and sterility. Delays in approvals by agencies like the FDA (USA) or CE (Europe) can slow down product launches and innovation.
Advancements in Minimally Invasive Procedures
Growing demand for minimally invasive surgeries has increased the use of catheters for diagnostic and interventional purposes. Catheter-based interventions reduce hospital stay and recovery time. For instance, in March 2025, Smart healthcare has made yet another significant advancement in response to the growing need for surgical accuracy and quicker patient recovery. Chang Gung Memorial Hospital has been at the forefront of using Da Vinci robotic surgical systems since 2006. The hospital established its dominance in the sector by performing more than 12,000 robotic surgeries by the end of 2024, making up one-sixth of Taiwan's robotic treatments. Chang Gung is leading Taiwan into a new era of minimally invasive surgery globally with its strong healthcare system, thanks to its technical know-how and clinical accomplishments.
The polyvinyl chloride (PVC) segment registered its dominance over the global market in 2024. PVC can be made soft and flexible when combined with plasticizers, which is ideal for tubing and catheters that must be pliable yet durable. Medical-grade polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is biocompatible, meaning it can safely come into contact with blood, tissues, and other bodily fluids without causing adverse reactions. PVC resists a wide range of chemicals and solvents, making it suitable for use with various drugs and sterilization agents. It can be sterilized using different methods, including steam (autoclaving), ethylene oxide (EtO), and gamma radiation, making it versatile for different healthcare settings.
The fluoropolymers segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years. These materials are highly regarded in medical devices for their distinctive characteristics, such as chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance, low friction, and ability to preserve sterility. Such materials can be easily extruded into various shapes and sizes and customized to meet specific hardness or flexibility demands, which is crucial for creating different types of tubing and catheters. Fluoropolymers-based medical tubings are commonly utilized in scenarios that require biocompatibility, efficient fluid handling, and precise control.
The bulk disposable tubing segment dominated the market in 2024 and is expected to maintain its position throughout the forecast period. Bulk disposable tubing ensures no cross-contamination between patients. It comes in pre-sterilized packaging, suitable for immediate surgical use. The bulk disposable tubing reduces the risk of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). It is made from medical-grade materials such as PVC, silicone, polyurethane, or TPE (thermoplastic elastomer). These materials are non-toxic and compatible with human tissues and fluids. The bulk disposable tubing is designed to be flexible enough for complex surgical maneuvers but durable enough to resist kinking or collapsing during use. Many tubes are transparent, allowing medical staff to visually monitor the flow of fluids or air. The bulk disposable tubing is able to withstand exposure to medications, body fluids, and sometimes heat if brief sterilization is needed before use. It can also be easily cut or connected with fittings, catheters, or surgical devices. It is produced in bulk at low cost, making it affordable for single-use in operating rooms.
The hospitals segment led the market with a significant share in 2024. Hospitals handle the majority of surgeries, many of which require extensive use of medical tubing and catheters for fluid management, drug delivery, drainage, and monitoring. Conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and kidney disorders often require catheter-based interventions, long-term IV access, or dialysis services, predominantly provided in hospitals. Older adults typically need more frequent and complex medical care, including catheterization, oxygen therapy, and infusion treatments, driving demand in hospital settings. Hospitals are equipped with the necessary infrastructure for advanced and high-risk procedures, which use a wider range of sophisticated tubing systems and catheters. Higher rates of hospital admissions—especially for acute conditions, infections, and post-operative care—increase the usage of disposable medical tubing and catheters. Hospitals increasingly adopt single-use, sterile devices like disposable tubing and catheters to prevent hospital-acquired infections, aligning with strict infection control protocols. Growth in hospital construction and modernization in countries like India, China, and Brazil is increasing institutional demand for medical consumables, including tubing and catheters.
North America held the largest share of the medical tubing and catheters market in 2024, owing to technology advancements and advanced infrastructure in the region. North America has a highly developed healthcare system with large hospital networks, surgical centers, and clinics that require massive volumes of medical tubing and catheters. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. FDA ensure the safety and efficacy of medical devices, which supports the growth of high-quality, standardized tubing and catheter products. In North America presence of leading medical device manufacturers supports the dominance. North America is a hub for medical innovation, with continuous development of specialized tubing materials.
The strong regulatory framework in the country drives the U.S. market. The U.S. has the highest per capita healthcare expenditure, driving demand for advanced medical devices, including catheters and tubing. Home to leading medical device manufacturers. The FDA ensures quality and safety, setting global standards that enhance trust in U.S.-produced devices. Streamlined approval pathways encourage rapid innovation and market access. The U.S. has a dense network of hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs), and specialized clinics that perform millions of procedures annually, many involving catheters and tubing. High standards for infection control drive demand for single-use disposable medical tubing, making the U.S. a major consumer of bulk tubing products.
Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the medical tubing and catheters market during the forecast period. Countries like China, India, and Southeast Asia are heavily investing in hospitals, diagnostic centers, and surgical facilities. The region has a rapidly growing elderly population, especially in Japan, China, and South Korea. Countries like Thailand, India, and Singapore are leading destinations for affordable, high-quality surgeries.
The strong domestic manufacturing facilities in the country drive the Chinese medical tubing and catheters market. China has one of the largest elderly populations, driving high demand for catheters and feeding or drainage tubes. China is a global hub for medical device manufacturing, including bulk production of medical tubing. Government programs like Healthy China 2030 promote greater access to quality healthcare. The NMPA is streamlining device approvals and encouraging innovation, especially for high-value consumables like catheters.
The India medical tubing and catheters market is driven by the expanding healthcare access in the country. India is a global destination for affordable surgeries, especially in cardiology, urology, and orthopedics, all involving catheter-based interventions. India is encouraging the Make in India manufacturing of medical devices. Government schemes like Ayushman Bharat aim to cover hundreds of millions with free or subsidized healthcare. India has a thriving private hospital network offering high-quality, cost-effective surgical care.
The European market is expected to grow at a notable rate in the foreseeable future. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Medical Device Regulation (MDR) ensure high safety, performance, and quality standards. Encourages widespread use of high-grade, biocompatible tubing and catheters, especially in surgical and critical care settings. Europe is a leader in R&D, particularly in medical device materials and minimally invasive technologies. In Europe, the presence of leading manufacturers like Coloplast (Denmark), B. Braun (Germany), and Fresenius Medical Care (Germany) supports technological leadership in catheter systems and tubing innovation. European manufacturers not only serve domestic markets but also export globally, particularly to North America, the Middle East, and Asia. Germany, France, and the Netherlands are major exporters of medical-grade polymer tubing and precision catheters.

By Material
By Application
By End-User
By Region




January 2026
January 2026
February 2026
February 2026
