Packaging Waste Management Market Growth, Innovations, and Market Size Forecast
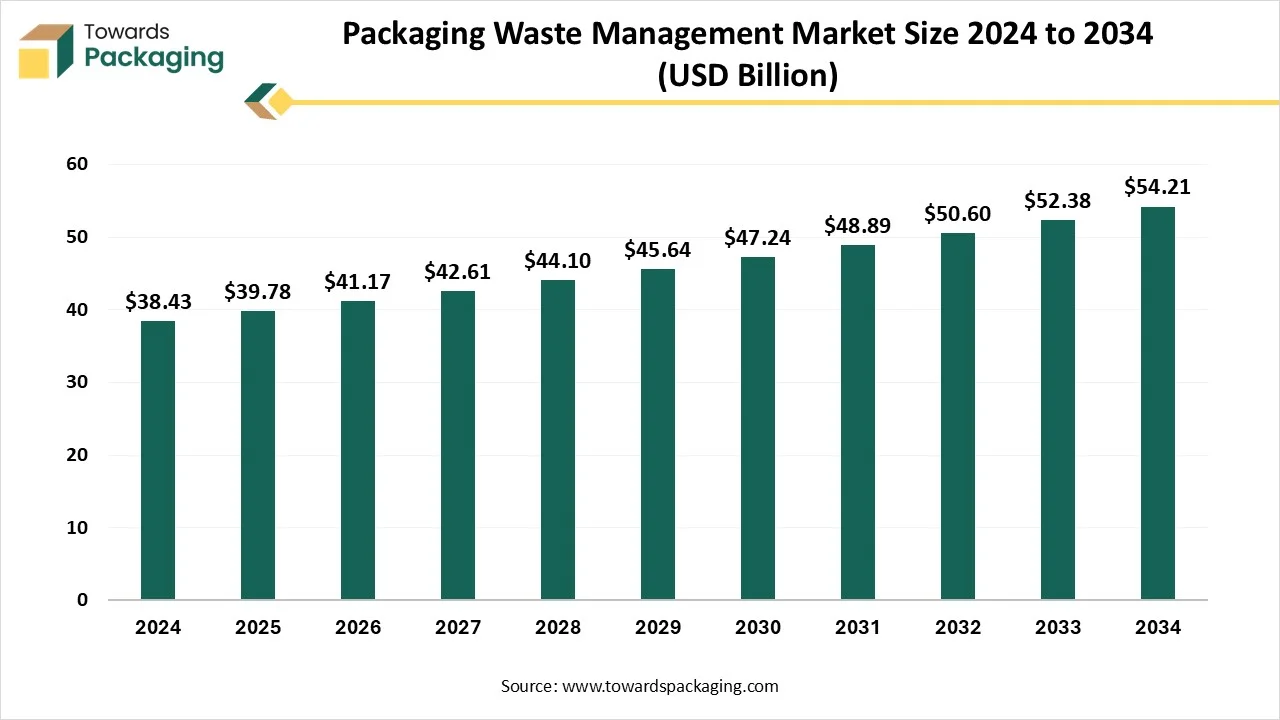
The packaging waste management market is forecasted to expand from USD 41.17 billion in 2026 to USD 56.11 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2026 to 2035. This market is driven by increasing environmental awareness, rising consumer demand for sustainability, and growing governmental regulations. Asia Pacific held a dominant 38% share in 2024, while plastic waste made up 40% of the waste type segment. Key players include Veolia Environnement S.A., Suez S.A., and Waste Management, Inc., who are advancing their technologies in recycling and resource recovery to meet the global demand.
Several key players operating in the packaging waste management market are focused on adopting growth strategies like acquisitions and mergers to develop advanced technology for packaging waste management, bolstering the market’s expansion in the coming years. In addition, the market is expanding exponentially in various developing and developed regions, particularly Asia Pacific, fuelled by the rising focus on sustainability and rising investment in recycling infrastructure.
Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the market is valued at USD 39.78 billion in 2025.
- The market is projected to reach USD 56.11 billion by 2035.
- Rapid growth at a CAGR of 3.5% will be observed in the period between 2025 and 2034.
- Asia Pacific dominated the packaging waste management market in 2024 with 38%.
- By waste type, the plastic waste segment held a dominant presence in the market in 2024, with 40%.
- By service type, the landfilling segment held the major market share of 45% in 2024.
- By service type, the recycling & resource recovery segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of between 2025 and 2034.
- By source, the residential sector segment contributed the biggest market share of 47% in 2024.
- By source, the industrial sector is expanding at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
- By end-use of recycled material, the new packaging production segment accounted for the dominating share of 35% in 2024.
- By end-use of recycled material, the construction segment is expected to witness a significant share during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The global packaging waste management market focuses on the collection, sorting, processing, and disposal or recovery of packaging materials after their intended use. This market is crucial for addressing the growing global issue of packaging waste, driven by the increased consumption of packaged goods and heightened awareness of environmental pollution. It encompasses various strategies, ranging from traditional landfilling and incineration to more sustainable approaches, such as recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy conversion, to minimize environmental impact and promote a circular economy for packaging materials.
How is Artificial Intelligence Integration Impacting the Growth of the Packaging Waste Management Market?
As AI technology continues to evolve, artificial intelligence integration holds great potential to reshape the landscape of the packaging waste management market by automating the packaging waste management process to meet sustainability goals and reduce environmental impact. Waste collection, sorting, and recycling are significantly enhanced through AI-powered automation, which assists in lowering the dependency on manual labor and reducing the risk of errors. Several companies are widely adopting AI-driven waste management systems, which assist in tracking and reducing packaging waste, facilitating circular economy initiatives. AI utilizes computer vision and machine learning to automate waste identification, optimizing collection processes, and improving sorting accuracy.
Key Metrics and Overview
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 39.78 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 56.11 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 3.5% |
| Leading Region | Asia Pacific |
| Market Segmentation | By Waste Type, By Service Type, By Source, By End-Use and By Region |
| Top Key Players | Veolia Environnement S.A., Suez S.A., Waste Management, Inc., Republic Services, Inc., Biffa plc, Waste Connections, Inc., Remondis AG & Co. KG, Stericycle, Inc., Covanta Holding Corporation. |
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Growth of the Packaging Waste Management Market?
- The rising focus on recycling services to reduce the landfill of packaging waste is expected to promote the growth of the packaging waste management market during the forecast period.
- The increasing environmental awareness, along with the rising focus on achieving a circular economy, is expected to contribute to the overall growth of the market.
- The surging investment of key market players in recycled and eco-friendly material innovation is expected to support the growth of the packaging waste management market during the forecast period.
- The rapid urbanization and industrialization have significantly increased the demand for packaging waste management practices and heightened the focus on environmentally responsible practices, accelerating the market’s revenue in the coming years.
- The increasing focus on innovations in material recovery technologies and growing consumer awareness around sustainability are likely to boost the recycling rates around the world, driving the market’s growth during the forecast period.
Market Outlook
Industry growth overview
The packaging waste management market is growing due to rising packaging consumption and stricter waste disposal regulations. Governments and industries are increasingly outsourcing waste collection, sorting, and recycling services. Growth in e-commerce and food packaging is adding to waste volumes, supporting service demand.
Sustainability trends
Sustainability efforts focus on reducing landfill use, increasing recycling rates, and improving material recovery. Circular economy policies and EPR frameworks are pushing companies to adopt responsible packaging waste solutions. Service providers are also investing in low-emission and energy-efficient processing systems.
Startup ecosystem
Startups play a key role in introducing digital waste tracking, smart collection systems, and advanced recycling technologies. Many focus on improving segregation, traceability, and data transparency. Innovation helps bridge gaps in traditional waste management systems.
Market Dynamics
Driver
How is the Rising Environmental Awareness Supporting the Market’s Growth?
The increasing awareness regarding the environmental impact of packaging waste, especially plastic, is spurring the demand for effective waste management solutions, which further boosts the growth of the packaging waste management market during the forecast period. Over 460 million metric tons of plastic are produced every year, according to the United Nations Environment Programme. Plastic is widely used in a wide variety of applications across various industries, from construction and vehicles to electronics and agriculture. An estimated 20 million metric tons of plastic litter end up in the environment every year.
Plastic pollution adversely affects all land, freshwater, and marine ecosystems, a major reason for biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation. Businesses and consumers are increasingly becoming more environmentally conscious, which creates the pressure to reduce packaging waste. Additionally, rising concerns regarding climate change and resource depletion have compelled industries, governments, and NGOs to adopt waste management solutions. Governments around the world are increasingly implementing regulations to promote packaging waste management practices such as extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, a ban on single-use plastic, and offering incentives to businesses to invest in recycling infrastructure.
- In November 2024, the Government of Canada is establishing a Federal Plastics Registry (the Registry) as part of its comprehensive plan to achieve zero plastic waste by 2030. This initiative aims to improve plastic waste management through data collection, transparency, and harmonization of extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies nationwide. (Source: Norton Rose Fulbright)
Restraint
High Initial Costs
The high upfront capital investment is required to establish waste management systems, including collection, sorting, and processing facilities, which can be a barrier for some companies and municipalities in middle and lower-income countries. In addition, a lack of consumer awareness regarding proper waste disposal often leads to improper sorting and a lower recycling rate. Such factors may hinder the growth of the global packaging waste management market during the forecast period.
Opportunity
Increasing Consumer Demand for Sustainability
The growing emphasis on sustainability is projected to create immense growth opportunities for the packaging waste management market in the coming years. Consumers are actively seeking eco-friendly alternatives and are willing to pay more for sustainable packaging options. The packaging waste management practices assist in significantly reducing pollution levels, marine debris, and landfill overflow, which often pose threats to both ecosystems and human health. The growing consumer preference for sustainable packaging materials is compelling businesses to invest in recycling technologies for eco-friendly packaging solutions. Several industries globally are increasingly adopting advanced sorting and processing technologies to make recycling facilities more efficient for developing recycled packaging materials, which significantly reduces the carbon footprint in the ecosystem.
Global Plastic Waste Management in 2019: Treatment and Disposal
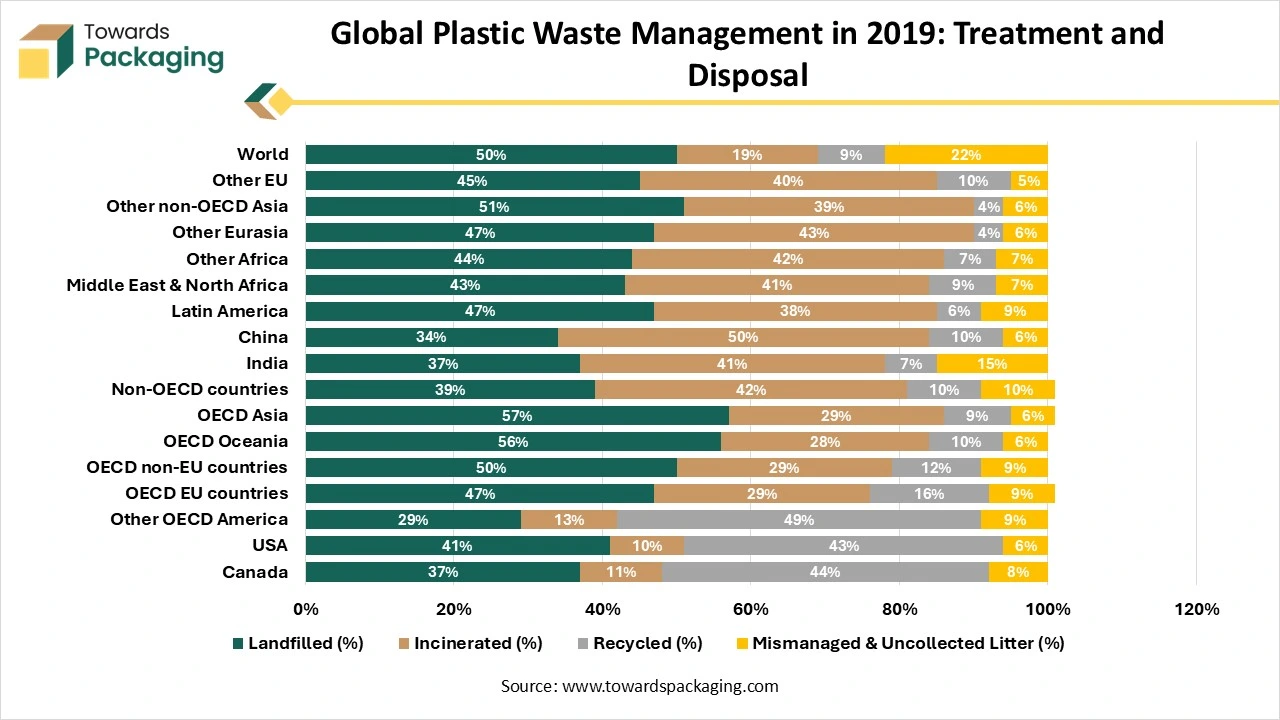
In 2019, global plastic waste reached 353 million tonnes, more than double the 156 million tonnes produced in 2000. A significant portion of this waste came from short-lifetime applications like packaging, consumer products, and textiles. However, only 15% (55 million tonnes) of this waste was collected for recycling, while 22 million tonnes became recycling residue, requiring additional disposal. Of the total plastic waste, 9% was recycled, 19% was incinerated, and nearly 50% was sent to sanitary landfills. Unfortunately, the remaining 22% was mismanaged, either dumped in uncontrolled sites, burned in open pits, or leaked into the environment.
EU Packaging Waste Outlook 2023-2034 Progress and Challenges
In 2023, the European Union made notable strides toward sustainability in packaging waste management. The EU generated 79.7 million tonnes of packaging waste, which amounts to 177.8 kilograms per person. While this was an improvement from 2022, with a decrease of 8.7 kg per person, it still remains 21.2 kg higher than in 2013, reflecting the growing demand for packaging materials over the years.
Paper and cardboard made up the largest share of packaging waste at 40.4%, followed by plastic at 19.8%, glass at 18.8%, and wood at 15.8%. Metal accounted for 4.9%, with the remaining 0.2% consisting of other materials. Each EU citizen produced, on average, 35.3 kg of plastic packaging waste, out of which 14.8 kg was recycled. Compared to 2022, this was a reduction of 1 kg in waste generated, but a slight increase of 0.1 kg in recycling. Over the past decade, plastic packaging waste per person has risen by 6.4 kg, but the recycling rate improved by 3.8 kg per person.
In terms of plastic recycling, the EU successfully recycled 42.1% of plastic packaging in 2023, an improvement from the 38.2% rate in 2013. However, recycling performance varies widely across EU member states. Belgium is a leader in recycling with a rate of 59.5%, closely followed by Latvia (59.2%) and Slovakia (54.1%). On the other hand, some countries like Hungary (23.0%), France (25.7%), and Austria (26.9%) have much lower recycling rates.
The EU has also made significant progress in reducing plastic bag usage. In 2023, the average person used 65 plastic bags, which is 30 fewer bags per person than in 2018. Countries like Sweden, Lithuania, and Latvia led the way with reductions of 131, 125, and 118 bags per person, respectively.
Several EU countries are already achieving the recycling target of 70% for packaging waste set for 2030. Belgium, Netherlands, Italy, Czechia, Slovenia, Slovakia, and Spain have already met or exceeded this target, while six other countries are close, with recycling rates above 65%.
While the EU has made significant progress, challenges remain, especially in countries with lower recycling rates. However, the overall reduction in plastic bag consumption and the growing number of countries surpassing recycling goals show that the EU is on track to achieve its long-term sustainability objectives.
Packaging Waste Generation in the EU
In 2023, the European Union generated 79.7 million tonnes of packaging waste, which equals 177.8 kg per person. While this is an improvement from 2022, where the average was slightly higher, it’s still a significant increase compared to a decade ago. The waste produced mainly consists of paper and cardboard (40.4%), followed by plastic (19.8%), glass (18.8%), and wood (15.8%). Although most countries followed this trend, Bulgaria was an exception, where plastic waste exceeded paper and cardboard.
Plastic Waste and Recycling Improvements
Plastic packaging waste continues to be a major concern. In 2023, each person in the EU produced an average of 35.3 kg of plastic packaging waste. This figure has risen by 6.4 kg per person since 2013. However, recycling efforts have improved. In 2023, 42.1% of plastic packaging waste was recycled, a significant increase from 38.2% in 2013. Belgium led the EU with a recycling rate of 59.5%, followed by Latvia (59.2%) and Slovakia (54.1%). On the other hand, Hungary had the lowest recycling rate, at just 23.0%.
In addition to recycling, the EU made progress in reducing plastic bag usage. The average person in the EU used 30 fewer plastic bags in 2023 compared to 2018, with Sweden, Lithuania, and Latvia seeing the biggest reductions.
Changes in Packaging Waste Generation and Recycling (2014-2023)
Over the past decade, packaging waste generation and recycling in the EU have fluctuated. In 2023, the amount of packaging waste per person decreased by 4.7%, reaching 177.8 kg, compared to 2022. The highest level of waste generation was in 2021, with 190.1 kg per person. Recycling followed a similar pattern. In 2023, 120.0 kg of packaging waste per person was recycled, a small drop from 121.8 kg in 2022. However, recycling rates generally rose from 2014 to 2021, despite a few minor declines in 2018 and 2020.
Packaging Waste Generation and Recycling Across EU Countries
Packaging waste generation varies greatly between EU countries. Ireland had the highest waste generation, with 223.1 kg per person, while Bulgaria had the lowest, at just 80.9 kg per person (data from 2022). Fifteen EU countries generated more than 150 kg of packaging waste per person. Countries like Italy, Germany, and Luxembourg exceeded 200 kg, while Bulgaria, Cyprus, and Croatia produced less than 100 kg of packaging waste per person.
Despite generating high amounts of packaging waste, countries like Italy, Germany, and Luxembourg also showed strong recycling efforts. Italy had the highest recycling rate at 162.2 kg per person, followed by Germany (149.3 kg), Luxembourg (132.4 kg), and Ireland (131.6 kg). On the other hand, Croatia, Bulgaria, and Romania recorded the lowest recycling rates.
The EU’s 2030 Recycling Targets
The EU has set ambitious recycling targets for 2030. It aims to recycle at least 70% of all packaging waste by weight. Specific targets include recycling 85% of paper and cardboard, 75% of glass, 55% of plastics, 80% of ferrous metals, 60% of aluminum, and 30% of wood. These targets reflect the EU’s commitment to creating a more sustainable and circular packaging system.
Segmental Insights
What Causes the Plastic Waste Segment to dominate the Market?
The plastic waste segment held a dominant presence in the circular economy in the packaging market in 2024. The growth of the segment is mainly driven by the rising environmental awareness of plastic pollution, rising regulatory pressures, and increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging. Plastic consumption has significantly increased in the packaging sector. Single-use plastics, such as packaging, bottles, caps, cutlery, and others, are the major contributors to plastic waste. These items are generally discarded after one use, which creates a significant environmental burden. According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, in February 2022, only 9% of plastic waste is recycled, while 22% is mismanaged globally.
According to recent secondary data, approximately 11 million tonnes of plastic enter the oceans annually, which poses a threat to marine life, as many species ingest plastic particles as they consider their food. As plastic waste is a major component of packaging waste, it increases the need for effective plastic packaging waste management for environmental sustainability. Moreover, rising government initiatives and regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting recycling infrastructure are expected to drive the segment’s growth during the forecast period.
- In June 2025, IW Capital announced a £3.3 million follow-on investment into Impact Recycling, a plastic recycling company. Impact Recycling has developed and commercialised a patented water-based density separation technology – Baffled Oscillation Separation System (BOSS). The company’s further investment in Impact Recycling takes place against a backdrop of regulatory tailwinds, such as the EU’s Plastic Packaging and Plastic Packaging Waste Directive, which is aimed at reducing the environmental impact of plastic packaging and requires 35% recycled content to be used in any plastic packaging by 2030, rising to 60% by 2040. (Source: Letsrecycle)
How Landfilling Segment dominate the Market in 2024?
The landfilling segment held a dominant position in the packaging waste management market in 2024. A large portion of packaging waste ends up in landfills, which creates the need for a landfilling method. Landfilling remains a dominant segment, owing to the various factors such as the presence of inadequate waste management infrastructure in undeveloped countries and reduced initial costs. Landfilling is a widely adopted method for packaging waste disposal, particularly for plastics. The importance of landfilling has substantially increased with the surge in plastic waste generation and increasing awareness of environmental degradation.
On the other hand, the recycling & resource recovery segment is expected to grow at a significant rate, owing to the rising environmental awareness, growing emphasis on sustainability, rising regulatory pressures, and increasing demand for recycling packaging materials. Recycling and resource recovery involve the collection, sorting, and reprocessing of packaging materials such as plastics, paper, glass, and metals. Recycling can be cost-effective and more sustainable when compared to landfilling or incineration, especially in the long run. Several prominent market players are increasingly investing in mechanical recycling and reusing packaging materials with an aim to reduce their carbon footprint and boost sustainability. Stringent government regulations and policies like Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes aim to promote waste reduction and recycling practices, bolstering the segment’s growth during the forecast period.
The Residential Sector Dominated
The residential segment accounted for a significant share of the packaging waste management market in 2024. The growth of the segment is mainly driven by the rising population and rapid urbanization. The market has witnessed the increased consumption of packaged goods in the residential sector, resulting in a high volume of household waste generation. The adoption of effective packaging waste management is a crucial step toward reducing the environmental impact on the ecosystem.
The industrial sector accounts for a significant portion of packaging waste originating from industrial activities, which has led to an increasing need for effectively managing packaging waste. These packaging waste management services focus on managing and processing the large volumes of industrial packaging waste with an aim to reduce landfill waste and promote a circular economy for packaging. Moreover, chemical recycling is gaining immense popularity to tackle the rising problem of waste plastic pollution by offering an innovative way to reuse and recycle plastic waste. It assists in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and relieves pressure on landfill capacity.
Which End-use of Recycled Material Holds the Majority of the Share?
The new packaging production dominated the packaging waste management market in 2024, owing to the rising consumer demand for recycled and eco-friendly packaging materials and surging investment in improving recycling technologies. Companies are increasingly focusing on developing recycled packaging solutions without compromising performance and functionality. In addition, the incorporation of recycled packaging materials marks a shift towards a circular economy, with a strong focus on optimizing the use of available resources. On the other hand, the construction segment is expected to grow at a notable rate during the forecast period, owing to the rising emphasis to promote of sustainability and lowering the dependency on virgin materials. Recycled materials are extensively utilized for various applications in the construction industry. The most common recycled materials include recycled steel, reclaimed wood, crushed concrete, recycled glass, recycled plastic, and others. The increasing use of recycled materials in the construction industry assists in conserving natural resources and significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with material extraction and production.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific is Dominating the Market with the Majority of the Market Share
Asia Pacific held the dominant share of the packaging waste management market in 2024. Consumers and businesses in the region are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, which has led to an increasing demand for recycled and reusable packaging solutions as well as the adoption of efficient waste management systems. The growth of the region is mainly attributed to the strong presence of packaging recycling infrastructure, rising concerns about the environmental impact of packaging waste, a supportive government framework, increasing innovation in sorting and processing technologies, rising demand for recycled packaging solutions, high consumer spending on sustainable packaging solutions, and growing focus on aligning with the principle of the circular economy.
The rapid urbanization in the region, particularly in developing countries, is anticipated to fuel the market expansion in the coming years. The urban areas generate more packaging waste, requiring robust packaging waste management infrastructure and services. Businesses operating in the region are facing regulatory pressure from investors, consumers, and the government to adopt eco-friendly practices for reducing packaging waste and boosting environmental sustainability. Furthermore, the surging investment in recycling and green technologies, such as chemical recycling, is substantially enhancing the possibilities for managing different types of packaging waste
- In July 2025, Eneos Corp. and Mitsubishi Chemical Corp. (MCC) recently announced the completion of construction on their chemical recycling facility at MCC’s Ibaraki Plant, located in Kamisu City. The Japan-based collaborators say the facility employs hydrothermal (Hydro-PRT) technology that features supercritical water as a solvent to chemically break down plastic scrap procured externally and turn it into oil. (Source: Recycling Today)
India Packaging Waste Management Market
India is one of the fastest-growing regions in packaging waste management. Growth is fueled by compostable packaging adoption, EPR policies, and stricter laws governing single-use plastics. The market is being accelerated by private sector involvement and government initiatives to enhance recycling infrastructure. Adoption of sustainable packaging is further accelerated by the growing demand for FMCG and e-commerce packaging.
Middle East and Africa Packaging Waste Management Market
MEA is a notable region with a growing focus on packaging waste management. Governments are beginning to fund recycling and circular economy programs as environmental concerns gain more attention. The use of sustainable packaging is increasing thanks to regional partnerships and governmental initiatives. Packaging waste volumes are increasing due to urbanization and industrial expansion, underscoring the necessity of efficient waste management systems.
UAE is dominating the market, driven by plastic bags and policies that support recyclable and reusable packaging, which are pushing businesses to use eco-friendly practices. Waste-to-energy initiatives and recycling facilities are receiving more funding. Advanced waste management solutions are being implemented by businesses in response to consumer demand for sustainable products.
Europe Packaging Waste Management Market
Europe dominated the market globally in packaging waste management as it is well organized due to strict EU regulations, mandatory recycling targets, and circular economy systems. Innovative, recyclable and compostable materials are becoming more and more popular. Europe's leadership in the field is reinforced by active corporate responsibility initiatives and high levels of public awareness.
Germany is a notable leader in Europe, as efficient waste management is fueled by cutting-edge recycling programs and strict adherence to environmental regulations. Businesses are concentrating on utilizing recyclable materials and lightening packaging. High recycling rates and continuous innovation are ensured by government and industry cooperation.
Value Chain Analysis
Raw materials sourcing
Feedstock mainly comes from post-consumer and post-industrial packaging waste collected through municipal and commercial channels. Improved segregation and source collection help increase recyclable material recovery. Consistent sourcing is critical for recycling efficiency.
Supply to the government and airlines
Governments rely on waste management firms for municipal packaging waste handling and regulatory compliance. Airlines and airports generate significant packaging waste from food service operations, driving demand for specialized waste collection and recycling solutions. Sustainability reporting is often included in these contracts.
Aftermarket services and upgrades
Aftermarket services include equipment maintenance, process optimization, and system upgrades. Digital monitoring and automation are increasingly used to improve sorting accuracy and operational performance. Service upgrades help reduce downtime and improve recovery rates.
Top Packaging Waste Management Market Players

- Veolia Environnement S.A.
- Suez S.A.
- Waste Management, Inc.
- Republic Services, Inc.
- Biffa plc
- Waste Connections, Inc.
- Remondis AG & Co. KG
- Stericycle, Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- FCC Environment
- Clean Harbors, Inc.
- Republic Services, Inc.
- Green Waste Management
- Recology
- China Everbright International Limited
- Urbaser S.A.
- Hitachi Zosen Corporation
- E.ON SE (in waste-to-energy)
- Renewi plc
- TerraCycle
Latest Announcement by the Industry Leader
- In July 2025, PyroGenesis Inc., a high-tech company that designs, develops, manufactures and commercializes advanced all-electric plasma processes and sustainable solutions to support heavy industry, announced that it has signed a contract for €379,000 with one of the world’s largest integrated environmental services companies, expanding PyroGenesis’ relationship with this client to include developing a solution for the plastic waste problem in Europe. (Source: The Manila Times)
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Chemco partnered with Kandoi to launch an INR 450-crore JV for the rPET project, creating a circular economy project, which is expected to transform PET waste into industrial packaging. Commercial production will begin by the end of 2025, and it will generate over 2,500 jobs and formalise India's waste value chain. (Source: What Packaging?)
- In March 2025, Danish-Indian collaboration launched the ‘From Beach to Big Bags’ recycling initiative. The partnership is focused on building a scalable and sustainable value chain that recycles both ocean-bound and inland plastic waste into recycled polypropylene (rPP) big bags for industrial use.
- In January 2025, the Coca-Cola Foundation (TCCF) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) are joining forces to tackle the escalating plastic waste crisis in Asia. With a grant of $15 million (nearly Rs 130 crore) from TCCF, this three-year program will be implemented across nine countries: Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, India, Maldives, Nepal, Philippines, Sri Lanka, and Vietnam. (Source: Times of India)
Packaging Waste Management Market Segments
By Waste Type
- Plastic Waste
- Paper & Paperboard Waste
- Glass Waste
- Metal Waste
- Other Packaging Waste (e.g., wood, multi-material)
By Service Type
- Collection & Transportation
- Sorting & Segregation
- Disposal
- Landfilling
- Incineration & Waste-to-Energy
- Recycling & Resource Recovery
- Composting & Anaerobic Digestion
By Source
- Residential
- Commercial (Retail, Office, etc.)
- Industrial (Manufacturing, Logistics, etc.)
By End-Use
- New Packaging Production
- Construction
- Automotive
- Textiles
- Other Industries
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Norway
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)
- South Africa
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Kuwait
Tags
FAQ's
Select User License to Buy
Figures (4)