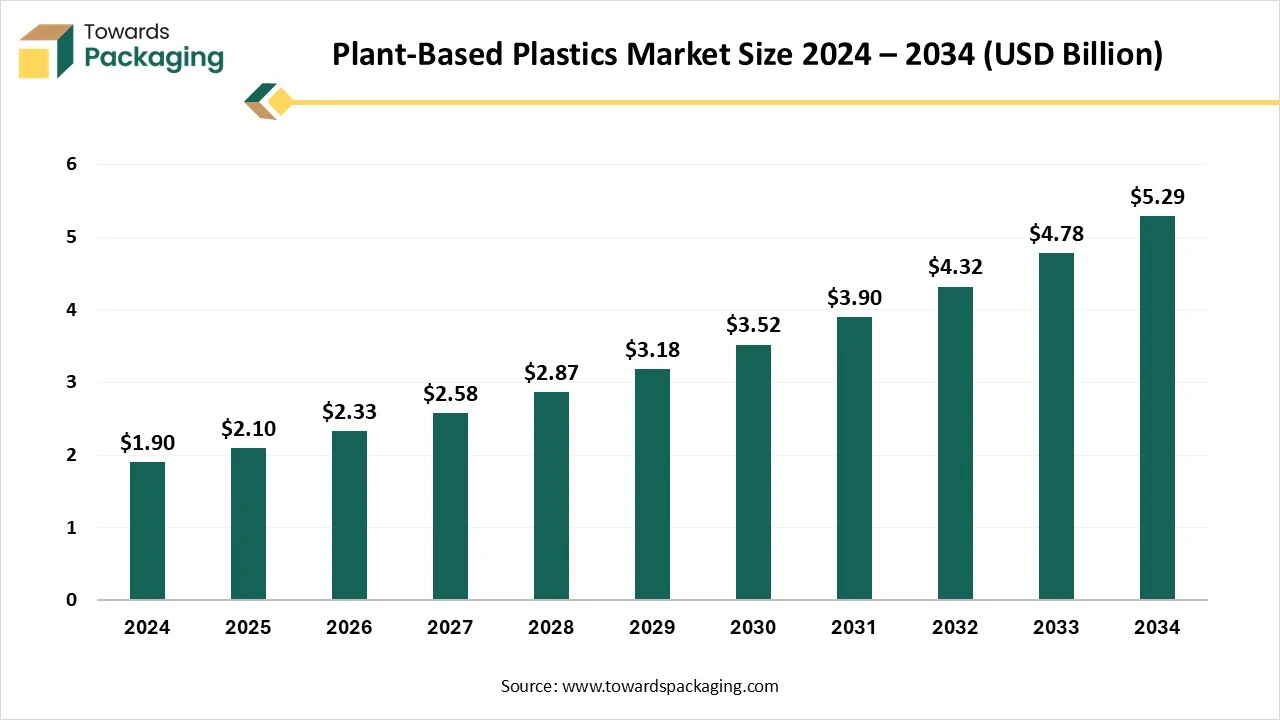
The plant-based plastics market is forecasted to expand from USD 2.33 billion in 2026 to USD 5.84 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 10.74% from 2026 to 2035. This report covers key market trends, including the rising adoption of polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), along with insights into biodegradable and non-biodegradable bioplastics.
Regional analysis highlights North America as the largest market, with Asia Pacific exhibiting the fastest growth.The report also includes a detailed breakdown by source, application, and end-use industry, along with competitive strategies adopted by leading players such as NatureWorks LLC, Braskem S.A., BASF SE, and TotalEnergies Corbion.
Sustainability is becoming a key focus and plays a crucial role in the packaging industry, allowing businesses to address various ongoing environmental challenges, including plastic pollution, climate change, and depletion of resources. Additionally, the market is growing at a significant rate in various developing and developed regions, particularly North America, driven by the stringent regulatory standards and increasing demand for plant-based plastic across various industries.
Plant-based plastics, also known as bioplastics, are a category of polymers derived from renewable biomass sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, cellulose, and other plant materials. These plastics may be biodegradable or non-biodegradable, but are distinguished by their bio-based origin rather than fossil-fuel sources. Plant-based plastics are increasingly used in packaging, agriculture, automotive, electronics, textiles, and consumer goods.
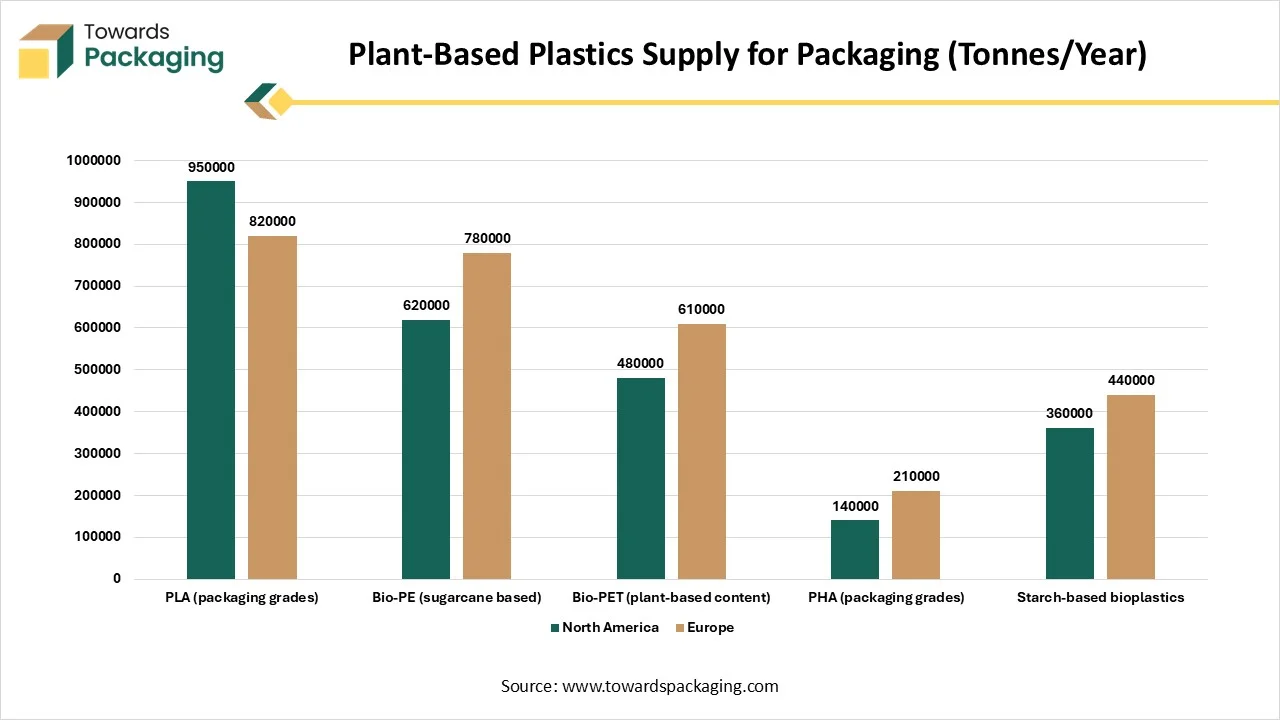
| Material Type | North America | Europe |
| PLA (packaging grades) | 950000 | 820000 |
| Bio-PE (sugarcane based) | 620000 | 780000 |
| Bio-PET (plant-based content) | 480000 | 610000 |
| PHA (packaging grades) | 140000 | 210000 |
| Starch-based bioplastics | 360000 | 440000 |
As technology continues to evolve, the integration of AI in plant-based plastics holds significant potential to impact the growth of the plant-based plastics market by improving manufacturing efficiency, reducing wastage, eliminating the chances of human error, and improving sustainability. AI-powered solutions in plant-based plastics make the process faster, cost-effective, and efficient. By leveraging machine learning (ML), scientists can study thousands of bioplastics to find the right combination of sustainability, strength, versatility, and manufacturability. With the assistance of AI-powered discovery, several industries can adopt eco-friendly and sustainable plant-based plastics solutions without losing performance.
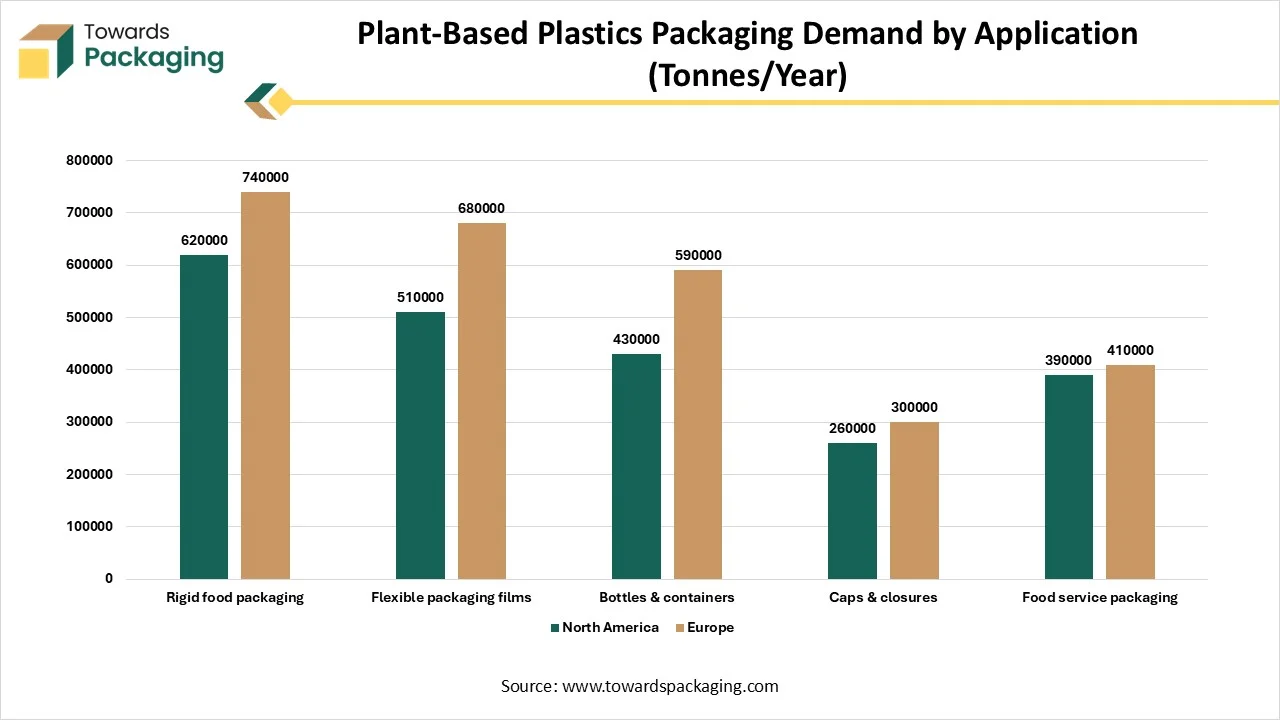
| Packaging Application | North America | Europe |
| Rigid food packaging | 620000 | 740000 |
| Flexible packaging films | 510000 | 680000 |
| Bottles & containers | 430000 | 590000 |
| Caps & closures | 260000 | 300000 |
| Food service packaging | 390000 | 410000 |
The growing need for sustainable plastics is expected to boost the growth of the plant-based plastics market during the forecast period. In 2023, Plastic production reached nearly 413.8 million metric tons, nearly 40% of which was used in packaging applications, and the remaining it serves to other industries such as automotive, construction, medical, and electronics.
Consumers around the world, particularly in developed and developing countries, are increasingly seeking sustainable alternatives and are willing to pay a premium for products that are generally made from renewable resources to reduce the environmental impact. Bioplastics, particularly PHAs, offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics that holds great potential to significantly lower the overall environmental footprint and promote economic circularity in the ecosystem.
The high cost is anticipated to projected to hamper the market's growth. High capital is required to produce plant-based plastics, which can be significantly higher than fossil-based plastics, and often results in less competitiveness in the market. In addition, various limitations of plant-based plastics in terms of barrier properties and functionality may restrict their use in high-performance applications.
The supportive government initiatives and guidelines for plant-based plastics are projected to offer lucrative growth opportunities to the plant-based plastics market in the coming years. Plant-based plastics are specifically designed to meet regulatory standards and reduce the carbon footprint. Several countries have implemented a ban on single-use plastics and introduced stringent recycling laws, which accelerate the adoption of plant-based plastics as a sustainable packaging solution. In addition, favourable supportive government policies, such as subsidies and tax breaks, encourage businesses to develop and use plant-based plastics.
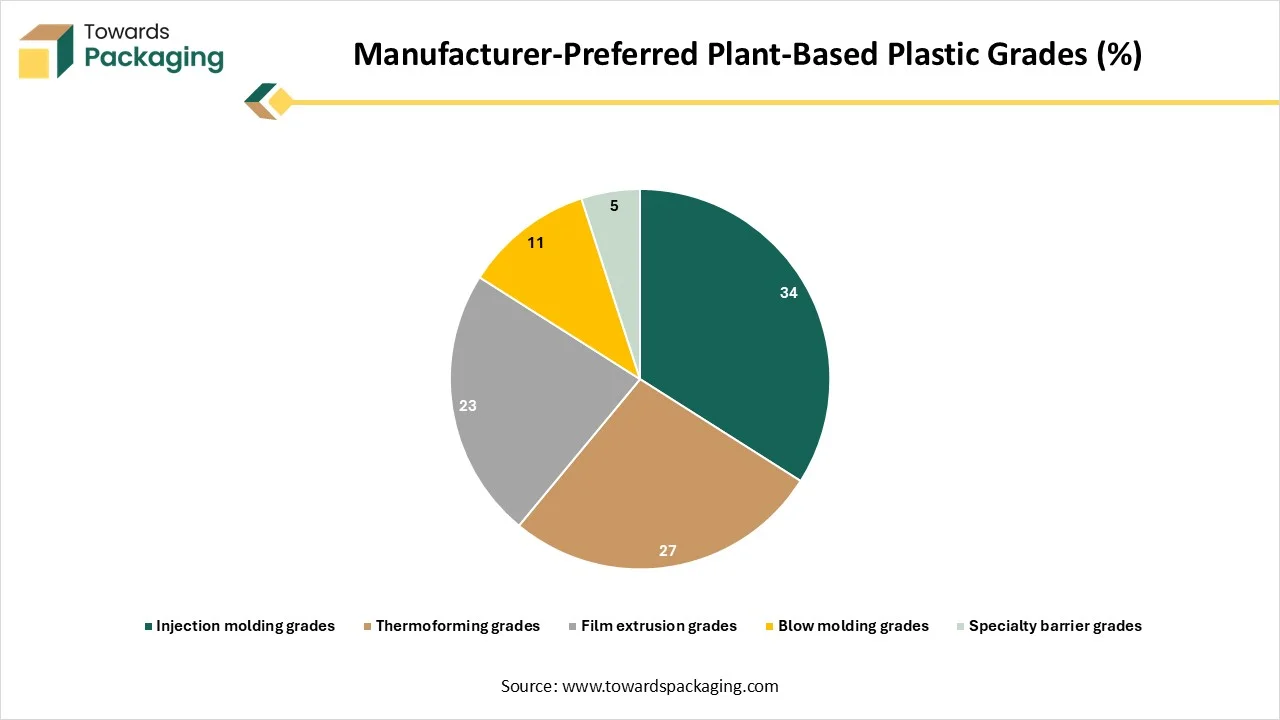
| Grade Type | Share |
| Injection molding grades | 34 |
| Thermoforming grades | 27 |
| Film extrusion grades | 23 |
| Blow molding grades | 11 |
| Specialty barrier grades | 5 |
The polylactic acid (PLA) segment accounted for the highest revenue share in 2024, owing to its efficient recyclability and biodegradability properties, which make it a suitable option for plant-based plastics. Polylactic acid is a type of bioplastic that is derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane, corn starch, and others. Polylactic acid offers a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics due to its biodegradability attributes.
On the other hand, the polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) segment is expected to grow at a significant rate. Polyhydroxyalkanoates are biodegradable and bio-based plastic and widely utilised as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastic films across agriculture, medical, packaging, and other industries. PHA offers a promising pathway as an alternative to conventional plastics owing to their higher thermal stability and biodegradability.
The corn dominated the plant-based plastics market in 2024. Corn starch is one of the most widely utilised materials to make bioplastics. Cornstarch is a renewable resource, and it is heated and processed to create polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable polymer. PLA is gaining rapid traction in food industries, such as containers, wraps, disposable cutlery, and others. The continuous research and development efforts by key market players to improve properties and wider applications for plant-based plastics, making them more popular over fossil-based traditional plastics.
On the other hand, the cellulose/wood segment is expected to grow at a notable rate during the forecast period. The growth of the segment is mainly driven by the rising demand for biodegradable and compostable materials. Some cellulose-based bioplastics generally can break down naturally under certain conditions. Cellulose/wood is a renewable resource and is derived from plants, making it a sustainable alternative as compared to fossil fuels.
The non-biodegradable (bio-based) segment accounted for the dominating share in 2024. Non-biodegradable (bio-based) materials are generally derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane, corn, and other plant-based materials. These materials are processed to develop sustainable plastics that offer similar attributes, like durability and strength, as conventional fossil-based plastics. Non-biodegradable bioplastics are specifically designed to last for a longer period, which makes them valuable for long-term usage products such as automotive parts, packaging materials, consumer goods, and others.
On the other hand, the biodegradable segment is expected to witness a significant share during the forecast period. The growth of the segment is mainly driven by the rising awareness of the environmental and health impacts of plastic pollution. Biodegradable plastics can be decomposed naturally by the action of living organisms. The two most common biodegradable bioplastics are PHAs and PLAs. Biodegradable plastics aim to reduce dependence on petroleum-based plastics, minimize environmental impact, and promote a circular economy.
The packaging segment held a dominant presence in the plant-based plastics market in 2024, owing to the increasing demand for plant-based plastics products in the packaging industry. Plant-based plastics offer an eco-friendly and biodegradable alternative to conventional fossil-based plastics in packaging for food items. In addition, the rising focus of food businesses to reduce their carbon and environmental footprint has significantly increased the demand for plant-based plastic packaging.
On the other hand, the automotive segment is expected to grow at a notable rate. The growth of the segment is mainly driven by the rise in eco-friendly innovations, increasing demand, and rising sustainability efforts by industry leaders. In the automotive industry, the rising adoption of sustainable solutions for reducing carbon footprints in the environment. Plant-based plastics are increasingly used in the automotive industry as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional fossil-based plastics. The use of sustainable materials offers various benefits such as lowering dependency on fossil fuels, lower CO2 emissions, and making lighter vehicles, which leads to potential fuel efficiency improvements.
The food and beverage segment dominates the plant-based plastics market. The rising concerns about environmental sustainability and the increasing accumulation of plastic waste have led to an increasing demand for plant-based plastics. In foodservice packaging, plant-based plastics play an integral role in replacing traditional plastics. This can include bowls, plates, compartment trays, takeaway containers, clamshells, and others. Products made from plant-based plastics require less energy and cause less pollution than plastic products.
On the other hand, the healthcare industry segment is growing at the fastest CAGR. Bioplastics offer a promising pathway toward a more sustainable future for the healthcare industry. Bioplastics or plant-based plastics have paved a new pathway toward a more sustainable future for the healthcare industry. Plant-based plastics are increasingly gaining immense popularity in the healthcare industry as a more sustainable alternative to fossil-based plastics. The major applications of plant-based based in the healthcare industry are medical devices, medical packaging, surgical instruments, implants and prosthetics, personal protective equipment (PPE), and others.
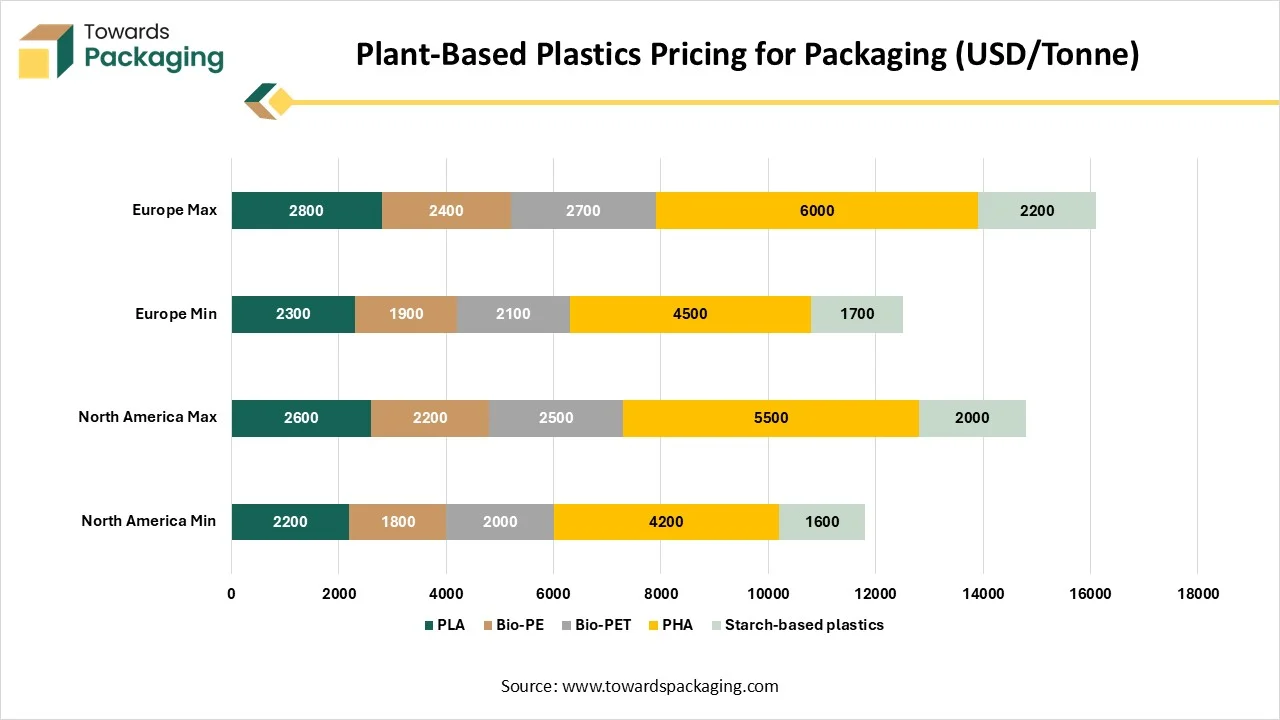
| Material | North America Min | North America Max | Europe Min | Europe Max |
| PLA | 2200 | 2600 | 2300 | 2800 |
| Bio-PE | 1800 | 2200 | 1900 | 2400 |
| Bio-PET | 2000 | 2500 | 2100 | 2700 |
| PHA | 4200 | 5500 | 4500 | 6000 |
| Starch-based plastics | 1600 | 2000 | 1700 | 2200 |
North America holds the largest share of the plant-based plastics. This is mainly attributed to the presence of prominent key players, increasing awareness of plastic pollution, stricter government regulation on single-use plastics, increasing consumer inclination for sustainable products, and rising focus on lowering the carbon footprint. The rapid shift toward biodegradable and compostable materials is mainly fueled by the increasing regulatory pressures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and evolving consumer preference for eco-friendly alternatives.
The demand from diverse end-use sectors such as food and beverage, healthcare, agriculture, automotive, and others is likely to drive the growth of the plant-based plastics market in the region. This is due to their growing emphasis on integrating plant-based plastics into their products, motivated by government sustainability efforts and the adoption of circular economy principles.
On the other hand, Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the market during the forecast period. The growth of the region is driven by the rising research and development efforts by prominent players to improve the properties of plant-based plastics, increasing consumer demand for sustainable alternatives, stringent government guidelines towards the usage of fossil-based plastics, and rising concern about plastic pollution in landfills, the ocean, and other ecosystems.
Asia Pacifics supportive government policies, including subsidies and tax breaks and are encouraging businesses to adopt plant-based plastics across various industries. Plant-based plastics are gaining immense popularity in the region as they generally have a reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional plastics, which makes them the most preferrable option among businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact and boost sustainability.
| Packaging Format | North America | Europe |
| Rigid food packaging | 20 – 40 | 30 – 55 |
| Flexible packaging | 15 – 30 | 25 – 45 |
| Bottles & containers | 10 – 25 | 20 – 40 |
| Food service items | 40 – 70 | 50 – 80 |
| Non-food packaging | 30 – 60 | 45 – 75 |
The plant-based food bioplastics market is forecast to grow from USD 1.15 billion in 2025 to USD 1.90 billion by 2034, driven by a CAGR of 5.7% from 2025 to 2034.
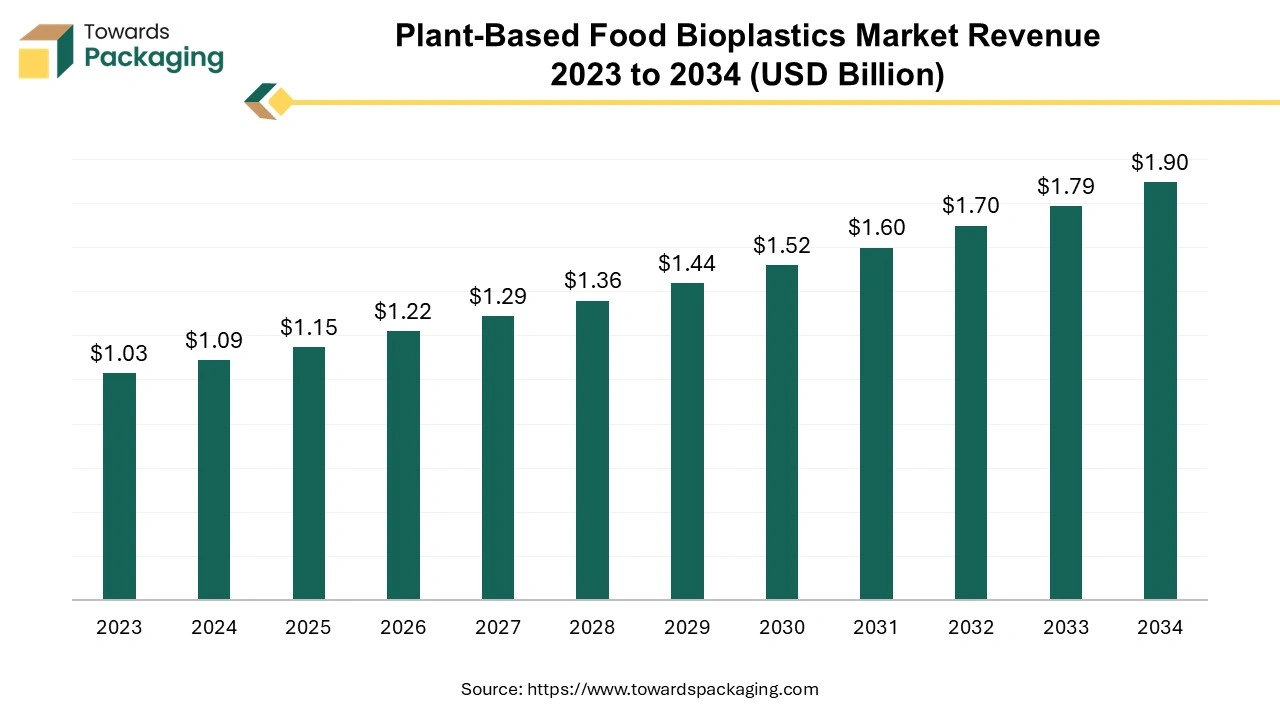
The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like acquisition and merger to develop advance technology for manufacturing plant-based food bioplastics which is estimated to drive the global plant-based food bioplastics market over the forecast period.
The food packaging developed from renewable biological sources, such as starch, cellulose, or proteins obtained from plant is known as plant-based food bioplastics. Unlike traditional plastics made from petroleum, these bioplastics are designed to be eco-friendlier. They can be biodegradable or compostable, meaning they can break down more easily in natural environments. These materials are often utilized for packaging food, utensils, and other products, aiming to reduce plastic waste and reliance on fossil fuels.
The plantable packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 157.17 million in 2025 to USD 435.13 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12.15% from 2025 to 2034.
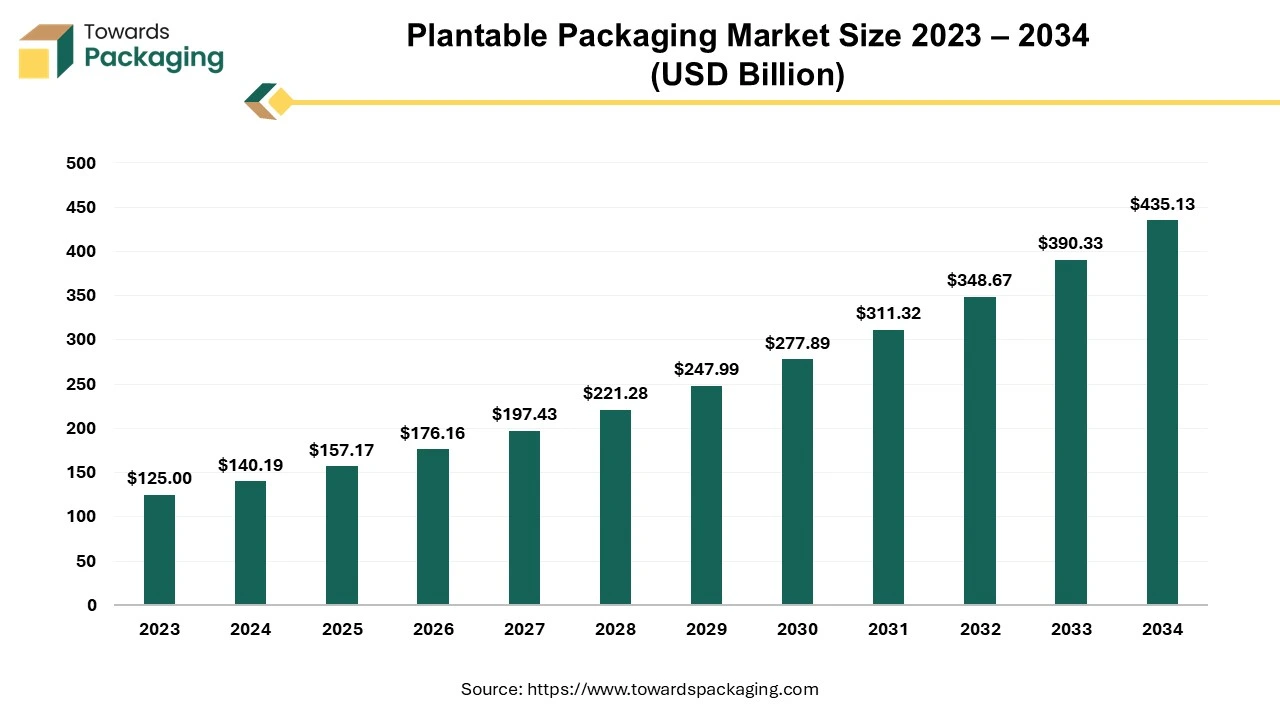
Customers' continuously Rising concern for reusable, Sustainable, and eco-friendly packaging has influenced the growth of this plantable packaging market. With growing awareness of environmental effects due to government initiatives, the demand for green packaging products has increased. Continuous improvisation in the packaging industry has increased the demand for the plantable packaging market.
The plantable packaging market plays a significant role in fulfilling the growing demand for sustainable packaging as people are aware of the adverse impact of plastic waste increasing in the environment. Plantable packaging offers materials embedded with seeds that help people plant packages after using the packaged product. It is a double-time usable packaging which is considered as both safe packaging for products as well as environmentally friendly.
| Parameter | Required Value |
| Melt Flow Index (g/10 min) | 8 – 40 |
| Bio-based carbon content (%) | 60 – 100 |
| Moisture content (%) | ≤ 0.3 |
| Odor rating (scale 1–5) | ≤ 2 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 0.90 – 1.25 |
| Heat resistance (°C) | 90 – 140 |
| Food-contact compliance | FDA / EFSA |

By Type
By Source
By Degradability
By Application
By End-Use Industry
By Region








February 2026
February 2026
February 2026
February 2026