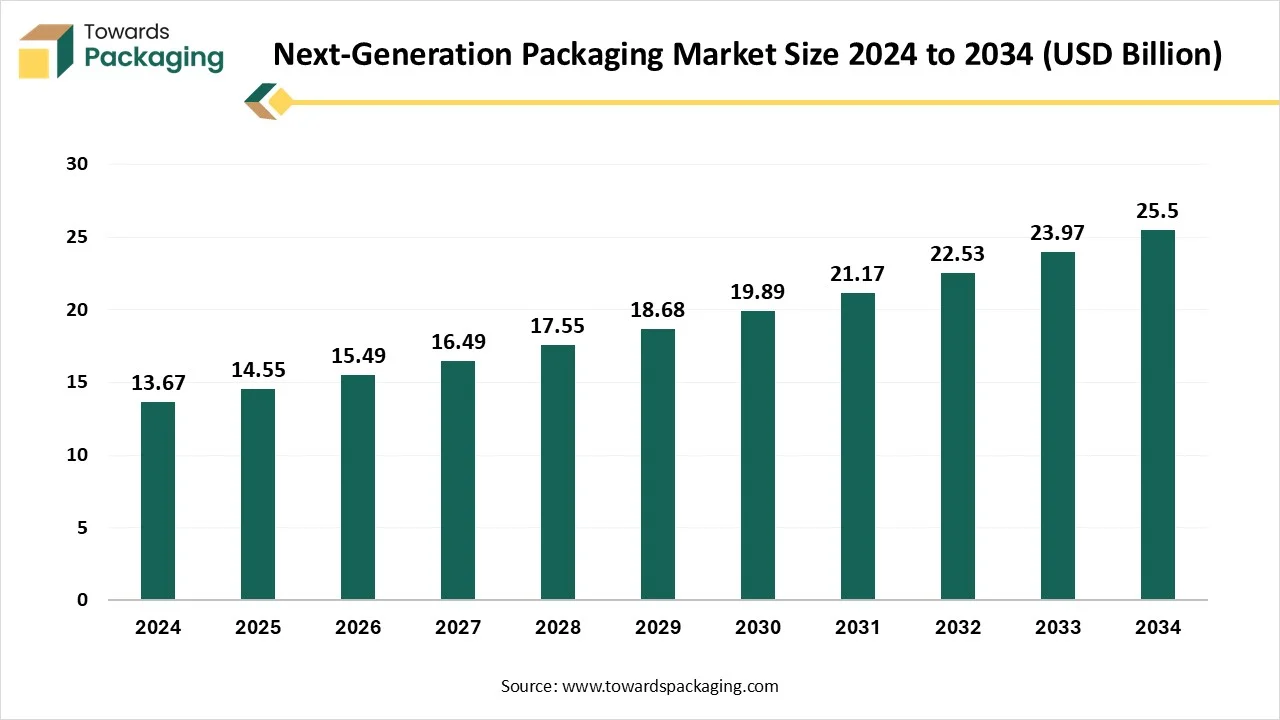
The next-generation packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 15.48 billion in 2026 to USD 27.13 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.43% from 2026 to 2035.This report covers a full spectrum of market insights including material segmentation, where biodegradable & compostable packaging leads with 36% share, followed by smart packaging at 28%. It examines packaging formats, highlighting the dominance of flexible packaging (45%), and studies applications where food & beverages hold 48% share.
Regional insights show North America leading with 34%, while Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market. The analysis includes a deep dive into the value chain, trade flows, supply chain structure, and competitive landscape, with major players like Amcor, Mondi, Berry Global, Sealed Air, and Sonoco Products contributing significant global revenues. The report also details manufacturer capabilities, supplier networks, and emerging technologies such as AI, IoT, adaptive materials, and smart sensors shaping next-generation packaging.
The next generation packaging goal is to make more sustainable, convenient, and effective packaging to protect and preserve the product. Some instances of next-generation packaging include packaging made from environmentally friendly or biodegradable materials, or reusable packaging, which can be returned to the producer or retailer for refilling or reuse. Latest advancements include adaptive packaging, which can transform its properties in response to environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, or light.
For instance, adaptive packaging might include a coating that becomes ambiguous in bright light to protect the product. Companies are also looking into intelligent packaging by including smart features like package traceability to align with consumer expectations. These count using radio frequency identification (RFID), sensors, tags, and indicators that enable packages to accept atmospheric changes, such as humidity, temperature, and oxygen level, to be tracked.
By influencing machine learning, AI can predict how various materials will perform under specific conditions, serving producers with valuable insights on which packaging to create that uses less material without compromising quality. The power of artificial intelligence in the growth stage is primarily the capability to encourage the performance of a plethora of various materials under many different environmental conditions, to make sure they align with durability standards while lowering waste. Depending on these findings, AI can then automatically examine and suggest the usage of the most biodegradable and lightweight material, which can lower the carbon footprint of packaging, while still maintaining durability and environmental impact.
The capability of AI in driving sustainable packaging innovations is huge and continuously growing. Future growth may include more cosmopolitan AI models for forecasting material performance, deeper combination of Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time tracking, and advanced machine learning algorithms for even more effective recycling procedures. As AI technology becomes more approachable and cost-effective, companies of all sizes will be able to use these tools to grow their sustainability efforts.
The next-generation packaging is driven by many main factors, including technological advancements, growing consumer expectations, and rising demand for sustainable solutions. There is a rigid emphasis on developing and accepting compostable, biodegradable, and recyclable materials like plant-based plastics, mushroom-based packaging, and recycled content, substituting recycled materials for single-use plastics. This includes crafting packaging for reuse, convenient recycling, and less waste throughout its lifecycle.
Lowering packaging materials and accepting lighter, simpler designs to lower the carbon footprint and transportation emissions. Government initiatives like the UK plastic packaging tax and the EU's packaging waste reduction targets encourage organizations to accept sustainable and effective packaging solutions. Communicative technologies like NFC (Near Field Communication ), QR codes, and sensors for developed tracking, authentication, and consumer engagement.
Despite their capability, next-generation films face challenges. Their hydrophilic nature limits water resistance, which makes them unsuitable for particular food uses. They also display mechanical weakness as compared to synthetic plastics, raising durability issues. Additionally, scalability and cost-effectiveness obstruct their commercial acceptance. Inventions in protein modification and nanotechnology serve solutions to these problems. By combining proteins with biopolymers or nanoparticles, researchers can develop mechanical power and the managed release of active compounds.
Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) is the focused modification of the gas composition within a package during the packaging procedure. This enables perishable and climate-sensitive products to be transported globally. To make sure that the goods reach their endpoint in the best possible condition. The internal surroundings of the packaging must be continuously tracked, maintained, and, if necessary, adjusted. The further relevance of MAP technology is deliberated in its potential to specifically expand shelf life, thereby lowering global food waste and marketing secure global food supply chains. It also assists the transport of pharmaceuticals such as vaccines, as shown during the COVID-19 PANDEMIC.
The growing demand for biodegradable packaging was possibly caused by regulatory, environmental, and consumer issues. Businesses are becoming more conscious and waking up to the significance of sustainability; consequently, eco-friendly packaging can now play a big part in businesses' direct needs for packaging solutions. Growing awareness toward environmental segmentation, especially plastic waste, has been one of the biggest drivers of this direction. Compostable packaging is crafted to solve three main spaces: tea bags, fruit labels, and foodservice packaging. There is a prevalent misconception that compostable products pollute recycling, leading to lower rates. But the recycling rates in this case are lower due to food contamination. To efficiently develop recycling rates in these areas, it's important to use materials that mix with food waste, protecting it from food contaminants. This is the main aim of compostable, they serve as an avenue for food, liquids, and food-stained products to leave together in one bin, leaving recycling streams dry and clean.
Active packaging has come up with a transformative solution in the domain of food packaging, which introduces functionalities that expand beyond regular passive contaminants. Active packaging technology plans to protect the quality and expand the shelf life of products via the incorporation of functional components into the packaging material. On the other hand, Smart packaging is greatly used in pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, supply chains, and retail and sustainability initiatives. In the food sector, it helps reduce waste and develop safety by utilising sensors which monitor temperature exposure and freshness indicators which display if a product is still safe to eat.
Flexible packaging is a crucial part of the global packaging sector, known for its cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and reliability. From food protection to ensuring food safety, flexible packaging plays an important role across many industries. However, as industry demand develops, so do the limitations. The growth of sustainability, increasing focus on performance-driven solutions, and rigid regulatory standards are redefining the landscape. Flexible packaging is more lightweight and cost-effective. The barriers and films that generate the pliable materials need fewer resources and energy to produce, while serving a more cost-effective strategy to shipping, logistics, and warehousing.
Like regular packaging procedures, smart packaging can catch and share valuable information automatically, lowering manual tasks and the risk of human error. The demand for quicker, more relevant deliveries is bigger than ever, and these industries are under heavy pressure to ensure smooth operations and customer satisfaction. Smart packaging aligns with these demands by serving precise, up-to-the-minute data on products as they shift through every stage of production and delivery. Also, smart packaging serves the main environmental advantages. By lowering errors and developing efficiency, it reduces wasted material and unwanted shipments, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint.
Next-generation packaging in the food and beverage sector concentrates on sustainable, smart, and functional solutions. This adds active packaging that expands shelf life by controlling moisture and oxygen, intelligent packaging with sensors or QR codes to track freshness and authenticity, and eco-friendly materials like compostable films and recycled content to cut environmental effects. These inventions develop food safety, reduce waste, and enhance consumer engagement, meeting both regulatory demands and developing expectations for sustainability and transparency. Additionally, personalised and interactive packaging integrates consumers and expands brand loyalty, making next-generation solutions a main driver of invention and competitiveness in the industry.
Next-generation packaging in healthcare and pharmaceuticals concentrates on compliance, safety, and patient engagement. Smart packaging solutions utilise RFID tags and sensors to manage humidity, temperature, and authenticity throughout the supply chain, lowering the risk of counterfeit drugs. Interactive packaging with QR codes and NFC technology serves patients with dosage reminders and detailed instructions, developing adherence. Child-resistant and temperature-resistant designs ensure product security, while sustainable materials like recyclable plastics and biodegradable films assist in lowering environmental impact. These inventions not only prevent sensitive medicines but also develop traceability, and overall patient experience and regulatory compliance.
Primary packaging mixes smart features and sustainable materials to protect products and engage consumers. It includes QR codes, intelligent labels, and sensors for actual time tracking, authentication, and freshness tracking. In pharmaceuticals and food, active packaging expands shelf life by absorbing oxygen or releasing preservatives. Lightweight recyclable films, bioplastics, and mono-material structures lower environmental impact while maintaining high barrier protection. This high-level primary packaging ensures product safety, compliance, and enhanced user experience.
Next-generation secondary packaging concentrates on automation, sustainability, and smarter logistics. Recyclable corrugated boxes, reusable crates, and lightweight materials lower waste and carbon footprint. QR codes, IoT sensors, and RFID tags enable efficient tracking, inventory management, and authentication. Modular designs and easy-open features improve handling and reduce damage during transport. In e-commerce, branded secondary packaging also enhances the unboxing experience and expands customer engagement.
Direct-to-consumer brands have dominated next-generation packaging by giving importance to convenience, personalization, and sustainability to meet growing customer expectations. Unlike regular retail, D2C companies control the complete supply chain, allowing them to design packaging that reinforces brand identity with custom prints, smart labels, and engaging unboxing experiences. They also invest in eco-friendly materials like compostable mailers and recyclable boxes to appeal to conscious consumers. Additionally, D2C depends heavily on data and automation to update packaging for safe delivery, efficient storage, and minimal waste, driving faster adoption of innovative packaging solutions across sectors.
North America dominated the next-generation packaging industry due to the rigid demand for advanced and sustainable solutions driven by heavy consumer goods, food industries, and healthcare. The region benefits from established infrastructure, high investment in packaging innovations, and early acceptance of smart technologies like IoT-enabled packaging and RFID. Strict regulations around food safety, recyclability, and labeling have also accelerated the shift to intelligent and eco-friendly materials. Major Players headquartered in the U.S. and Canada further fuel growth with constant R&D, assisting North America in maintaining its leadership in next-generation packaging adoption.
In Asia Pacific, the next-generation packaging sector is increasing rapidly, driven by booming e-commerce, rising disposable incomes, and demand for easy and sustainable solutions. Countries like India, China, and Japan are embracing smart packaging technologies, such as QR codes and sensors, to develop traceability and consumer engagement. The region's large food, pharmaceutical, and beverage industries are driving the adoption of high-level materials and eco-friendly formats. Additionally, government policies assisting recycling and waste reduction are pushing brands to encourage innovative and sustainable packaging to stay competitive.
Latin America is experiencing a growing demand for next-generation packaging, as shown by rising consumer awareness about sustainability, stricter environmental development, and growing expectations for product safety and freshness. Brands in countries like Mexico, Brazil, and Argentina are increasingly accepting intelligent packaging solutions (indicators, sensors), active packaging (gas scavengers and antimicrobials), and changed atmosphere packaging to expand the shelf life and lower spoilage. The region’s flexible packaging segment is also experiencing the use of recyclable and biodegradable materials, while the growth of e-commerce is encouraging demand for packaging that is lightweight yet protective.
The region’s strong growth stems from a demanding user base, specifically in the food and beverage, personal care, and pharmaceutical industries. The growth in disposable income and user awareness about environmental sustainability has also played an important role in environmentally friendly packaging solutions. Hence, governmental regulations that concentrate on lowering plastic waste have led to a move towards recyclable and biodegradable materials. The UAE Packaging Sustainability Charter has revealed the compulsory business to align with packaging practices with the country's sustainability goals. The charter outlines particular guidelines for lowering plastic usage, marketing biodegradable materials, and increasing recycling rates. Companies need to comply with these regulations to lower the surrounding impact.
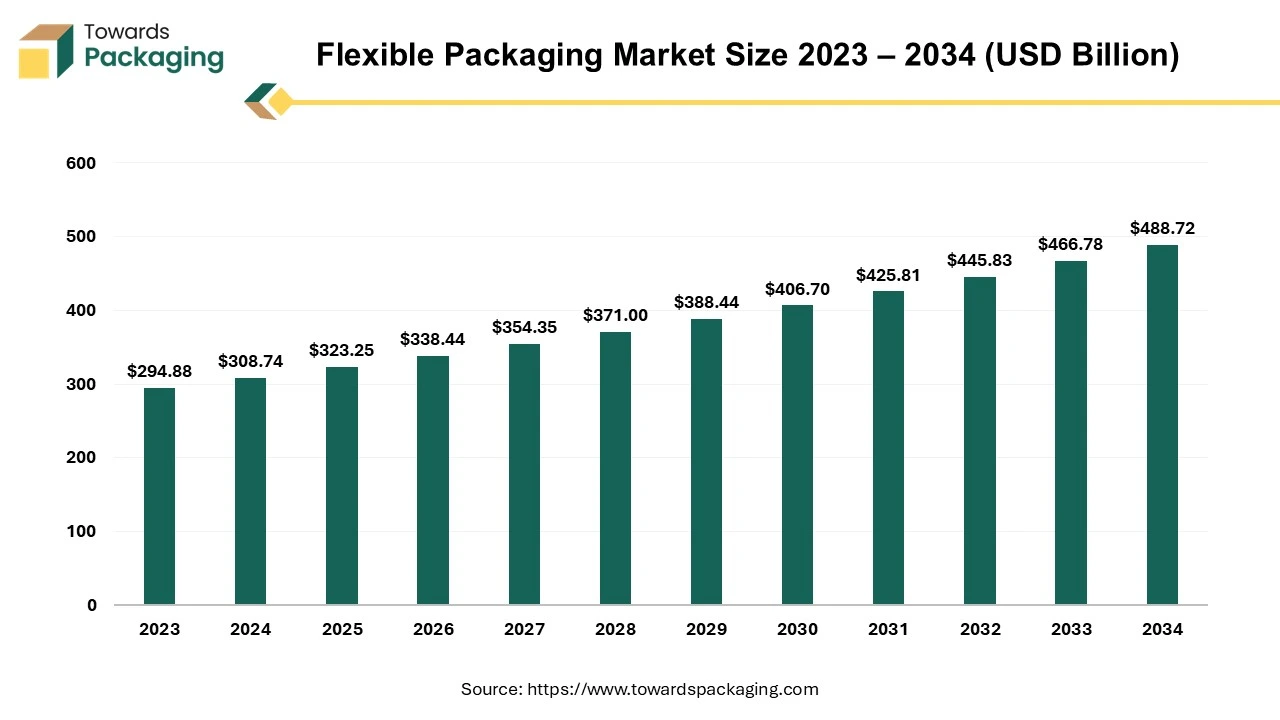
The flexible packaging market is expected to increase from USD 323.25 billion in 2025 to USD 488.72 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.7% throughout the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The shift in consumer behavior toward convenience, coupled with regulatory pressure for eco-friendly solutions, has accelerated market adoption across industries.
The packaging type in which packaging materials is used which can easily change shape, typically manufactured from paper, plastic, foil, or a combination of these. Unlike rigid packaging such metal cans or glass jars, bottles, flexible packaging is lightweight, durable adaptable to various product types. The common types of flexible packaging are bags, pouches, sachets, and wraps & films. The flexible packaging is lightweight, cost effective, has extended shelf-life, sustainable option and convenience features. The flexible packaging is extensively utilized for personal care, pharmaceuticals, industrial applications and food & beverages.

Material Type
Packaging Type
Application
End‑Use
Distribution Channel
Region



February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
