Active and Intelligent Packaging Market Growth 2025-2035 Breakdown, Competitive Benchmarking, Trade Flows
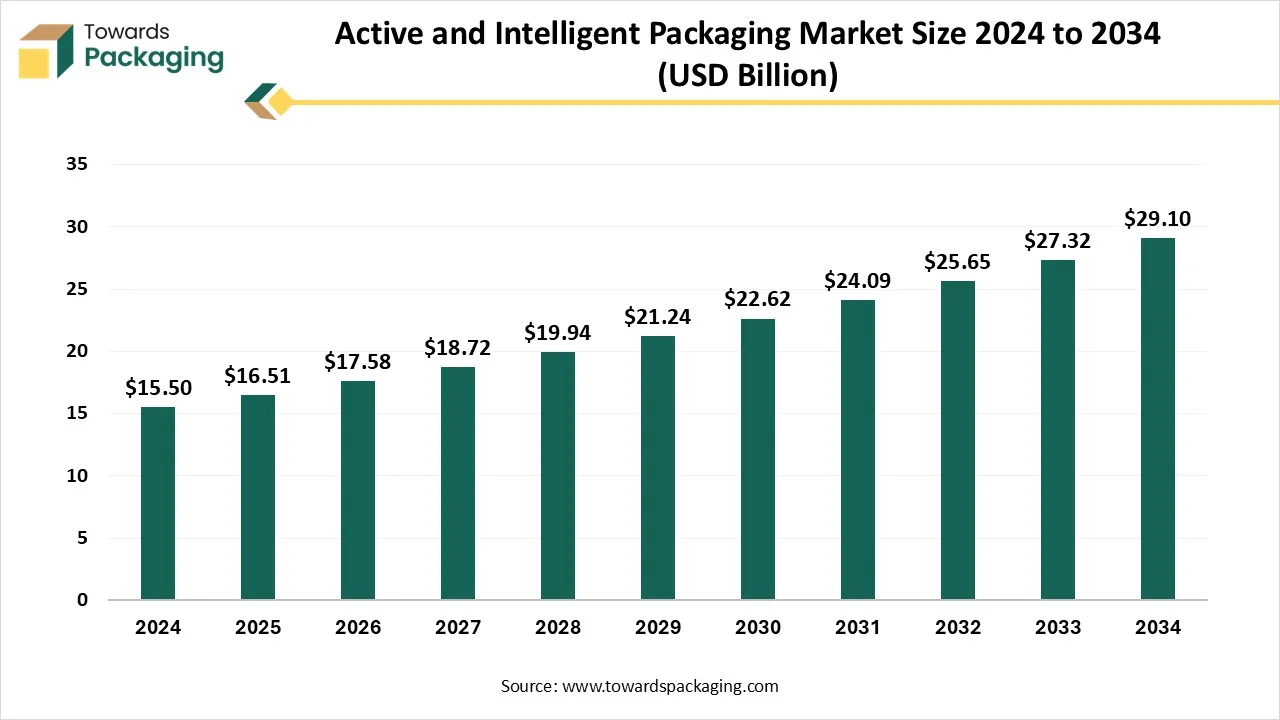
The active and intelligent packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 17.58 billion in 2026 to USD 30.99 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2026 to 2035. The report covers trends such as RFID, TTIs, smart labels, QR/NFC, AI integration, and provides quantified data by function (shelf-life extension 50%, product integrity monitoring 20%, etc.), material (plastics 55%, biopolymers 7%, and others), and end-use industries (food & beverage 48%, healthcare & pharmaceuticals 20%, etc.), along with trade data, value chain analysis, and detailed manufacturer & supplier information.
Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the market is valued at USD 16.51 billion in 2025.
- The market is projected to reach USD 30.99 billion by 2035.
- Rapid growth at a CAGR of 6.5% will be observed in the period between 2025 and 2034.
- North America dominated the active and intelligent packaging market with the largest revenue share of 34% in 2024.
- The Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the market.
- By technology type, the active packaging segment contributed the biggest revenue share of 60% in 2024.
- By technology type, the intelligent packaging segment will expand at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By material type, the plastics segment contributed 55% revenue share in 2024.
- By material type, the biopolymers segment will expand at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By function, the shelf life extension segment dominated the market with a share of 50% in the year 2024.
- By function, the product integrity monitoring segment is expected to grow significantly over the studied period
- By end-use industry, the food and beverage segment contributed 48% revenue share in 2024.
- By end-use industry, the healthcare and pharmaceuticals segment will expand at a significant CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
Market Overview
The global active & intelligent packaging market involves advanced packaging systems that go beyond traditional containment and protection by enhancing shelf life, monitoring product conditions, and improving consumer interaction. These solutions are widely applied across industries like food & beverage, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, logistics, cosmetics, and electronics. Smart packaging pertains to packaging that utilises technology to develop the user experience. It consists of the main elements: active packaging and intelligent packaging. Active packaging communicates with the product. It can incorporate oxygen or release preservatives. This assists in expanding shelf life and tracking quality. Intelligent packaging serves to convey information about the product's condition. It may contain sensors that examine freshness or temperature.
Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market Trends
- RFID Technology: RFID tags are electronic devices that use radio waves for transferring data to RFID readers. These tags have an antenna and a microchip to store the information about tagged items. One of the benefits of Ultra High Frequency (UHD) is the capability to manage items in real time throughout the supply chain. They also have anti-counterfeiting capabilities and can be utilised for inventory management.
- Smart Labels: Quick-response (QR) codes are two-dimensional bar codes that store information. Whenever scanned with a smart device, QR Codes can easily pass a certain procedure, whether it's directing the user to a particular website or beginning a payment transaction. In Active and intelligent packaging, QR codes can take patients to descriptions or take patients to particular content, such as directional video content on how to use the product.
- Tamper-Evident Packaging: TTI’s and tamper-evident packaging are utilised for tamper-evident packaging, displaying indicators that the packaging has already been opened. Most particular tamper-evident packaging uses closures, labels, and seals. Organizations that invest in tamper-evident seals, holographic seals, and sterilization from unauthorized labels, helping patients to stay safe and secure and grow compliance with sector and standards.
- Temperature Monitoring: Time-temperature indicators (TTI) are intelligent devices that manage thermal history. The device imaginarily shows if a product has been discovered to be at a temperature beyond a particular threshold for a particular condition. The temperature indication assists in determining whether the product is still secured. In addition to TTI, chemical indicator inks show whether particular conditions, such as sterilisation or chemical exposure, have been met.
- Microchips: Sensors or microchips are utilised to record data on the packaging and product. Built-in sensors gain data from an activity that involves the package or product and upload the data to a cloud source.
AI Integration in Active and Intelligent Packaging Market
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is fastly changing sectors across the globe, and the packaging industry is no exception. From production and design to quality control and logistics, AI-powered software is making sure the latest era of sustainability, efficiency, and invention. AI is changing the way packaging is crafted. Generative design algorithms can quickly make hundreds of capable packaging designs depending on particular elements like material constraints, product information, and even aesthetic choices. This ultimately develops the design procedure that allows companies to discover a wider range than would be possible with regular procedures.
Algorithms can examine historical sales data, market trends, and other factors to predict upcoming demand for packaging materials. This assists companies in reducing waste, inventory levels, and avoiding stockouts. AI-powered systems can update warehouse layouts and inventory management, develop efficiency, and lower storage costs.
Market Dynamics
Driver
The global active and intelligent packaging technologies can significantly expand the shelf life of vegetables and fruits. BY constantly tracking internal conditions, these systems can track temperature and humidity fluctuations, preventing contamination and spoilage. A main takeaway is that the dual role of smart packaging is food security. Primarily, it makes sure that optimal storage conditions are met, lowering risks linked with decomposition and microbial growth. Secondarily, its tracking characteristics serve users with real-time insights into food quality, allowing more informed purchasing decisions.
Restraint
The incorporation of high-level technologies like trackers and sensors can increase the cost of packaging. Medium-scale and small businesses may find it challenging to use them. Executing active and intelligent packaging needs to meet current systems, such as supply chain management software. This can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, too. Collecting and keeping consumer data creates privacy problems that need to be solved through robust data security measures and compliance with regulations. The cost of incorporating high-level technologies can be high, and there may be issues about data security and privacy, specifically with IoT-enabled packaging. Furthermore, a huge spread of acceptance needs partnerships between producers, retailers, and users to ensure compatibility and effectiveness.
Opportunity
Like regular packaging procedures, active and intelligent packaging can capture and share valuable information automatically, lowering manual tasks and the risk of human error. The urge for faster, more accurate deliveries is greater than ever, and sectors are under pressure to ensure smooth operation and customer satisfaction. Smart packaging aligns with these demands by serving precise, up-to-the-date data on products as they shift through every stage of delivery and production. Furthermore, smart packaging serves important environmental advantages. By vanishing errors and developing effectiveness, it cuts down on wasted materials and unwanted shipments, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint. This is heavily important as consumers and businesses alike prioritize sustainability.
Segmental Insights
How did Active Packaging Dominate the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market?
Active packaging brings a step forward by communicating with the product or its surroundings to maintain quality. For example, oxygen absorbers in food packaging prevent wastage, while moisture absorbers control moisture levels. Some pharmaceutical organizations use temperature-regulating material to make sure that medicines stay stable during transit. This kind of packaging is especially expensive for sensitive goods and products. In sectors like pharmaceuticals, food, and electronics, tracking and controlling product integrity is important.
Active packaging expands its shelf life and lowers waste by diminishing damage or spoilage during transportation. Active packaging plays a crucial role in expanding the shelf life of products. It communicates with the product or the surroundings to track freshness and quality. Oxygen scavenger elements in packaging incorporate oxygen, which can cause food spoilage. By removing oxygen, the packaging maintains the product fresh longer.
- On 23 June 2025, Vidre+ has developed product servings, increased profits with active packaging, and reduced markdowns. Fresh Inset's technology allows growers to be perfectly equipped for longer transport paths for their produce and does not require the latest infrastructure.
Intelligent Packaging is the Fastest-growing Technology Type in the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market.
Intelligent packaging includes technologies like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification ), NFC ( Near Field Communication), sensors, and QR Codes. This packaging includes packaging with a bustle, changing it into a dynamic area of invention and information. An important element of intelligent packaging is its potential to serve real-time data analytics. Intelligent packaging has adopted augmented reality to create captivating brand experiences. Users can scan packaging with their smartphones to unlock communicative materials, developing engagement and viral product trials, and leaving a lasting impression.
How Have Plastics Dominated the Material of the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market?
Plastic is prevalently utilised in different industries because of its low cost, long durability, and long performance too. It is specifically well-suited for packaging, as many forms of plastic are allowed to withstand heavy environmental conditions. Hence, it is accurately using elements that also make it non-biodegradable and toxic to the environment. Governments and international organisations can impose regulations that solve the main exporters and polluters, while also fostering worldwide co-operation.
Biopolymers/ Bio-based Materials are the Fastest-growing Material for the Active and Intelligent Packaging Market.
Biopolymers are gaining attention as an environmentally friendly alternative to regular petroleum-based plastics, especially in the packaging sector. PLA and starch-based plastics stand out, for example, celebrated for their biodegradability and compostability. These materials are derived from renewable resources such as sugarcane or corn-starch procedure, which only contributes to lowering carbon emissions but also assists in decreasing the accumulation of waste in landfills.
The acceptance of PLA and biopolymer in different packaging uses -from disposable cutlery to agricultural films and food packaging-shows their practical utility and rising adoption in industries such as actively finding sustainable alternatives. Further expanding their capability beyond packaging, research is diligently discovering the potential of biopolymers in high-value uses that were regularly dominated by conventional plastics and metal.
How did the Shelf-life Extension Function Dominate the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market?
The importance of shelf life extension is complicated. For users, it transforms food waste at home and provides access to products that remain fresh for a longer time. For businesses, it means to stretch market reach, decrease spoilage loss, and develop possibilities. From a huge societal point of view, effective shelf life extension invests in huge food security, resource conservation, and environmental sustainability by lowering waste and improving resource utilization. Going beyond passive updation, active packaging includes elements that release or absorb substances into or from packaged food or the headspace.
Product Integrity Monitoring is the Fastest-growing Function in the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market.
Global active and intelligent packaging ensures product safety by making sure and by tracking quality in real-time and examining issues like spoilage, contamination, or temperature fluctuations. For instance, in the food industry, active packaging can identify unsafe conditions during production and transportation, and lower waste through proactive alerts. This potential makes sure products remain safe while lowering losses. By using active and intelligent packaging technologies like moisture regulators and oxygen absorbers, smart packaging creates perfect surroundings inside the package, which prevents spoilage and extends freshness. These solutions are specifically valuable for sensitive products, mainly reducing product adaptability by preserving quality for longer periods.
How do Food and Beverage Company Uses the End-use Industry for the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market?
Active and Intelligent packaging is widely utilized in the food and beverage industry. In the food sector, it assists in reducing waste and improving safety by utilizing sensors that manage temperature exposure and freshness indicators that display if a product is still safe to consume. Smart labels also serve expiry dates and storage details, which make sure consumers have precise product information. For example, oxygen scavengers, which are specifically composed of iron-based compounds, are widely used in food packaging to lower oxygen levels inside a sealed package. This slows down oxidation, an initial cause of food deterioration. Meat and dairy products, which are highly vulnerable to spoilage because of oxygen exposure, benefit mainly from these solutions.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals are the Fastest-growing End-user Industries for Global Active and Intelligent Packaging.
In pharmaceuticals and healthcare solutions, active and intelligent packaging solutions can protect against drug degradation by tracking environmental conditions. For instance, temperature-sensitive packaging can track drug viability, with reports showcasing effectiveness levels remaining about 90% throughout shipping. This growth in smart packaging, subject to nanotechnology, is changing how sectors monitor and maintain track integrity, which leads to enhanced safety and quality assurance for users.
By Region
How did North America dominate the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market?
North America has a strong concentration on invention and technology. Several companies are investing in active and intelligent packaging to improve product safety and freshness. Users are also very aware of safety and food quality, which drives the demand for packaging that serves more information and protection, too. Additionally, the trend towards sustainability has encouraged organizations to accept eco-friendly packaging solutions. Consumer choices, strict regulatory standards, and major investments in technological growth are further fueling the region's industry expansion.
Asia Pacific is the Fastest-growing Region in the Global Active and Intelligent Packaging Market.
The urge for active and intelligent packaging is rising quickly in Asian Countries due to growing food security, urbanization, and a stretched middle class. Countries like China, India, and Japan are experiencing increased use of packaged food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, too, driving the demand for packaging that expands the product shelf life, tracks product quality and ensures safety. Active packaging solutions such as oxygen scavengers, moisture absorbers and antimicrobial growth are gaining attention across pharma, food and FMCG sectors. Furthermore, rigid regulations and growing exports are pushing producers to accept smart and functional packaging technologies.
- On 1 July 2025, Cilicant, which is India's top name in the active packaging industry, continues to have remarkable strides in ensuring product safety, sustainability across industries, and shelf life extension. At the currently finished ProPak Asia 2025 held from 11th to 14th June 2025 in Bangkok, Thailand, Manisha Jain, who is a co-founder and managing director of Cilicant, has shared the company's inspiring journey, inventions, and aim for the future.
Future of Active Packaging Market
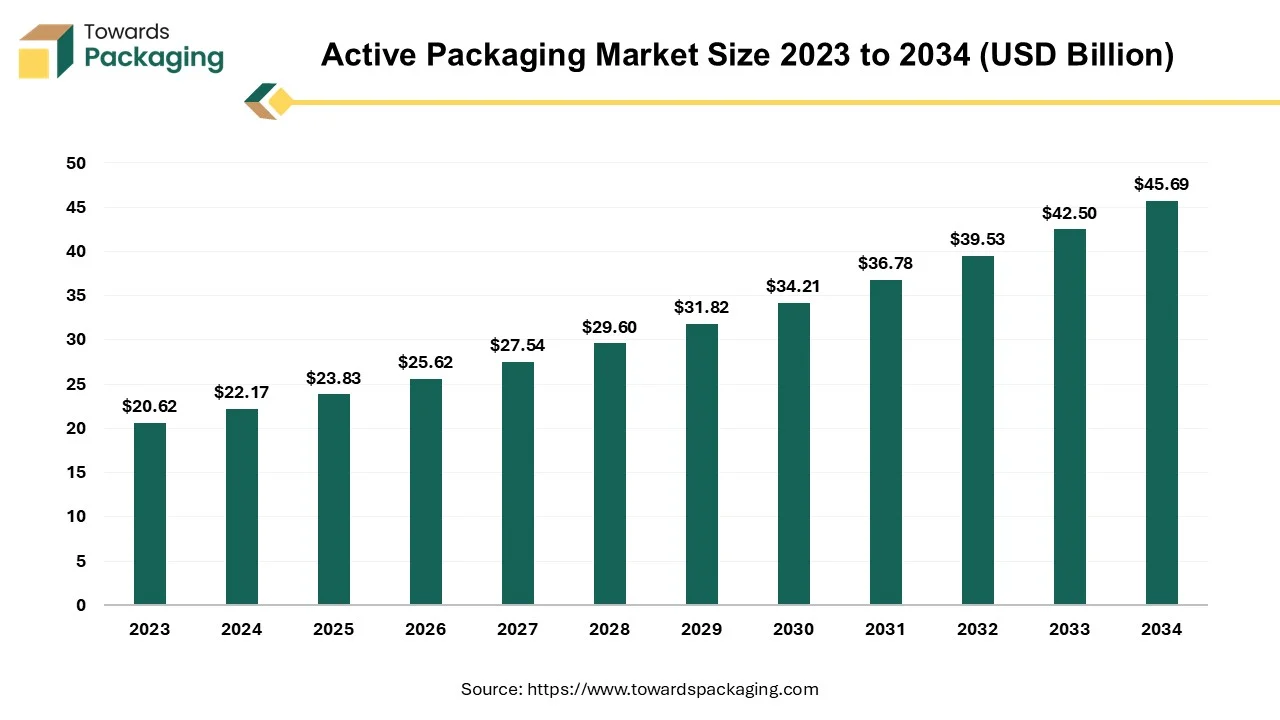
The active packaging market is projected to reach USD 45.69 billion by 2034 growing from USD 22.17 billion in 2024, expanding at a rapid CAGR of 7.5% between 2025 and 2034. The rising consumer demand for fresh and minimally processed products drives the need for packaging that preserves quality and extends shelf life. The expansion of online food and pharmaceutical sales increases the requirement for packaging that ensures product safety and freshness during transportation.
The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like acquisition and merger to develop advance technology for manufacturing active packaging which is estimated to drive the global active packaging market over the forecast period.
The advanced type of packaging engineered to interact with the product which contains to extend shelf-life, maintain quality, and enhance safety is known as active packaging. The active packaging only serves as a passive barrier, active packaging actively responds to environmental changes and improves the condition of the packaged product. The key functions of active packaging are extending shelf life, maintaining freshness, enhancing safety, and improves product quality.
Future of Intelligent Packaging Market
The global intelligent packaging market is set to grow from USD 29 billion in 2025 to USD 65.09 billion by 2034, with an expected CAGR of 9.4% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The rise in demand for safer, traceable, and tamper-proof products across sectors like food, pharma, and e-commerce is driving the shift toward advanced solutions. The growing consumer need for transparency, combined with regulatory pressure to ensure product integrity, is accelerating market expansion.
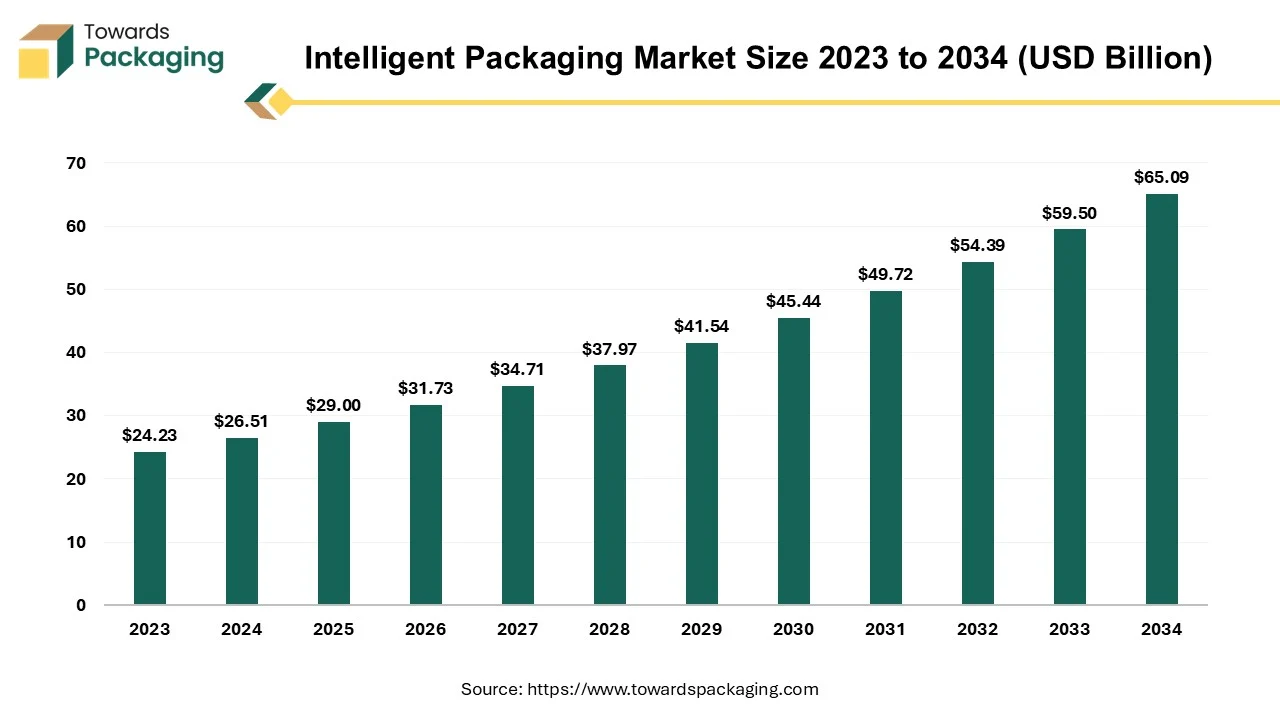
Intelligent packaging creates interactive and useful packaging solutions by fusing cutting-edge technologies with conventional packaging. It is made to satisfy consumer demands for longer shelf lives, safer food products, and better customer service. The packaging interacts with the environment and provides clients with extra benefits by utilizing cutting-edge technology like sensors, RFID tags, and QR codes. It can trace the goods along the supply chain, keep an eye on its condition, and give customers pertinent information. Furthermore, cutting-edge elements like augmented reality (AR) experiences are frequently used in smart packaging to improve the overall customer experience.
Top Companies in the Active and Intelligent Packaging Market

- Amcor Plc
- Sealed Air Corporation
- Avery Dennison Corporation
- Tetra Pak International S.A.
- 3M Company
- Thinfilm Electronics ASA
- BASF SE
- R.R. Donnelley & Sons Company
- Temptime Corporation (now part of Zebra Technologies)
- Smartrac N.V. (Avery Dennison)
- Freshpoint (Mitsubishi Gas Chemical)
- Cryolog S.A.
- Huhtamaki Oyj
- Multisorb Technologies (Filtration Group)
- Vitsab International AB
- Stora Enso Oyj
- UPM-Kymmene Corporation
- Identiv, Inc.
- Sorbent Systems (IMPAK Corporation)
- Systech International (a Markem-Imaje company)
Segmentation of the Active & Intelligent Packaging Market
By Technology Type
- Active Packaging
- Oxygen Scavengers
- Moisture Absorbers
- Antimicrobial Packaging
- Ethylene Absorbers
- CO₂ Emitters
- Intelligent Packaging
- Time-Temperature Indicators (TTIs)
- Smart Labels & RFID
- Near Field Communication (NFC) Tags
- QR Codes & Augmented Reality (AR) Features
- Sensors (gas, freshness, leakage)
By Material
- Plastics (PET, PE, PP, etc.)
- Paper & Paperboard
- Glass
- Metal
- Biopolymers / Bio-based Materials
- Films & Coatings (Barrier, Antimicrobial, Nanocoatings)
By Function
- Shelf-Life Extension
- Product Integrity Monitoring
- Consumer Engagement
- Anti-counterfeiting & Authentication
- Traceability & Supply Chain Visibility
By End-Use Industry
- Food & Beverage
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Logistics & Cold Chain
- Consumer Electronics
- Industrial & Chemicals
- Retail & E-Commerce
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
List of Figures
- Figure 1. Global Active & Intelligent Packaging Market Size (USD Billion), 2025–2034
- Figure 2. Market Share by Region, 2024 – North America 34%, Europe 25%, Asia Pacific 20%, Latin America 12%, Middle East & Africa 9%
- Figure 3. Market Share by Technology Type, 2024 – Active Packaging 60%, Intelligent Packaging 40%
- Figure 4. Breakdown of Active Packaging, 2024 – Oxygen Scavengers 20%, Moisture Absorbers 12%, Antimicrobial Packaging 10%, Ethylene Absorbers 8%, CO₂ Emitters 10% (remaining 40% other active technologies)
- Figure 5. Breakdown of Intelligent Packaging, 2024 – Time-Temperature Indicators 10%, Smart Labels & RFID 12%, NFC Tags 6%, QR Codes & AR Features 6%, Sensors (gas/freshness/leakage) 6%
- Figure 6. Market Share by Material, 2024 – Plastics 55%, Paper & Paperboard 15%, Glass 10%, Metal 8%, Biopolymers 7%, Films & Coatings 5%
- Figure 7. Market Share by Function, 2024 – Shelf-Life Extension 50%, Product Integrity Monitoring 20%, Consumer Engagement 12%, Anti-counterfeiting & Authentication 10%, Traceability & Supply Chain Visibility 8%
- Figure 8. Market Share by End-use Industry, 2024 – Food & Beverage 48%, Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals 20%, Cosmetics & Personal Care 10%, Logistics & Cold Chain 8%, Consumer Electronics 6%, Industrial & Chemicals 5%, Retail & E-commerce 3%
- Figure 9. CAGR Growth by Technology Type, 2025–2034 – Fastest: Intelligent Packaging
- Figure 10. CAGR Growth by Material, 2025–2034 – Fastest: Biopolymers / Bio-based Materials
- Figure 11. CAGR Growth by Function, 2025–2034 – Fastest: Product Integrity Monitoring
- Figure 12. CAGR Growth by End-use Industry, 2025–2034 – Fastest: Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
- Figure 13. Value Chain Analysis of Active & Intelligent Packaging
- Figure 14. Competitive Landscape: Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3 Companies
List of Tables
- Table 1. Global Active & Intelligent Packaging Market Size (USD Billion), 2025–2034
- Table 2. Regional Market Share, 2024 – North America 34%, Europe 25%, Asia Pacific 20%, Latin America 12%, Middle East & Africa 9%
- Table 3. Technology Type Market Share, 2024 – Active Packaging 60%, Intelligent Packaging 40%
- Table 4. Active Packaging Sub-segments, 2024 – Oxygen Scavengers 20%, Moisture Absorbers 12%, Antimicrobial Packaging 10%, Ethylene Absorbers 8%, CO₂ Emitters 10%, Others 40%
- Table 5. Intelligent Packaging Sub-segments, 2024 – Time-Temperature Indicators 10%, Smart Labels & RFID 12%, NFC Tags 6%, QR Codes & AR Features 6%, Sensors (gas/freshness/leakage) 6%
- Table 6. Material Market Share, 2024 – Plastics 55%, Paper & Paperboard 15%, Glass 10%, Metal 8%, Biopolymers 7%, Films & Coatings 5%
- Table 7. Function Market Share, 2024 – Shelf-Life Extension 50%, Product Integrity Monitoring 20%, Consumer Engagement 12%, Anti-counterfeiting & Authentication 10%, Traceability & Supply Chain Visibility 8%
- Table 8. End-use Industry Market Share, 2024 – Food & Beverage 48%, Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals 20%, Cosmetics & Personal Care 10%, Logistics & Cold Chain 8%, Consumer Electronics 6%, Industrial & Chemicals 5%, Retail & E-commerce 3%
- Table 9. Key Market Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities
- Table 10. Emerging Innovations in Active & Intelligent Packaging (RFID, NFC, QR, TTI, Antimicrobial Films)
- Table 11. AI Integration in Packaging – Applications Across Design, Forecasting, and Supply Chain
- Table 12. Regional Growth Opportunities & Regulations Supporting Smart Packaging
- Table 13. Value Chain Analysis – Material Selection, Manufacturing, Distribution, Consumer Engagement
- Table 14. Competitive Landscape – Profiles of Leading Companies
- Table 15. Recent Developments & Strategic Initiatives (2024–2025)
Tags
FAQ's
Select User License to Buy
Figures (4)