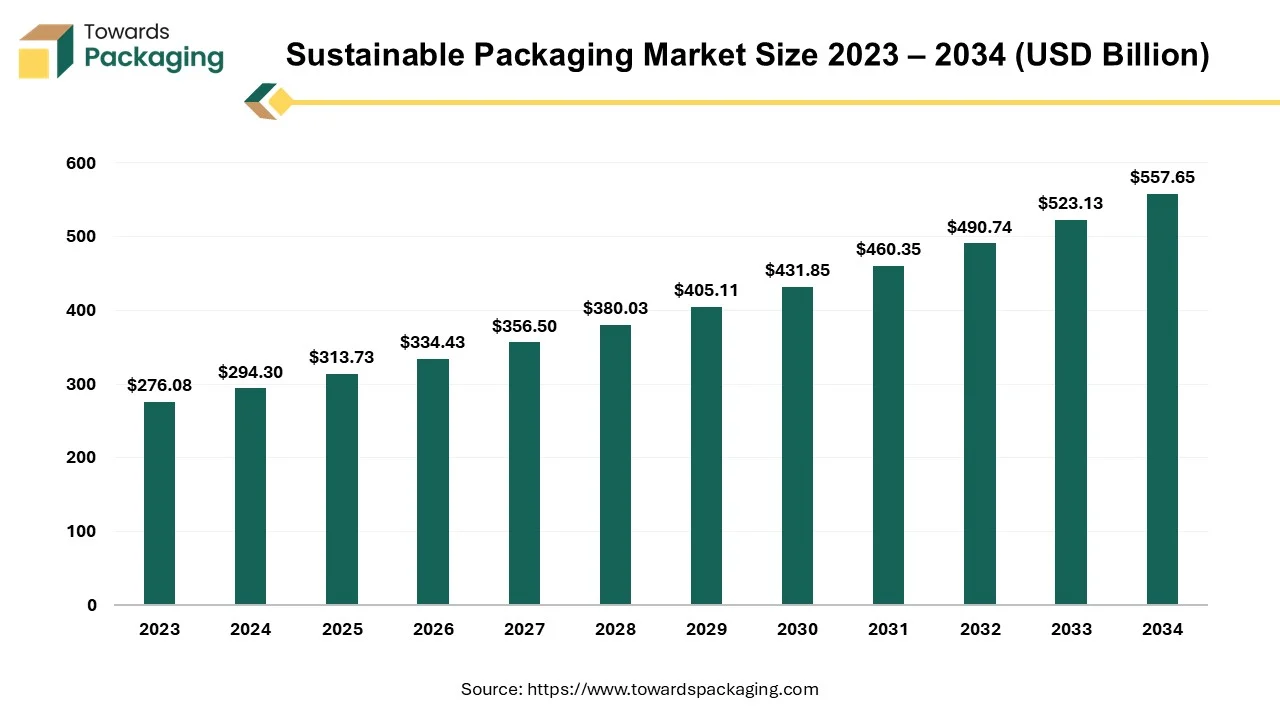
Sustainable Packaging Market Size, Segment Analysis by Material, Packaging Type, Process, and Regional Insights (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa)
The sustainable packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 334.43 billion in 2026 to USD 594.46 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2026 to 2035. The market spans various materials such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal, with significant innovations in biodegradable and compostable packaging. The increasing demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions is driven by consumer concerns, government regulations, and rising awareness about environmental sustainability.
Regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific are leading the charge, with major companies like Amcor, Smurfit WestRock, and Mondi innovating in sustainable packaging technologies. This market also includes packaging types like bags, boxes, and pouches, with the focus shifting to reusable and recyclable materials.
Report Highlights: Important Revelations
- This expansion is growing at a CAGR of 6.6% over the period from 2025 to 2035.
- Pioneering sustainable packaging development in the Asia Pacific region.
- Emergence of North America as a key player in sustainable packaging innovation.
- Paper holds dominance as the leading material in sustainable packaging.
- Evolution of sustainable packaging: bags leading the way.
- Growing importance of reusable packaging in today's sustainable packaging landscape.
Sustainable packaging is the use of environmentally friendly materials to package, store, distribute, or display products. Sustainable packaging incorporates materials with a low environmental impact throughout their existence. This strategy entails employing environmentally friendly and renewable materials, reducing waste, and lowering carbon emissions connected with packaging manufacturing, transportation, and disposal. The entire weight of packaging was 3.6 million tonnes in 2022. Unsurprisingly, more businesses are switching from plastic-based packaging to eco-friendly, plastic-free alternatives, as 76% of consumers actively seek sustainable items to fulfill their eco-friendly pledges. Flexible packaging was utilised in 29.88 million tonnes globally in 2023. The demand for high-performance, low waste packaging is now much more pressing, given the sharp rise in online shopping and e-commerce delivery.
The primary purpose is to protect the product while also minimizing the environmental impact of its packaging. Packaging can achieve sustainability through a variety of means, including the use of recycled materials, the implementation of reusable packaging to extend its lifespan, and the adoption of production practices with low environmental impact. Sustainable packaging procedures have various benefits, including reduced waste, lower carbon emissions, and a better reputation for organizations that adopt eco-friendly strategies.
Sustainability goals extend to packaging, which accounts for $1 trillion in global spending each year. According to studies, these promises focus on three major areas: prioritizing full recyclability and a significant increase in recycled materials (60% of commitments), reducing overall plastic usage (26%), and encouraging innovation to promote packaging usage changes (14%).
Sustainable packaging also comes with problems and constraints, such as more excellent material and production costs, more efficient recycling and waste management systems, and potential implications for packaged items' quality and safety. Sustainable packaging has gained popularity as a realistic approach for reducing the environmental impact of product packaging over its entire lifecycle. With a growing population and more consumer knowledge of environmental issues, India enthusiastically embraces this trend. This study investigates the many types of sustainable packaging used in India, performing a thorough market analysis and forecasting future trends.
For Instance,
- In December 2022, introduced Greenpackt, a novel approach to packaging that employs only recyclable materials, streamlines production, ensures humidity resistance, protects children's safety, and reduces the carbon footprint of each package created by the equivalent of about 4 million young trees in a year.
Sustainable Packaging Market Trends
- Increasing trend for packaging materials that biodegrade spontaneously, minimizing packaging waste's environmental impact.
- Trending lightweight packaging materials, eliminating unnecessary layers, and adopting minimalist designs to reduce material consumption and transportation-related emissions.
- Sustainable packaging materials include edible packaging, films made from seaweed, and mushroom-based packaging.
- Increased use of e-commerce and packaging solutions that minimize waste while safeguarding goods during transportation is required.
AI in Sustainable Packaging Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast Analysis
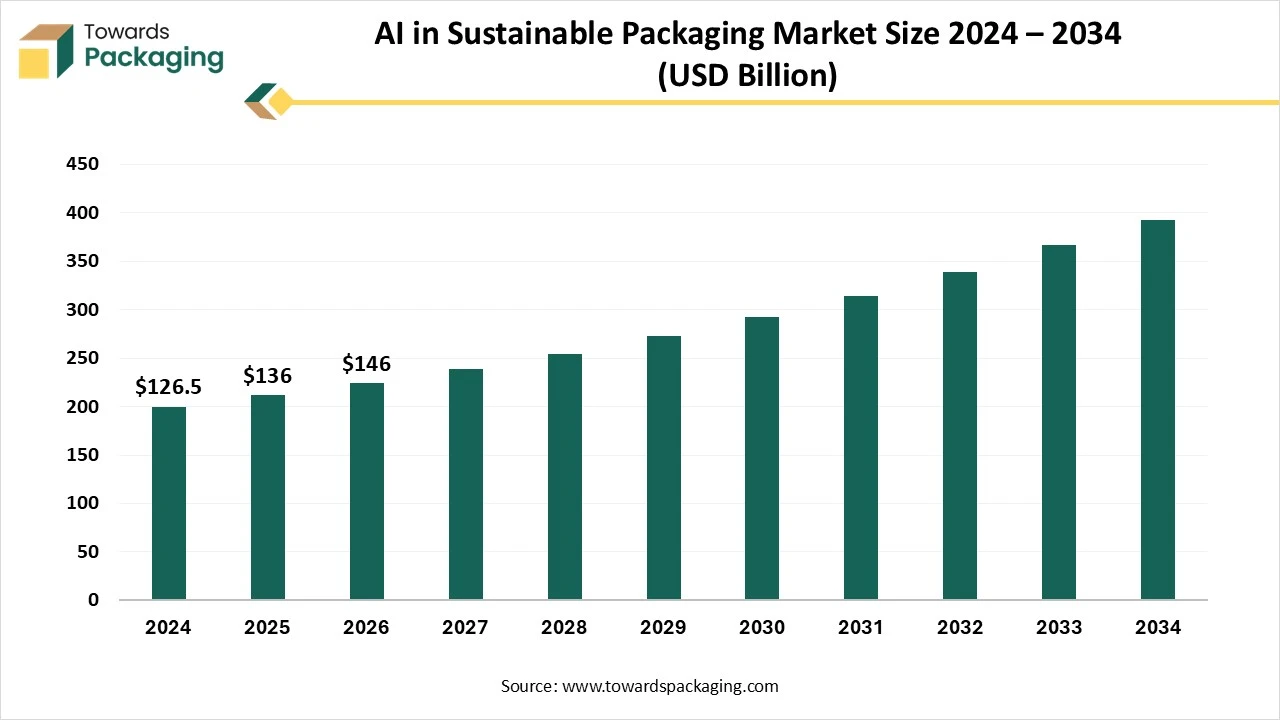
The global AI in sustainable packaging market is accelerating, with forecasts predicting hundreds of millions in revenue growth between 2025 and 2034, powering sustainable infrastructure globally. The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like acquisition and merger to develop advance technology for manufacturing sustainable packaging. The market is growing rapidly, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions and efficiency in production.
AI technologies optimize material usage, reduce waste, and enhance packaging design for recyclability. They also support smart supply chain management and predictive maintenance. Brands are adopting AI to meet sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. Integration of machine learning and computer vision further improves quality control and automation. This market is poised for strong growth across industries like food, beverages, cosmetics, and e-commerce.
Asia Pacific Sustainable Packaging Market Trends
Asia Pacific is expected to grow fastest during the forecast period. The market growth in the region is driven by the increasing flexible packaging solutions, increasing environmental awareness and growing forestry and agricultural products. India is fastest growing country in packaging industry due to the e-commerce growth and urbanization. EcoPack India is a major manufacturer of sustainable packaging solutions.
- In April 2025, Shri Prataprao Ganpatrao Jadhav, Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare inaugurated a National Stakeholder Consultation on “Sustainable Packaging for Food Business
Asia Pacific is expected to grow fastest during the forecast period. The market growth in the region is driven by the increasing flexible packaging solutions, increasing environmental awareness and growing forestry and agricultural products. India is fastest growing country in packaging industry due to the e-commerce growth and urbanization. EcoPack India is a major manufacturer of sustainable packaging solutions. The Asia Pacific region is leading in the development of the sustainable packaging industry due to growing concerns about sustainability, especially in Asia's developing countries.
Comprehending the viewpoint of consumers is crucial for packaging enterprises seeking to leverage the rapidly expanding expansion potential in this area. Asia's position as the primary growing market for packaging solutions has been cemented as China has surpassed the US to become the most significant global packaging market.With the increasing use of packaging materials in Asia, there is also a rise in the ecological footprint due to significant packaging material leakage into the environment. The fact that there needs to be more infrastructure for recycling and waste collection to keep up with the rapid increase in demand for packaging materials exacerbates this situation.
China, India, and Indonesia are the three rapidly developing Asian economies that have the most influence over the development of the sustainable packaging industry. Customers in these nations are more conscious of and concerned about sustainability issues, and they are also more prepared to pay for products that are better for the environment. Compared to consumers in other countries, they place comparatively less emphasis on waste generation and instead focus primarily on air and water pollution.
For Instance,
- In August 2023, Amcor, a leader in the global field of developing and producing sustainable packaging solutions, said it has expanded its presence in the rapidly increasing Indian market by acquiring Phoenix Flexibles.
Manufacturers, merchants, and legislators of fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) have united in their attempts to reduce packaging waste due to increasing pressure. Even with these efforts, there is still a noticeable level of consumer anxiety; respondents from China, India, and Indonesia exhibit the most significant concern worldwide. Interestingly, this worry has grown since the COVID-19 outbreak, highlighting how vital sustainable packaging practices are in the current socioeconomic environment.
For Instance,
- In October 2023, compostable packaging solutions producer Pakka Limited (formerly Yash Pakka Limited) unveiled India's first flexible compostable packaging. In keeping with pakka's emphasis on sustainability, the partnership with Brawny Bear, an Indian leader in date-based food processing.
North America has emerged as the second most important region in the sustainable packaging arena. Consumer opinions of sustainable packaging have evolved significantly. Before the pandemic, there was a notable increase in public awareness of the environmental impact of packing materials. Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) businesses and retailers actively committed to sustainable packaging techniques, while regulatory agencies took decisive action to address the issue.
For Instance,
- In January 2024, Mondi plc (Mondi), a leading global producer of environmentally friendly packaging and paper, successfully acquired the Hinton Pulp plant in Alberta, Canada.
The United Nations highlights a frightening reality: if the global population hits 9.6 billion by 2050, the resources equivalent to roughly three planets will be required to support existing lifestyles. This emphasizes the necessity and relevance of adopting sustainable practices across various packaging industries. Packaging recycling prevents the production of greenhouse gases during the decomposition process in landfills, increases the life of a priceless natural resource, and decreases the quantity of waste dumped there. In the US, 50% of packaging made of all materials gets recycled.
The increasing significance of sustainability considerations in consumer purchasing decisions. As awareness grows and consumers become more discerning about the environmental impact of products, the demand for sustainable packaging solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory in North America and beyond. Consequently, businesses and regulatory bodies must prioritize sustainability initiatives to meet evolving consumer preferences and address pressing environmental challenges.
For Instance,
- In January 2023, Print & Pack, a leader in the sustainable packaging sector, announced its official launch, ushering in a new age of eco-friendly packaging solutions for small businesses and environmentally concerned brands across North America.
Europe dominated the sustainable packaging market in 2024. The market growth in the region is attributed to the eco-friendly packaging solutions and rising innovations for improving sustainable packaging. Europe is the largest sustainable packaging country and focuses solely on sustainability in packaging.
- For instance, in March 2025, a new 2300m² research and customer experience center, FlexStudios in Steinfeld, Germany was inaugurated by Mondi. The aim behind this launch was to promote a more sustainable future and foster the co-creation of flexible packaging solutions.
US Consumers Confusion Over Sustainable Packaging and Global Regulatory Trends
Most consumers in the US are unclear about which packaging materials are truly sustainable. While compostable and plant-based options are widely seen as the most eco-friendly (72% and 70% of consumers respectively), other types of packaging, such as those combining plastic, paper, and aluminum foil, are still considered sustainable by around 29% of people, despite their lower ranking.
About half of consumers express a willingness to pay more for sustainable packaging, though most are only ready to spend a modest premium. Specifically, 50% are prepared to pay an extra 1 to 3%, 25% are willing to pay 4 to 7%, and around 12% would stretch to 7 to 10%. A small percentage (4 to 7%) are even open to paying more than 10%, while 5 to 8% won’t pay any additional cost.
Recent years have seen a surge in sustainable-packaging regulations extending beyond just shopping bags and select food-service items. A comprehensive review of regulations in 30 countries reveals that nearly all are now addressing sustainable packaging. These regulations focus on various aspects:
- Packaging Specifications: Requirements for composition, size, and weight.
- Attributes: Emphasis on recyclability and biodegradability.
- Primary Use: Guidelines on labeling and traceability to empower consumers.
- Packaging Chain: Regulations covering raw material sourcing, disposal, collection, sorting, and recycling targets.
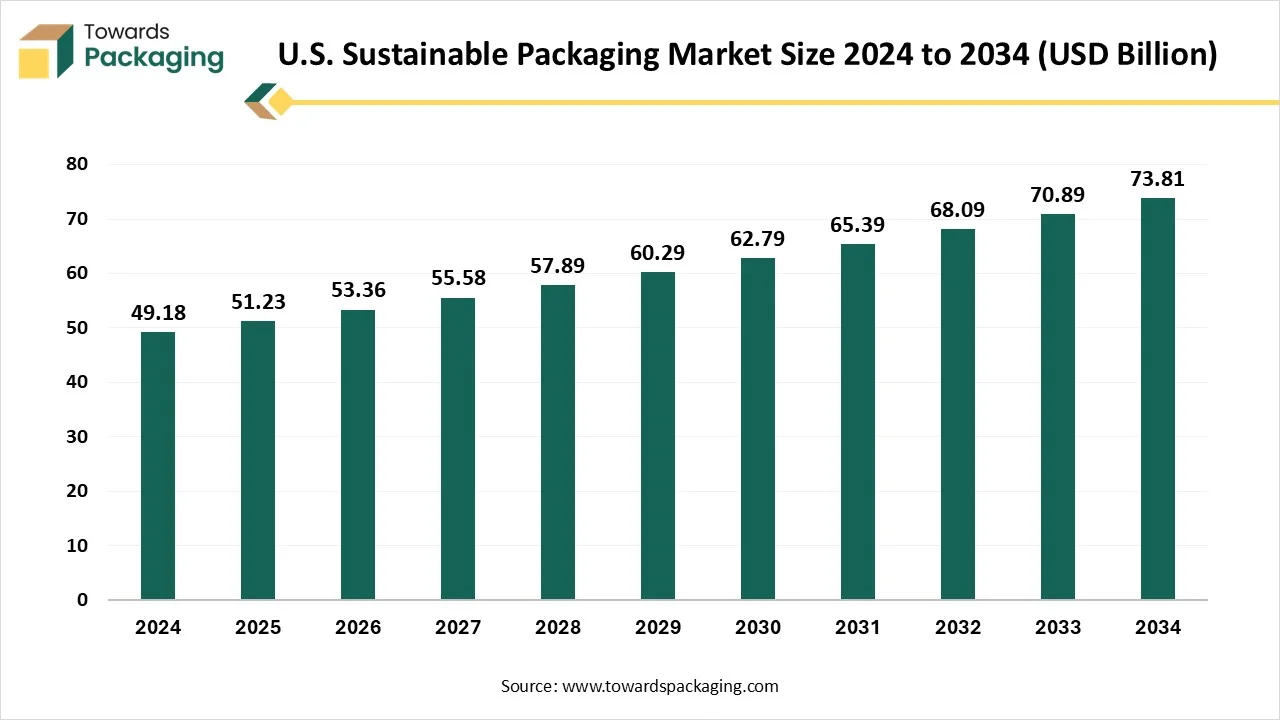
Future of U.S. Sustainable Packaging Market
The U.S. sustainable packaging market is predicted to expand from USD 51.23 billion in 2025 to USD 73.81 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.15% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The increasing awareness regarding the environmental impact of plastic packaging materials is expected to drive the global U.S. sustainable packaging market over the forecast period.
Sustainable packaging refers to any eco-friendly material that is widely used to store, wrap, ship, and shelf products. Sustainable packaging focuses on the development and use of packaging solutions that are generally made from materials such as recyclable PET or HDPE plastics, paper, and cardboard. It also includes compostable materials such as PLA (a starch-based material) and cellulose, which biodegrade in compost, providing an eco-friendly alternative. Sustainable Packaging has a minimal environmental impact and footprint through the use of renewable or recycled resources.
Most countries have started by limiting certain materials and enhancing waste management through extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes. More advanced nations have also developed infrastructure to support better design, recycling capabilities, and increased use of recycled materials. Out of the 30 countries analyzed, 28 have EPR schemes or regulations in place or in progress, with over 40% already implementing them.
Sustainable Packaging Market, DRO
Demand:
- Growing consumer concern over the effects of packaging materials on the environment is fueling the demand for sustainable substitutes.
Restrain:
- The expense of switching from conventional packaging materials to sustainable substitutes is one of the primary barriers to sustainable packaging in the market.
Opportunity:
- Smart packaging materials can be made using plant-based polymers, bio-based plastics, and cutting-edge recycling techniques.
Paper Reigns Supreme Leading Material in Sustainable Packaging
Paper is the dominant material in the sustainable packaging sector. Paperboard cardboard stands out as an excellent example of sustainable packaging. Crafted from recycled paper pulp, it is lightweight, easily shaped, and cut, making it an ideal choice for shipping boxes. Consumers choose paper-based packaging because of its eco-friendliness, such as recyclability and compostability, as well as practical benefits, such as storage convenience. Glass packaging is praised for its reusability and ability to protect items, making it a popular choice among customers. In contrast, plastic packaging does not rank first for any attribute, showing a lower consumer preference.
For Instance,
- In February 2024, the UK-based manufacturer of paper and board, Mondi plc, will be getting ready for a possible takeover offer for another UK-based manufacturer of paperboard and packaging, DS Smith plc.
Based on consumer preferences, packaging made of paper and cardboard stands out as the most sustainable option. Features that make paper-based packaging more appealing to consumers include its ease of recycling, environmental friendliness, and home compostability.
Recycle rates for cardboard and paper packaging are remarkable; 88% of cardboard and 73% of paper packaging are recycled. Despite this, a significant myth persists among consumers: 41% think that more than 50% of paper packaging in the United States is recycled.
The widespread acceptance and use of paperboard cardboard as a sustainable packaging option demonstrates its importance in resolving environmental concerns while meeting consumer desires. As customers prioritize sustainability in their purchase decisions, the demand for eco-friendly packaging materials such as paperboard cardboard is expected to rise further.
For Instance,
- In March 2023, the new packaging for AEG and Electrolux small appliances will be made of paper and recycled materials and will use 70% less ink, according to the Electrolux Group.
Paper-Based Sustainable Packaging Market Growth, Innovations and Market Size Forecast
The paper-based sustainable packaging market is booming, poised for a revenue surge into the hundreds of millions from 2025 to 2034, driving a revolution in sustainable transportation. The paper-based sustainable packaging market is experiencing rapid growth due to increasing environmental concerns and global efforts to reduce plastic waste. Governments, consumers, and brands alike are pushing for eco-friendly alternatives, making paper-based solutions more popular than ever. Asia-Pacific dominates the market thanks to strong manufacturing capacity, rising environmental regulations, and large consumer demand. Latin America, meanwhile, is the fastest-growing region, driven by shifting consumer awareness and growing export orientation.
The market for paper-based sustainable packaging is evolving as industries transition away from single-use plastics. Paper is biodegradable, recyclable, and increasingly sourced from responsibly managed forests, making it ideal for green packaging strategies. Major sectors like food & beverage, cosmetics, and e-commerce are leading adopters, using paper for boxes, cartons, wraps, and pouches. Technological innovations have improved durability and water resistance, allowing paper to compete with plastic in functionality. Demand for packaging with a low carbon footprint is also driving investment in recyclable and compostable paper alternatives.
Bags Are Shaping the Future of Sustainable Packaging
Sustainable bags have emerged as the leading product in sustainable packaging, attracting customers and retailers from various industries. These bags are strong and dependable shopping companions, whether for food, clothes, electronics, or decorative items, and they provide significant environmental benefits.
Paper bags, in particular, have attracted attention for their adaptability and resilience in transporting a wide range of things while easily enduring transportation problems. Their outstanding performance is due to the high quality of the material and the bag's construction. Paper bags are made from pure kraft paper and built explicitly for demanding packaging demands. They have long natural fibers that give mechanical solid strength. The use of glue and the skillful fabrication of handles improve the longevity of these bags.
Sustainable bags have a much lower global warming potential than low-density polyethylene (LDPE). Furthermore, these bags biodegrade in a relatively short time, usually two to five months, helping promote environmental sustainability. Using natural water-based colors for printing and starch-based adhesives enhances their eco-friendliness, ensuring they do not harm the environment.
Paper bags are not only environmentally friendly, but they also function as valuable marketing tools. According to research, a substantial majority of passersby, around 85%, notice messages printed on paper bags they come across on the street. 80% of consumers think companies printed on paper bags are more appealing and engaging, indicating the opportunity for brands to use sustainable packaging to improve their image and successfully communicate with their target audience.
In the world of sustainable packaging, paper bags, in particular, are becoming increasingly popular because they offer a pleasing balance between environmental responsibility, practicality, and marketing effectiveness.
Why Does Transparency Matter So Much in Sustainable Packaging?
Clear labeling is now a key driver of trust in sustainable shopping. About 70% of consumers prefer packaging that clearly communicates its sustainability credentials. Yet, not everyone notices:
- 20% always spot sustainability labels
- 25% never do
- 55% sometimes notice them
Interestingly, one in five shoppers (20%) avoid products altogether if they lack clear sustainability information. This shows how visibility directly influences brand credibility. Looking ahead, 69% of consumers expect companies to adopt sustainable packaging by 2025, making it a fundamental expectation rather than a bonus. And they’re willing to invest in it 49% of Gen Z, 47% of Millennials, 41% of Gen X, and 37% of Boomers say they’re ready to pay more for eco-friendly packaging.
Recycling remains the foundation of sustainable packaging practices. About 50% of consumers recycle frequently, while another 31% recycle fairly often. An impressive 83% of shoppers consider recyclability an essential feature, and 31% say it’s very important when making purchase decisions. Moreover, 61% of consumers prefer minimalist packaging, valuing simplicity, efficiency, and reduced waste over excess materials.
What Do Shifting Consumer Preferences Reveal About Industry Progress?
Global consumer trends show a clear move toward greener materials. Today, 54% of shoppers prefer recyclable, compostable, or reusable packaging, and 51% favor reduced plastic use. Additionally, 31% prefer paper-based options, highlighting growing demand for renewable and biodegradable materials.
Among industries, food and packaged goods lead the shift toward sustainable packaging, followed by clothing (35%) and beauty (30%). However, 46% of consumers feel that the automotive sector is falling behind in adopting eco-friendly packaging initiatives.
Which Industries are Leading and Which are Falling Behind?
Consumers are becoming more vocal about industry performance:
- Electronics and tech are recognized for their progress, with 45% of consumers acknowledging improvements.
- Toys and games follow closely at 43%.
- Medical and pharmaceutical industries face criticism, as 35% of shoppers believe they haven’t embraced sustainable packaging enough.
- Even cosmetics and beauty, where 30% of consumers see improvement, still receive mixed feedback 34% say more progress is needed, and 28% think cleaning products could do better with greener packaging.
What’s Holding Back the Adoption of Eco-Friendly Packaging?
Despite high awareness, several practical barriers prevent widespread adoption. The top challenges consumers cite include:
- High costs (39%)
- Limited availability (36%)
- Unclear labeling (16%)
- Greenwashing concerns (9%), where brands exaggerate their environmental claims
These barriers highlight a crucial need for greater transparency, affordability, and accessibility to make sustainable packaging truly mainstream.
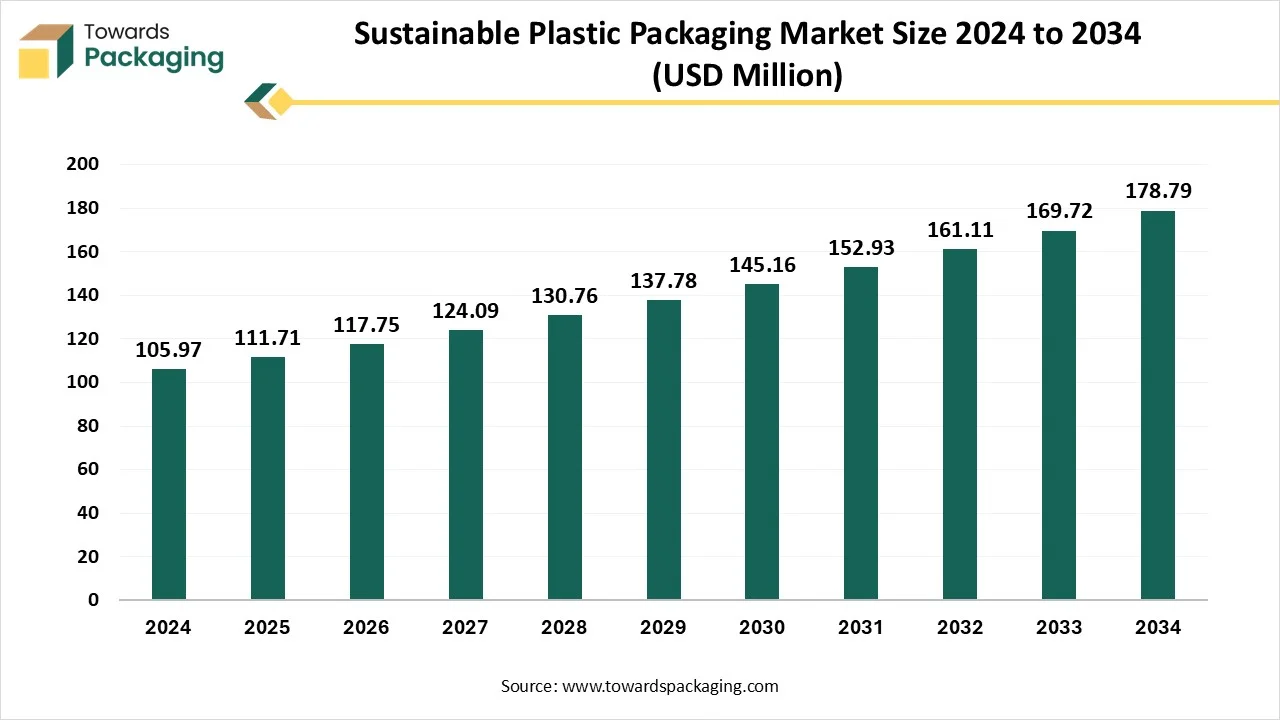
Sustainable Plastic Packaging Market Size, Share, Trends and Growth
The sustainable plastic packaging market is forecast to grow from USD 111.71 million in 2025 to USD 178.79 million by 2034, driven by a CAGR of 5.43% from 2025 to 2034.
The rising awareness of ecological issues has raised the demand for sustainable packaging of products. Due to the presence of small-scale businesses, there is a huge demand for packaging which are cost-effective, where plastic materials play a significant role. The Asia Pacific region is considered to be dominating in the production of sustainable plastic packages due to the continuous advancement in technology of its production and packaging techniques.
The sustainable plastic packaging is enthusiastically evolving the packaging sector as it offers advanced solutions to the most pressing ecological challenges of today’s world. With a rising customer base and resulting professional demand for environment-friendly products, industries are progressively accepting plastic sustainable packaging to decrease their ecological footprint. The drive for sustainable plastic packaging has seen significant progress in recent years, mainly due to rising awareness of ecological concerns like waste and pollution and waste.
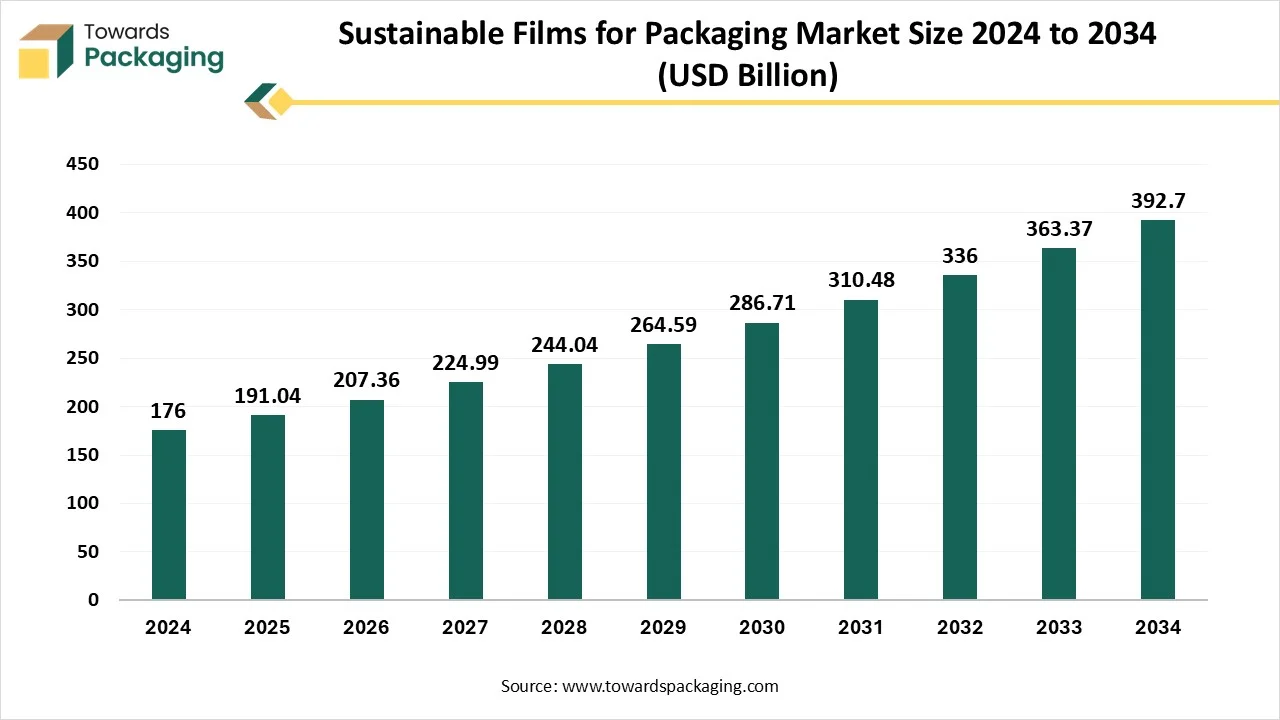
Sustainable Films for Packaging Market Size, Trends, Share and Innovations
The global sustainable films for packaging market is projected to reach USD 392.7 billion by 2034, expanding from USD 191.04 billion in 2025, at an annual growth rate of 8.54% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The growing consumer demand for fresh fruits and vegetables, rising environmental awareness, supportive government regulations promoting eco-friendly alternatives, and rising innovation in packaging materials are expected to drive the growth of the global sustainable films for packaging market over the forecast period. Sustainable packaging films are increasingly becoming the key focus and greatest option for lowering plastic waste.
Several companies operating in the market are focused on adopting sustainable materials to develop sustainable packaging films and align with the principles of the circular economy. The market is also experiencing significant growth, driven by the growing demand from various end-use businesses, including food and beverage, pharmaceutical, consumer goods, and others, which require high-quality standards and sustainable films for packaging. Additionally, the market is expanding rapidly in Europe, fuelled by stringent government initiatives, rising focus on adopting biodegradable packaging, and growing demand from multiple industries.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the sustainable packaging market is dominated by established industry giants such as Amcor Plc, WestRock LLC, Berry Global Inc, Huhtamaki Oyj, Detmold Group, Pactiv LLC, DS Smith Plc, International Paper Company, Smurfit Kappa Group PLC and Genpak LLC. These giants compete with upstart direct-to-consumer firms that use digital platforms to gain market share. Key competitive characteristics include product innovation, sustainable practices, and the ability to respond to changing consumer tastes.
Amcor and industry leaders highlight sustainable opportunities and illustrate real-world commitments that benefit businesses and the environment. Amcor has vowed to make all their packaging recyclable or reused by 2025.
Westrock innovates to help customers achieve their sustainability goals and succeed in the market. They set science-based goals for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, serving natural resources, and working for complete safety. Become the employer of choice. Through these and other activities, we hope to help businesses, customers, team members, investors, and communities realize the promise of a sustainable future.
For Instance,
- In September 2023, Westrock has been recognized in Newsweek's America's Most Responsible Companies, Barron's 100 Most Sustainable U.S. Companies, and North America's Dow Jones Sustainability Index for the third year running.
Berry Global provides ideal solutions adapted to your company's sustainability requirements, regardless of the manufacturing process. We have the manufacturing capability to serve different markets for any customer of any size, including injection molding, extrusion, and nonwoven technologies.
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, Banner Chemicals is pleased to announce that the 2M Group of Companies launched Sustainable Packaging Technologies, a new packaging focused business unit. The aim behind this launch was to promote their growing portfolio of biomaterial technologies.
- In July 2024, a National Mission on Sustainable Packaging solutions was launched by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). This solution aimed at a net-zero future by developing indigenous, advanced and integrated innovations, leveraging the combined strengths of its affiliate laboratories across the country and onboarding industry partners.
Sustainable Packaging Market Players

- Amcor Plc
- WestRock LLC
- Berry Global Inc
- Huhtamaki Oyj
- Detmold Group
- Pactiv LLC
- DS Smith Plc
- International Paper Company
- Smurfit Kappa Group PLC
- Genpak LLC
Sustainable Packaging Market Segments
By Material
- Paper
- Plastic
- Glass
- Metal
- Others
By Packaging Type
- Bags
- Boxes
- Trays
- Pouches
- Bottles
By Process
- Reuseable Packaging
- Recycled Packaging
- Compostable Packaging
- Biodegradable Packaging
By Region
- Asia Pacific
- North America
- Europe
- LA
- MEA
Tags
FAQ's
Select User License to Buy
Figures (6)