The mono-material barrier packaging market is growing rapidly, with revenue set to reach the hundreds of millions by 2034, driven by the shift toward 100% recyclable packaging. This market analysis covers the complete picture market size from 2025 to 2034, CAGR trends, and regional insights across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. It also includes detailed segmentation by type (PE, PP, PVC, others) and application (food & beverage, medicine, consumer goods). Readers will gain insights into leading companies like Amcor, Mondi, Sealed Air, and Constantia Flexibles, as well as competitive analysis, merger activities, value chain mapping, global trade flow, and supplier/manufacturer profiles. All statistical data provided helps decision-makers understand demand patterns, production capabilities, and market forecasts.
Mono-material barrier packaging refers to packaging made primarily from a single type of material that includes barrier properties to protect products, especially food and pharmaceuticals, from external factors like moisture, oxygen, light, or aroma. "Mono" means single, so the packaging is made almost entirely from one type of polymer. This contrasts with multi-material packaging, which combines layers of different materials, making recycling difficult. Mono material packaging is designed to be more easily recyclable because it doesn’t require the separation of layers. Barrier properties are crucial for preserving shelf life and ensuring product safety.
| Metric | Details |
| Key Market Drivers |
- Rise in e-commerce and on-the-go packaging demand |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Market Segmentation | By Type, By Application and By Region |
| Top Key Players | Amcor, Mondi Group, Sealed Air, Constantia Flexibles, and Smurfit Kappa Group |
Manufacturers are developing mono-material films that are compostable or biodegradable, offering sustainable end-of-life solutions for products with short shelf lives. These innovations cater to the growing demand for eco-friendly packaging options across various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care.
There is a notable trend towards developing mono-material films with advanced functionalities, such as antimicrobial properties, oxygen scavenging capabilities, and compostability. Additionally, smart packaging solutions integrating technologies like RFID tags and QR codes are being introduced for improved traceability and consumer engagement.
Companies are focusing on improving the recyclability of mono-material films by developing better recycling infrastructure and technologies. This includes the introduction of advanced sorting systems and innovative recycling methods, such as chemical recycling, to reclaim mono-material films and produce new high-grade materials.
Innovations like Zotefoams' ReZorce mono-material barrier packaging have been recognized for their sustainable design and recyclability. ReZorce won the Product Innovation category at the 2024 Reuters Sustainability Awards, highlighting its potential to replace non-recyclable composite materials in beverage cartons.
Stricter regulations on packaging waste and increasing consumer demand for sustainable packaging solutions are driving companies to adopt mono-material packaging. For instance, the European Union's "Circular Economy Action Plan" aims to make all packaging recyclable by 2030, prompting companies like Coca-Cola to shift to mono-material solutions.
Monomaterials are easier to recycle than multi-layer composites, which often end up in landfills. Supports circular economy goals by allowing single-material packaging to be more effectively reused and repurposed. Increased awareness of the environmental impact of packaging is pushing brands to choose eco-friendly alternatives.
Advances in polymer science are enabling mono-material films to provide barrier properties previously only possible with multi-layer composites. New coatings, additives, and lamination techniques allow mono-materials to mimic the high-performance properties of traditional packaging. AI and machine learning are accelerating design, testing, and production.
Companies like Nestlé, Unilever, and Coca-Cola have made public commitments to make all packaging recyclable, reusable, or compostable by 2025 or 2030. ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are putting pressure on brands and their supply chains to innovate. Investors increasingly favour sustainable companies, giving brands a financial reason to shift.
AI-powered simulations can model how different mono-materials behave under stress, temperature, or humidity to develop optimal barrier properties. Machine learning (ML) helps in designing multi-layered mono-material films that replicate the performance of multi-materials, while remaining recyclable. AI can also predict long-term material performance, enabling more accurate shelf-life projections and reducing over-packaging. Computer vision systems powered by AI can detect micro-defects in films in real time during production. Predictive maintenance powered by AI minimizes downtime of extrusion and lamination equipment by forecasting machine failures.
AI can analyze historical and real-time data to predict demand trends for specific packaging formats, helping manage raw materials efficiently. Inventory optimization algorithms reduce overstocking and waste of raw mono-material films. Logistics AI ensures efficient transportation of packaging products, reducing the carbon footprint. AI can track life cycle assessments (LCAs) more accurately, helping companies make informed decisions about material choices and end-of-life strategies. Machine learning models improve sorting and recycling technologies, especially in automated material recovery facilities (MRFs), by distinguishing mono-materials from composites.
AI analyses consumer behaviour and preferences via e-commerce and retail data to help brands tailor packaging design and communication. Natural language processing (NLP) can assist in creating clear, compliant, and engaging labeling for sustainability messaging. AI tools can monitor global regulations and alert manufacturers to changes affecting recyclable and sustainable packaging standards. The AI integration helps to identify risks in the supply chain and suggest proactive mitigation strategies. Process optimization algorithms can tune parameters to reduce energy use and waste.
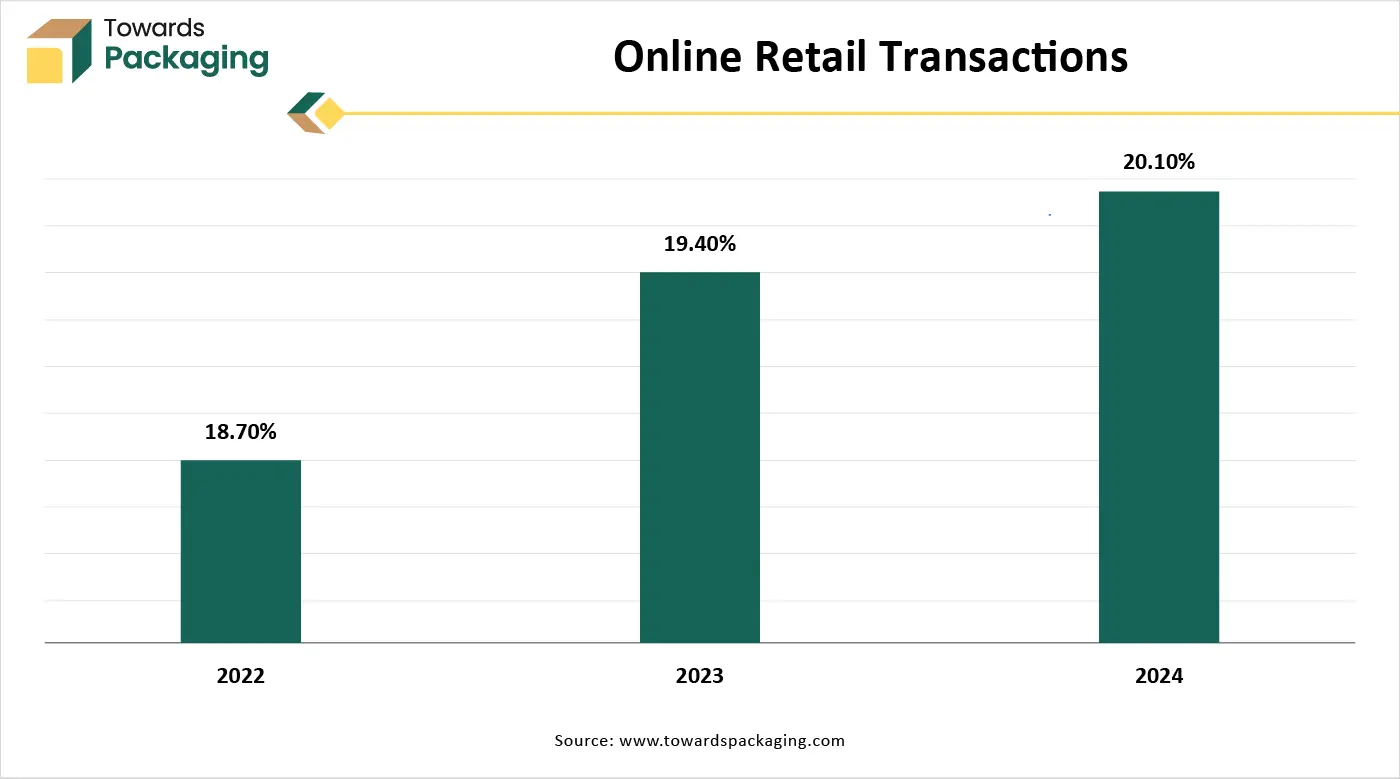
Growth in On-the-Go Packaging and E-Commerce Industry
E-commerce and food delivery demand durable, lightweight, and sustainable packaging, which mono-materials can fulfil. The push for flexible and stand-up pouches (often mono-material) is growing rapidly in cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals. According to the B2B eCommerce Association, 83% of consumers research products online before visiting a store, with 44% beginning their purchasing experience on a search engine and 41% doing so directly on websites run by businesses or online retailers like Amazon. Additionally, 14% of individuals prefer to begin their online purchasing experience on social media. Walmart's overall revenue increased 2.5% year over year in the first quarter, from USD 161.51 billion to over USD 165.61 billion. In the meantime, during the past ten quarters, Walmart's online sales have increased by more than 15% annually.
Recycling Infrastructure and Compatibility and Regulatory and Certification Hurdles
The key players operating in the mono-material barrier packaging market are facing issues due to recycling infrastructure and regulatory hurdles. While mono-materials are designed to be recyclable, many regions lack the infrastructure or policies to handle them properly. Consumers may still improperly sort mono-materials if they resemble multi-material packaging, reducing actual recycling rates. New mono-material solutions must undergo safety and performance testing to comply with food contact and environmental regulations. Absence of uniform standards for "recyclability" and "mono-material" claims can cause confusion and slow adoption.
Government Regulations and Support
Policies like the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan and bans on non-recyclable plastics are accelerating the shift to recyclable mono-materials. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) regulations make producers accountable for packaging waste, incentivizing the use of easily recyclable materials. Global plastic taxes and packaging waste reduction goals are making compliance a financial necessity. In order to encourage the use of mono-material packaging and reduce trash generation, states such as Maryland, U.S., are enacting EPR legislation that makes producers accountable for managing their packaging waste. There is a compelling case for mono-material packaging due to the increased focus on circular economy concepts and programs encouraging recycling and waste minimization.
The Polyethylene segment dominates the market as it is extensively used for manufacturing mono-material barrier packaging because it offers a favorable combination of mechanical, processing, and barrier properties, while also aligning well with sustainability and recyclability goals. Mono-material PE packaging is fully recyclable within the existing polyethylene recycling streams. Multi-material structures are difficult to recycle due to the incompatibility of layers, so switching to all-PE structures supports circular economy targets. While PE on its own has limited barrier properties, new technologies allow enhancement through coatings or PE-based barrier resins.
Advanced PE films can be co-extruded or laminated in mono-material formats with acceptable barrier performance for many food and pharma products. The PE packaging offers excellent sealability, toughness and puncture resistance, flexibility, and formability. These are essential for packaging formats like pouches, bags, and films. The PE material works well with standard extrusion, lamination, and printing processes. The PE material can be adapted to form-fill-seal machines and other high-speed packaging lines. PE is widely available and cost-effective compared to specialty plastics. Increasing demand from brand owners and regulators for 100% recyclable or mono-material solutions is accelerating the shift to PE-based mono-material barrier packaging.
The polypropylene (PP) packaging segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. The polypropylene is gaining traction in the market due to its strength, chemical resistance, and versatility. It is particularly suitable for applications requiring higher temperature resistance and is increasingly integrated with advanced technologies to create interactive and intelligent packaging solutions.
Single polymer type means the packaging can go into a single recycling stream. Traditional multi-layer packaging (e.g., PET/Alu/PE) is difficult or impossible to recycle. Brand owners and regulators are pushing for Design for Recycling (DfR) compliance to meet Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) goals. Example: Mono-PE pouches can be recycled in LDPE streams, making them attractive for sustainable product lines. Food and beverage packaging requires barriers against oxygen, moisture, and light. Monomaterials that use enhanced barrier technologies such as EVOH layers still qualify as monomaterials if under certain thresholds.
Bread bags with mono-PE plus EVOH layers for oxygen barrier. Mono-material films, especially PE and PP, work on high-speed packaging lines and provide good sealability, even in contamination-prone conditions. The mono-material barrier packaging allows transparent or printable surfaces for branding and regulatory information. For example: Stand-up pouches for juice or yogurt with all-PP laminate structures. EU Green Deal, U.S. Plastic Pact, and many national frameworks require recyclable or compostable packaging by 2025–2030. Major FMCG companies such as Nestlé, Unilever, and Coca-Cola are shifting to mono-material structures to meet these goals.
North America has a more developed recycling infrastructure compared to many other regions. Mono-material formats are more likely to be accepted and processed by municipal recycling facilities (MRFs). There is a growing focus on chemical recycling and closed-loop systems. Companies like NOVA Chemicals and Dow are investing in mono-material packaging that works well with both mechanical and advanced recycling systems. The region is a global leader in polymer science, film extrusion, and barrier coating technologies. North America has a well-established packaging industry with High automation, Extensive retail distribution networks, and demands for scalable, recyclable packaging formats. North American consumers are increasingly eco-conscious, especially millennials and Gen Z. Brands actively use sustainability labeling to win shelf space in major retailers like Walmart, Target, and Whole Foods.
U.S. states like California, Oregon, New York, and Canadian provinces have introduced: Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws, Single-use plastic bans, and Mandatory recyclability labelling. These policies pressure brands and converters to switch from multi-material, non-recyclable formats to mono-material solutions that meet legal and environmental standards. For instance, California SB 54 mandates that all packaging be recyclable or compostable by 2032. Global and regional FMCG giants are headquartered or heavily active in North America. These companies have public sustainability goals to shift to recyclable, mono-material packaging by 2025–2030.
Massachusetts is home to several prominent packaging companies that are at the forefront of adopting and advancing mono-material barrier packaging technologies: UFP Technologies specializes in custom-engineered packaging solutions, including sterile packaging for medical devices. Their expertise in materials science positions them as leaders in developing sustainable packaging alternatives. Seaman Paper Company, a major producer of tissue and crepe paper products, Seaman Paper is exploring sustainable packaging solutions, aligning with the industry's shift towards eco-friendly materials. Everfresh Packaging offers innovative flexible packaging solutions that help maintain product freshness, contributing to the adoption of recyclable mono-material packaging.
Massachusetts has implemented policies that encourage the adoption of sustainable packaging solutions. These regulations create a conducive environment for companies to innovate and transition towards mono-material barrier packaging, aligning with global trends towards reducing plastic waste and enhancing recyclability. The presence of renowned universities and research institutions in Massachusetts fosters collaboration between academia and industry. These partnerships facilitate the development of advanced materials and technologies that are crucial for the growth of the mono-material barrier packaging market.
The Asia Pacific market is growing rapidly due to well-established local manufacturing capabilities and resin availability in the region. The e-commerce boom demands lightweight, protective, and recyclable packaging—ideal use cases for mono-material films and pouches. Brands are shifting from traditional multilayer plastics to mono-PE pouches for snacks and dry goods due to recyclability and lighter weight. Global brands operating in Asia have made global commitments to switch to recyclable or mono-material packaging. These brands are driving regional supplier upgrades to meet their global sustainability targets.
Countries like China, India, South Korea, and Japan have rolled out plastic waste reduction laws: India's Plastic Waste Management Rules, China’s bans on non-recyclable plastics, and Japan’s Plastic Resource Circulation Act. These regulations push industries to switch to recyclable mono-material solutions to avoid penalties and meet compliance standards. Several Asia Pacific countries are investing in mechanical and chemical recycling systems. Asia-Pacific is home to some of the world’s largest plastic resin producers. Lower raw material and labor costs make the region a manufacturing hub for both local use and export.
China Market Trends
China's mono-material barrier packaging market is driven by the massive packaging manufacturing base. China is the world’s largest producer of packaging materials, including flexible and rigid plastics. It has thousands of film extrusion, converting, and lamination plants that are rapidly adopting mono-material technologies. Chinese companies and research institutes are investing in advanced barrier coatings, oriented film technologies, and functional additives. The leaders like Kingfa, China XD, Wipak China, and others are developing recyclable barrier materials. China controls a large part of the global polymer supply chain from resin production to film conversion and printing.
The Chinese government is aggressively promoting plastic waste reduction and circular economy policies: a National ban on non-recyclable single-use plastics. Mandatory recycling targets and eco-design guidelines. Encouragement of eco-labeling and recyclable packaging standards. These policies have created strong incentives for manufacturers to shift from multi-layer to mono-material designs. Moreover, China is a key exporter of packaging films and finished flexible packaging to global markets. International brand owners increasingly demand recyclable and sustainable packaging, so Chinese suppliers have adapted quickly to maintain export relevance. China’s manufacturing ecosystem allows rapid prototyping, scaling, and adjustment.
Strict EU Regulations and Circular Economy Directives. The EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) and the European Green Deal mandate: 100% recyclable packaging by 2030, Plastic reduction targets, and a Ban on certain non-recyclable multi-layer structures. The Single-Use Plastics (SUP) Directive and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws push brands toward fully recyclable, mono-material solutions. Many European countries have high waste sorting rates, advanced mechanical and chemical recycling facilities, and Robust collection systems for plastics. Mono-material packaging, especially PE and PP-based, is easily integrated into these existing recycling streams. For instance, Germany’s “Green Dot” system rewards companies for using recyclable packaging formats like mono-material films.
European companies have committed to using 100% recyclable or reusable packaging by 2025–2030. Retailers like Tesco, Carrefour, and Aldi are increasingly demanding mono-material packaging from suppliers as part of plastic reduction roadmaps. European consumers are highly informed and demand sustainable packaging. Products with labels like "100% recyclable," "mono-material," or "eco-friendly" have a strong competitive advantage. Countries like Sweden and Germany rank among the highest globally in consumer demand for sustainable products. Europe is home to packaging tech leaders who are developing barrier-grade mono-material films. Initiatives like RecyClass and CEFLEX provide guidance and certification for mono-material packaging designs. These frameworks ensure harmonized recyclability standards across EU countries, making mono-material packaging more commercially viable.

By Type
By Application
By Region
January 2026
January 2026
January 2026
January 2026