Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market Size, Growth Forecast, Value Chain & Trade Flows, Manufacturers
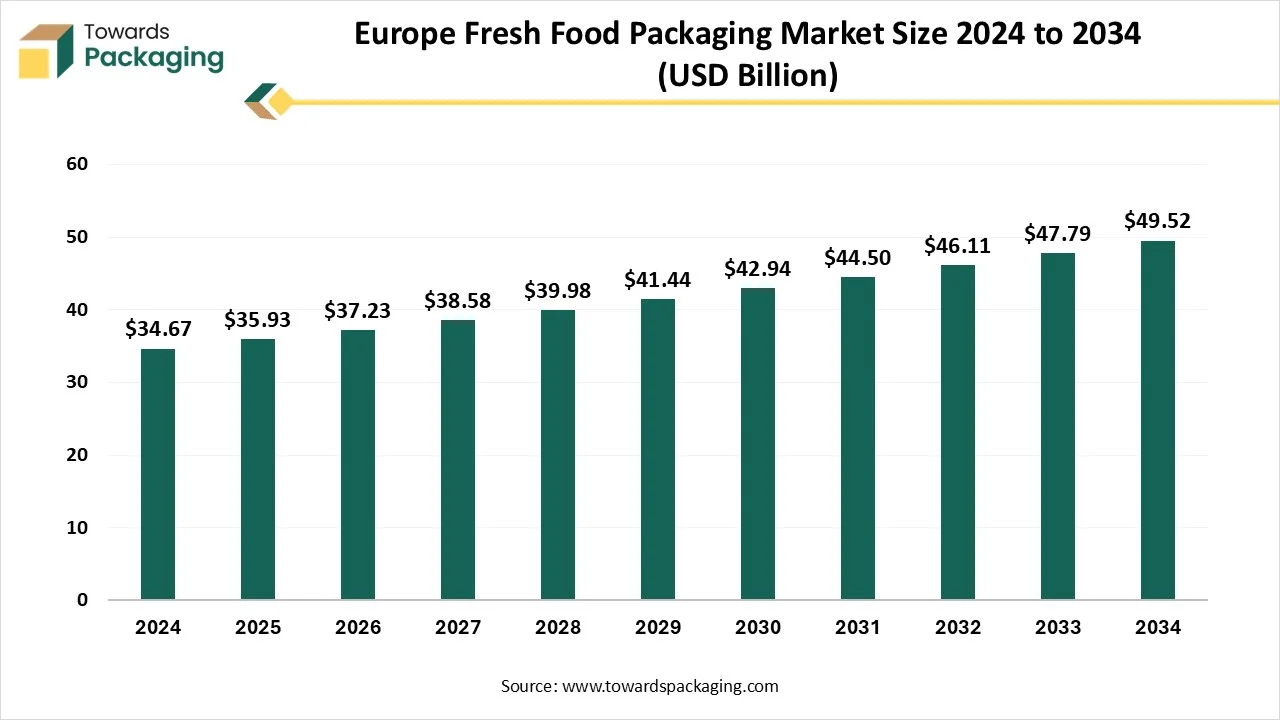
The Europe fresh food packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 37.23 billion in 2026 to USD 51.32 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 3.63% from 2026 to 2035. The market is led by Western Europe in 2024, with Northern Europe as the fastest-growing region, and is driven by demand for fresh, convenient, and sustainably packed food.
Our report covers detailed market size and growth data, including segment shares such as flexible packaging (40% in 2024), plastic materials (50%), fruits & vegetables (35%), shelf-life extension functionality (45%), and MAP technology (30%). It also benchmarks Europe within global trends, including the global fresh food packaging market (USD 95.0 to 132.08 billion, 3.35% CAGR), food packaging (USD 427.40 to 746.98 billion, 5.7% CAGR), frozen food, seafood, and hot-fill packaging.
Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the market is valued at USD 35.93 billion in 2025.
- The market is projected to reach USD 51.32 billion by 2035.
- Rapid growth at a CAGR of 3.63% will be observed in the period between 2025 and 2034.
- Western Europe dominated the global market with the largest revenue share in 2024.
- Northern Europe is expected to grow at a notable CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By packaging type, the flexible packaging segment contributed the biggest revenue share of 40% in 2024.
- By packaging type, the rigid packaging segment is expected to be the fastest growing segment, growing at a CAGR in 2024
- By material, the plastics segment dominated the market in 2024 with a 50% share.
- By material, the biodegradable /compostable segment is expected to grow significantly over the studied period.
- By technology, the modified atmosphere packaging segment dominated the market in 2024, with a share of 30%.
- By technology, the active packaging segment is the fastest-growing one.
- By end-use food category, the fruits and vegetables segment dominated the market in 2024 with a 35% share.
- By end-use food category, the ready-to-eat meals segment is expected to grow significantly over the studied period.
- By Functionality, the shelf life extension segment dominated the market in 2024 with a 45% share.
- By functionality, the convenience and on-the-go packaging segment is expected to grow significantly over the studied period.
Functions and Importance
The Europe fresh food packaging market refers to the industry involved in the design, manufacturing, and distribution of packaging solutions used to preserve the freshness of food products across various categories. This market includes packaging solutions for fruits, vegetables, meat, poultry, seafood, dairy, bakery products, and ready-to-eat meals, aimed at extending shelf life, ensuring safety, and enhancing convenience. It encompasses a wide range of materials such as plastic, paper, glass, and metal, along with specialized packaging technologies such as modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), vacuum packaging, and active packaging.
Sustainable packaging is also crucial. Options like compostable, biodegradable, or recyclable packaging meet with eco-conscious brand values, with several consumer flavors. For instance, paperboard and cardboard are widely recyclable, while bioplastics are compostable in industrial settings. One of the main functions of oxygen is to encourage food's freshness and shelf life. Current developments in food packaging have allowed for the usage of modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) and oxygen scavengers to help regulate the amount of oxygen that comes into contact with food. This assists in stopping oxidation and the growth of toxic microbes, which can lead to spoilage.
Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market Trends
- Sustainable packaging solutions: As sustainability remains a main priority, the manufacturing sector is heavily concentrating on eco-friendly packaging solutions to align with consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices and less waste. Compostable and biodegradable options like PLA (polylactic acid), cellulose films, and mushroom-based packaging are substituting for regular plastics. Also, materials like seaweed wraps and cellulose films assist in lowering waste and dependence on fossil fuels while supporting the circular economy by decomposing without toxic residues.
- Minimalist and reduced packaging: Minimalist packaging is becoming a crucial step in the produce sector to lower waste and environmental effects. By utilising fewer materials, like reducing plastic layers and accepting durable designs, lightweight organizations can protect the environment while decreasing material usage. This trend matches with user demand for more sustainable options and assisting businesses in adhering to rigid environmental regulations.
- Edible packaging: Edible packaging is expected to experience significant development, specifically in the manufacturing industry. Created from plant-based materials like starch, seaweed, edible films, or rice, can be consumed together with the produce, vanishing packaging waste completely. This creative solution not only lowers environmental effects but also develops user experience by incorporating the packaging into the product itself, being part of the food instead of waste.
- Smart packaging for freshness and traceability: Smart packaging is transforming the way produce is managed, tracked, and supervised. Technologies like QR Codes, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Tags), and freshness sensors are allowing real-time tracking of produce throughout the supply chain. These inventions assist in making sure that produce is fresh, reducing food waste and spoilage. This packaging also serves transparency, enabling consumers to conveniently access information about a product's origin, nutritional content, and sustainability practices.
- Plant-based and natural fibre packaging: Plant-based materials, such as hemp, bamboo, and palm leaves, are becoming heavily popular in the manufacturing packaging sector because of their biodegradability, strength, and sustainability. These natural packaging materials are perfect for packaging heavy produce such as potatoes, onions, and bananas, as they serve effective protection during storage and transportation while reducing environmental effects.
- Recyclable and reusable packaging: Reusable and recyclable packaging is ready to become a foundation of sustainability in the assembling sector, mainly reducing its environmental footprint. Packaging created from recycled PET (rPET) and other recyclable materials serves as an effective solution to reduce the backbone of single-use plastics, which are the main source of pollution.
AI Integration in Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation in packaging manufacturing will considerably improve sustainability and efficiency within the manufacturing industry. AI-driven systems can update packaging patterns and designs, making sure that materials are utilised more effectively, while diminishing waste and resource consumption. Automated production lines will accelerate the procedure, lower human error, and streamline operations, leading to more accurate and constant packaging.
These technologies will also build supply chain management, enabling better tracking of packaging materials and finished goods, which can reduce inefficiencies and delays. AI systems allow for real-time data analysis, allowing companies to guess demand, adjust packaging accordingly, and ensure that products are packaged in the most sustainable way possible.
Market Dynamics
Driver
The packaging should be personalized to the particular storage conditions of the product. Whether the food needs to be frozen, refrigerated, or stored at room temperature, the packaging must resist these conditions without compromising the product's quality. For frozen foods, puncture-resistant packaging and flexibility are perfect, while shelf-stable items might benefit from packaging that includes UV Protection to prevent degradation from light exposure. Also, the packaging design plays a crucial role in attracting users. Easy-to-open designs, clear labelling, and resealable features can mainly improve the user's experience. A perfectly designed package can convey the brand's values and messages, making the product more appealing on the shelf. Furthermore, different ingredients have several sensitivities to environmental elements. For instance, dried fruits and nuts are more open to moisture, while dairy products need more protection.
Restraint
Research has identified over 36,000 chemicals from food packaging that are detected in the human body, with at least 76 hazardous. Bisphenols are found in metal and plastic can linings, as these endocrine disruptors have been linked to reproductive problems and hormonal imbalance. Phthalates are utilised to make plastics more flexible; these chemicals can interfere with hormone function, that have been linked with developmental disorders. Polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are being identified in grease-resistant fast food wrappers, microwave popcorn bags, and pizza boxes as these "forever chemicals " have been linked to cancer, immune suppression, and thyroid dysfunction. Apart from this, small plastic materials from bottles and packaging have been found in food, water, and even human organs. Babies consuming from plastic bottles may consume up to 4.5 million microplastic particles daily.
Opportunity
High Pressure Processing (HPP) Packaging utilises high-pressure cold water to kill pathogens while protecting flavors and nutrients. This procedure expands the shelf life of fresh juices, dairy products, and ready-to-eat meals without heat-based pasteurization, tracking a more natural texture and taste. Nanotechnology is developing as a transformational path to food preservation. Nano-coatings on packaging materials make antimicrobial barriers, avoiding bacterial oxidation and growth. The nano-encapsulation procedure also enables controlled release of antimicrobials and antioxidants to keep food fresh for a long time. Buyers demand more clarity regarding nutritional information, ingredient sourcing, and environmental impact. Latest regulations require packaging to include recyclability, clean labelling, carbon footprint indicators, and allergen warnings.
- On 21 January 2025, the European-funded REDYSIGN project has been concentrating on doing its part to reduce the polluting plastic packaging for fresh meat products. The projects' sustainable alterations to fossil-based packaging are recyclable and bio-based solution, which includes the use of wood-derived materials.
- On 21 May 2025, Freshr had finished an oversubscribed seed funding round for its proprietary antimicrobial coating for recyclable, recycled, and compostable fresh fish packaging, a solution crafted to expand shelf life, save money, and reduce waste.
Segmental Insights
How did Flexible Packaging Dominate the Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market?
Flexible packaging has dominated the market because the main objective of food preservation is to make a protective environment that shields the inherent qualities of the food. The barrier features of flexible packaging shield prevent contents from exterior factors, texture, and preserve flavor and nutritional value. By lowering the exposure to light and moisture, flexible packaging hinders the procedure, which leads to spoilage. This, then, expands the shelf life of food products, lowering the food waste and making sure that users delight in products at their freshest. Various food products have different preservation demands. Flexible packaging enables personalization, making sure that the packaging solution is particularly crafted to match the needs of the enclosed food item, whether it's sensitive fresh produce or strong snack items.
- On 9 July 2025, Karri Koskela, the CEO of Wipak, was chosen and elected chair of Flexible Packaging Europe (FPE), which is a trade association representing over 80 companies in the European flexible packaging sector. He succeeds Jakob A Masser, who had the role for five years.
Rigid packaging is the fastest-growing packaging type Rigid packaging, such as some plastics and glass, is a huge part that can be recycled. These materials are more sustainable when accurately controlled. They lower the reliance on virgin resources and enable effective recycling. This kind of packing is a component of the circular economy, in which resources are kept in use for as long as possible due to being recyclable. Rigid packaging serves as perfect and long-lasting protection and is utilised for products such as canned drinks and food. With the assistance of rigid packaging, products stay fresh for a longer time, reducing food waste and significantly assisting environmental sustainability.
How did Plastic Dominate the Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market?
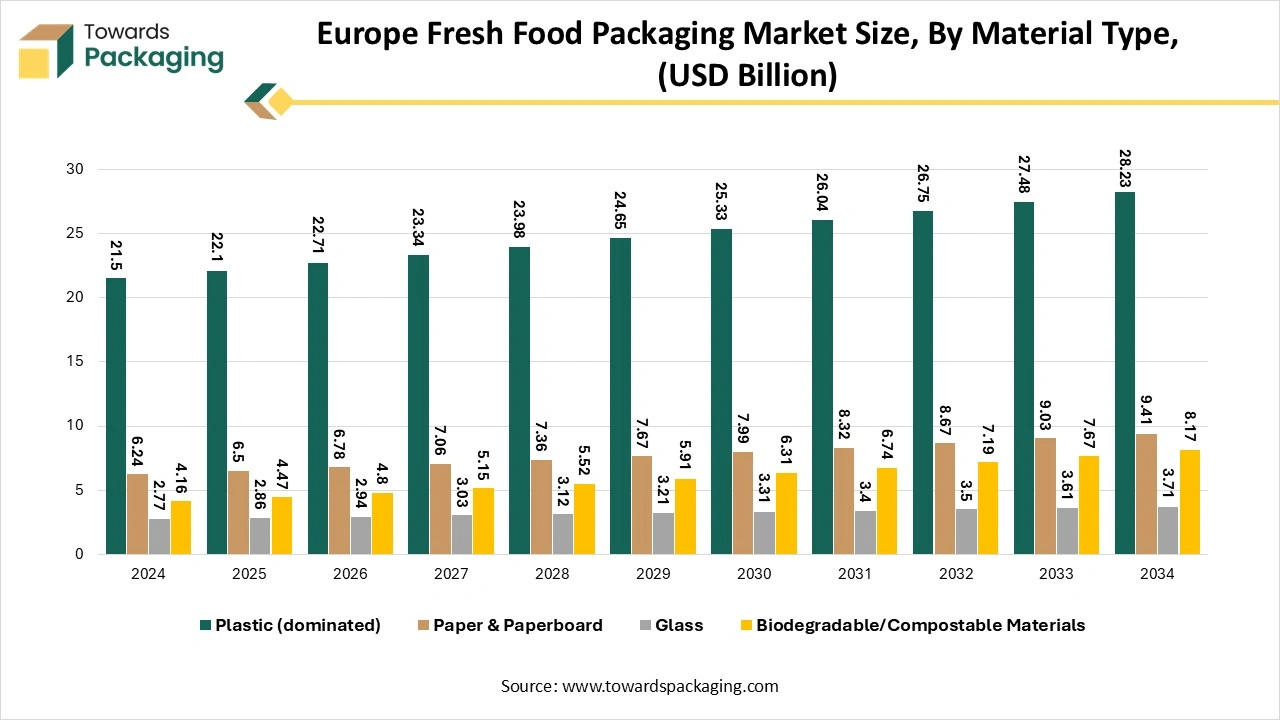
Plastic packaging has dominated the market as it assists in protecting food from natural deterioration over time. It performs this via physical, chemical, and biological protection. Plastic is the most effective material when it comes to preventing these sources. Other gases and oxygen are specifically toxic to most foods. These gases assist in accelerating the deterioration process, which is why plastic is utilised as a protective barrier. It has chemical protection against the different chemicals in the environment. Physical protection refers to the prevention of food from physical damage, such as unexpected force during carrying. It also protects from mechanical damage, which occurs during shipping. The plastic actually assists in absorbing much of the shock after vibration, which is prevalent during distribution and shipping.
- On 3 March 2025, plastics technology licensor Axens and plastics recycling organization company SOREMA revealed the collaboration to serve integrated solutions for the mechanical and chemical recycling of plastic waste.
Biodegradable /Compostable Materials are the Fastest-growing Material
One of the most important trends in the food packaging sector is the move towards compostable and biodegradable materials. These eco-friendly alterations are created from renewable, natural sources like sugarcane, cornstarch, and cellulose. Just like regular plastics, which can take many years to decompose, biodegradable packaging breaks down naturally, lowering the strain on landfills and reducing pollution. While biodegradable packaging is initially known for its environmental advantages, it also plays an important role in food protection. Several biodegradable films have perfect barricade properties that protect the food from oxygen, moisture, and bacteria, thereby expanding the shelf life. The adaptability of these materials enables their use in a wide range of food packaging products, from pouches to bags to containers.
- On 7 May 2025, the latest Horizon Europe-funded FRECO project serves inventive biodegradable, bio-based, and recyclable food packaging depending on novel PLA Copolymers, additives, functional coatings, and green catalysts.
How did Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) Dominate the Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market?
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP ) has dominated the market as it adjusts the air inside the package to expand the shelf life of fresh food products. The most commonly used gases include carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and oxygen, although this relies on the product. For instance, oxygen is generally utilised for packaging red meat products as it controls the myoglobin levels to keep the meat bright red. Hence, punctures, rips, or improper packaging result in issues throughout the supply chain, damage the seal integrity of the package, and indirectly affect product quality. Integrated with continuous cooling, MAP can significantly improve the freshness and can result in a shelf life 2 to 5 times higher than packages with regular air.
On 3 February 2025, StePacPPC collaborated with Windham Packaging to create a series of bulk modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), whose goal is to develop shelf life for fresh produce heading to rescue waste, foodservice outlets, and develop operational efficiency.
Active Packaging is the Fastest-growing Technology
Active packaging also leads to food preservation, which directly communicates with the ingredient or the surroundings to maintain quality. Famous instances include antimicrobial coatings and moisture-absorbing sachets. Moisture control inhibits food from becoming saturated or dead, as found with baked snacks and goods. Furthermore, antimicrobial films that use substances such as organic lids or silver ions assist in reducing the development of harmful microorganisms. Producers often mix antimicrobial properties into the packaging material, including the growth of harmful fungi and bacteria, which is important for storing sensitive items such as meat and seafood.
- On 14 February 2025, Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology have packaged canned Tuna included in the water-based solution of amino acid cysteine, which removes up to 35% of the accumulated mercury.
How did the Fruits and Vegetables Dominate the Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market?
Fruits and vegetables have dominated the end-use market because, with the initial concentration on packaging to ensure food safety, they also play a crucial role in marketing. Informative and attractive packaging can catch the user's attention and communicate the product's benefits and quality. Also, fruits and vegetable packaging behave as a barrier against impurities like viruses, bacteria, and physical debris. Accurate packaging materials prevent contamination, storing the product fresh and safe for consumption. Proper packaging plays a crucial role in expanding the shelf life of food products. By protecting food from environmental factors like moisture, oxygen, and light, packaging helps preserve the nutritional quality and taste of the food.
Ready-to-eat Meals are the Fastest-growing End-use Food Category
Ready-to-eat meals, which are sometimes known as Ready-to-serve or Ready-to-cook, refer to a variety of packaged quantities that users can consume with minimal additional preparations, along with simple reheating. Also, they are coordinated with a rising trend named grab-and-go foods. But these classifications sometimes can intersect; the grab-and-go category is more concentrated on snack-sized portions and includes several lighter food choices. Ready-to-eat meals are most likely to serve the advantage of whole nutritional meals, including multiple ingredients and dishes or entree-style servings.
How did the Shelf-life Extension Dominate the Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market?
Shelf-life extension has dominated the market as it relies on several factors, including the type of food, the environment in which the food is stored, and the material in which the food is packed. In addition to extending the shelf life, barrier packaging also assists in keeping food free from pollutants and microbial growth, which makes it easier to transport and helps sensitive foods maintain their nutritional value while they're in storage for an extended period of time. Shelf life extension enables manufacturers to reach a huge industry, lowering the frequency of restocking and updating inventory management. Hence, balancing freshness with grown longevity serves as a limitation.
Convenience and On-the-go Packaging are the Fastest-growing Functionalities
Convenience and on-the-go packaging mean food products that offer consumers options for quick snacks, easy take-home meals, and healthy fresh foods. It includes any pre-packaged food items crafted for instant consumption without additional preparation. These products are commonly portioned for particular usage, kept in refrigerated and ambient showcases, and intended to be grabbed quickly by busy consumers. It can be found in various settings than ever, including easy grocery chains, stores, airports, cafes, and institutional settings like hospitals and schools. The convenience and on-the-go packaging is classified by its importance on portability, speed, and minimal hassle: no waiting in line with hot preparation, no demand for utensils beyond what is counted.
By Region
How did Western Europe Dominate the Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market?
Western Europe has completely dominated the market as users, specifically Gen Z, heavily find healthy and functional foods, which are wrapped in fresh food packaging, which is an opportunity for grocers. The demand for healthy options is rising, especially for functional, fresh, and clean food. Healthy food and options that serve additional food advantages are considered functional food. Gen Z is the group of users finding healthy selections as it has the highest growth of shoppers, focusing on healthy nutrients. As compared to the previous year, the net intent of Gen Z shoppers to focus on healthy eating increased by several percentage points. Furthermore, one in three members of Gen Z shows a willingness to pay more for luxury, premium, and perfectly packaged healthy food.
Northern Europe is the Fastest-growing Region
Northern Europe is the fastest growing region due to several reasons, like Fairtrade bananas from Colombia, Ecuador, the Dominican Republic, and Peru can be found in several supermarkets in Northern Europe. On the other hand, Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom (Northern Europe) are the biggest destinations for fruits and vegetables from developing countries. Consumers from these countries have gained a lot of experience in importing fresh fruits and vegetables from developing countries. European buyers from Northern Europe urge high-quality fresh produce with consistent quality, size, and freshness.
Future of Fresh Food Packaging Market
The fresh food packaging market is valued at USD 95 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 132.08 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 3.35% from 2025 to 2034. This steady expansion is driven by increasing demand for sustainable and efficient packaging solutions worldwide. The market is observed to grow due to the rising demand for convenience food items availability and to extend the shelf-life period of the food by premium packaging.
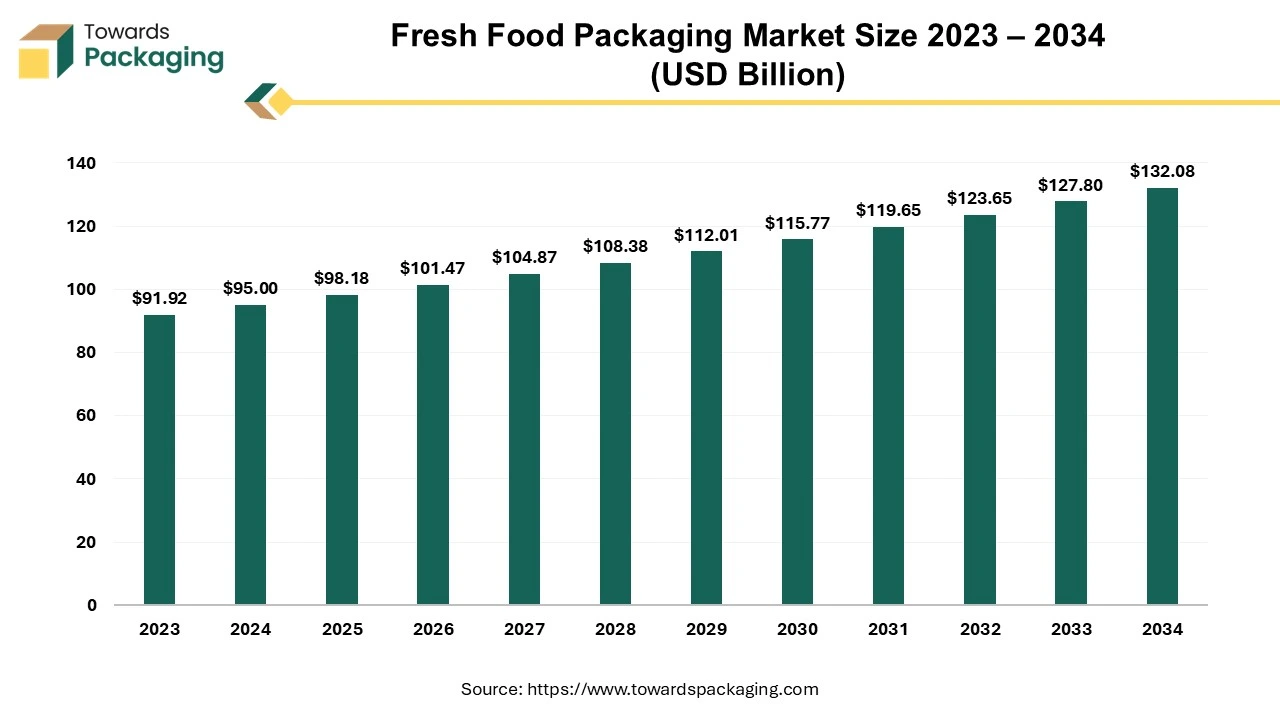
The fresh food packaging market is growing significantly due to the advanced packaging systems available. The rising tendency to eat healthy food has raised the concern for convenient, sustainable, and safe packaging. The major focus is to pack food to protect the quality of the food for a longer period and provide convenience to the consumers. This market contains a wide range of materials to manufacture suitable packaging products such as glass, plastic, paper, and various other biodegradable options. Rising concern for manufacturing eco-friendly products has raised the development of these packaging. The major factor behind the growth of this market is the increasing preference for fresh packaged foods, mainly in this changing lifestyle and rising awareness about the health and wellness of people.
Future of Food Packaging Market
The food packaging market is projected to reach USD 746.98 billion by 2034, growing from USD 427.40 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The rising demand for convenient, sustainable, and smart solutions driven by changing consumer lifestyles, health awareness and e-commerce growth is fueling market expansion. The surge in processed food consumption and global trade is also pushing innovation in material science and packaging functionality.
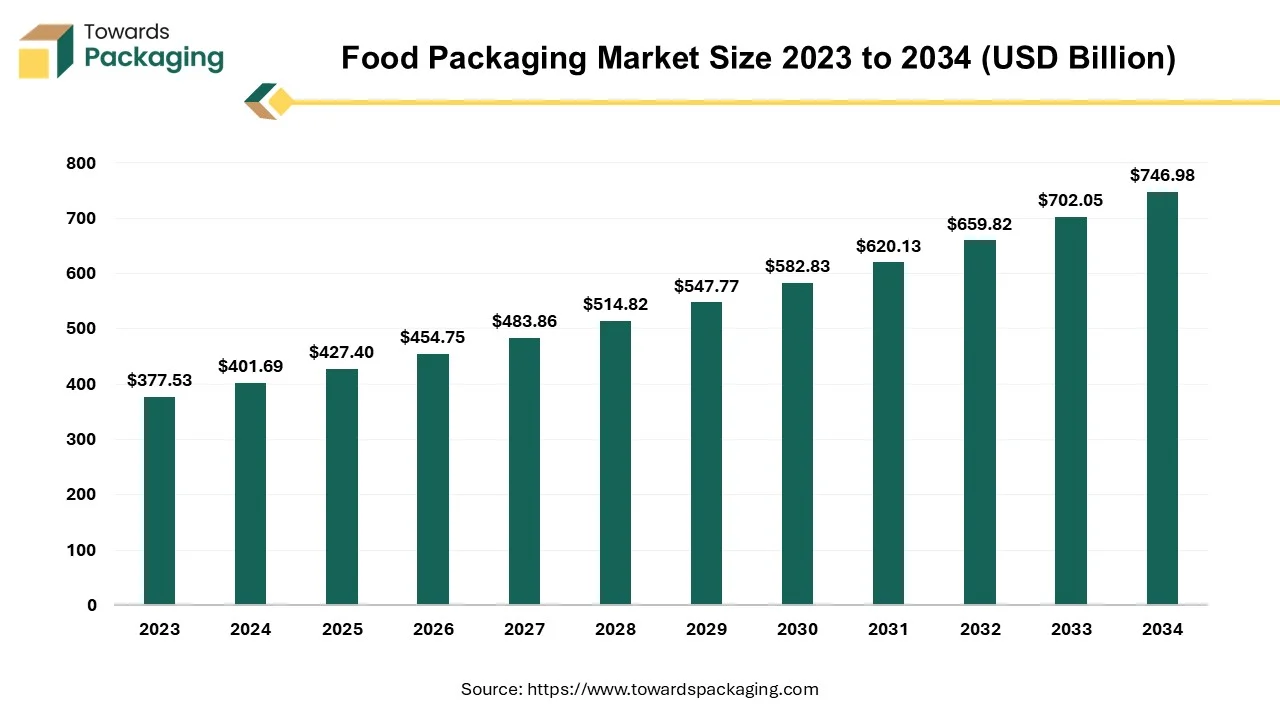
The methods and materials utilized to protect, contain, preserve, transport, and present food products is known as food packaging. It acts as a barrier between food and external factors like moisture, contamination, light, air, and physical damage ensuring the food remains fresh, safe, and appealing from production to consumption. The food packaging serves as practical purposes like: providing information (nutritional facts, expiry date, ingredients), facilitating storage and handling, supporting marketing and branding through design and messaging.
Future of Frozen Food Packaging Market
The frozen food packaging market is projected to reach USD 79.59 billion by 2034, growing from USD 47.94 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The growing preference for convenient, ready-to-eat meals and the rapid expansion of e-commerce grocery platforms have significantly fueled the market. The rise in cold chain logistics and smart, sustainable packaging innovations has further accelerated industry adoption.
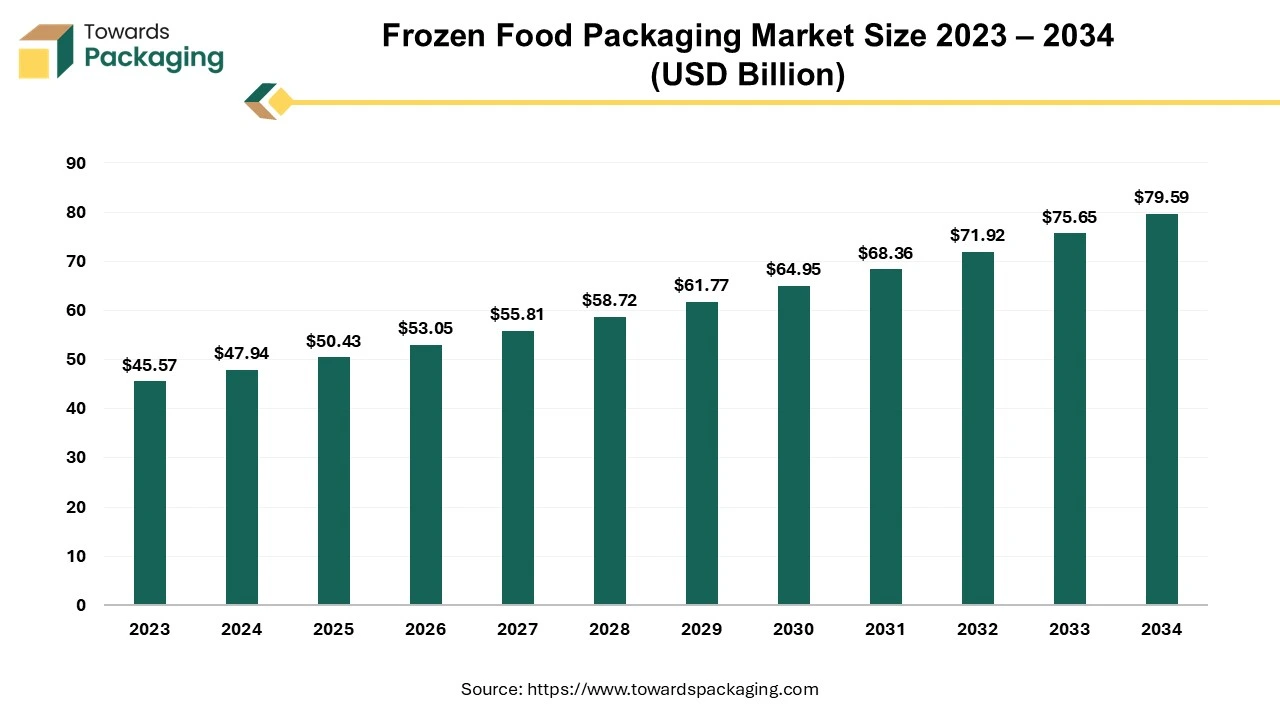
The specialized packaging materials and designs that protect food products stored at sub-zero temperatures (-18 degree Celsius) is known as frozen food packaging. It ensures food safety, freshness, extended shelf life by preventing moisture loss, freezer burn, and contamination. The frozen food packaging is temperature resistant, moisture resistant and vapour barrier. Different types of material utilized for manufacturing frozen food packaging have been mentioned here as follows: aluminium foil, plastic films, paperboard & cardboard, vacuum, and clamshell containers and rigid trays.
Future of Seafood Packaging Market
The global seafood packaging market size reached USD 15.58 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 27.12 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The rising consumption of seafood worldwide requires improved methods to preserve freshness and extend shelf life during distribution. The growing emphasis on environmental responsibility and regulatory compliance motivates the development of more sustainable and efficient solutions.
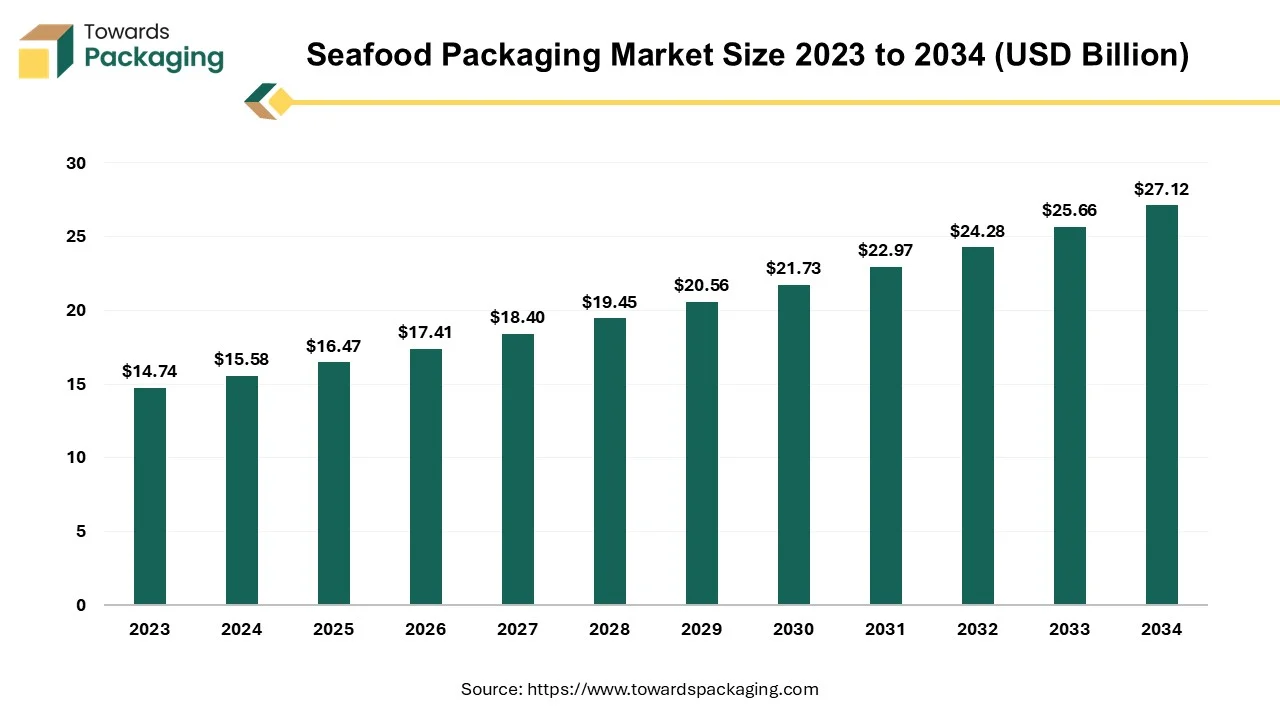
Seafood packaging refers to the specialized materials and techniques used to store, transport, and preserve seafood products while maintaining freshness, safety, and quality. Since seafood is highly perishable, packaging solutions must provide temperature control, moisture resistance, and protection from contamination. Fresh & frozen seafood packaging removes oxygen to slow bacterial growth and extend shelf life. Seafood packaging prevents spoilage by maintaining optimal temperature, humidity, and oxygen levels.
Future of Hot-fill Food Packaging Market
The hot-fill food packaging market is projected to reach USD 74.82 billion by 2034, growing from USD 53.67 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 3.76% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
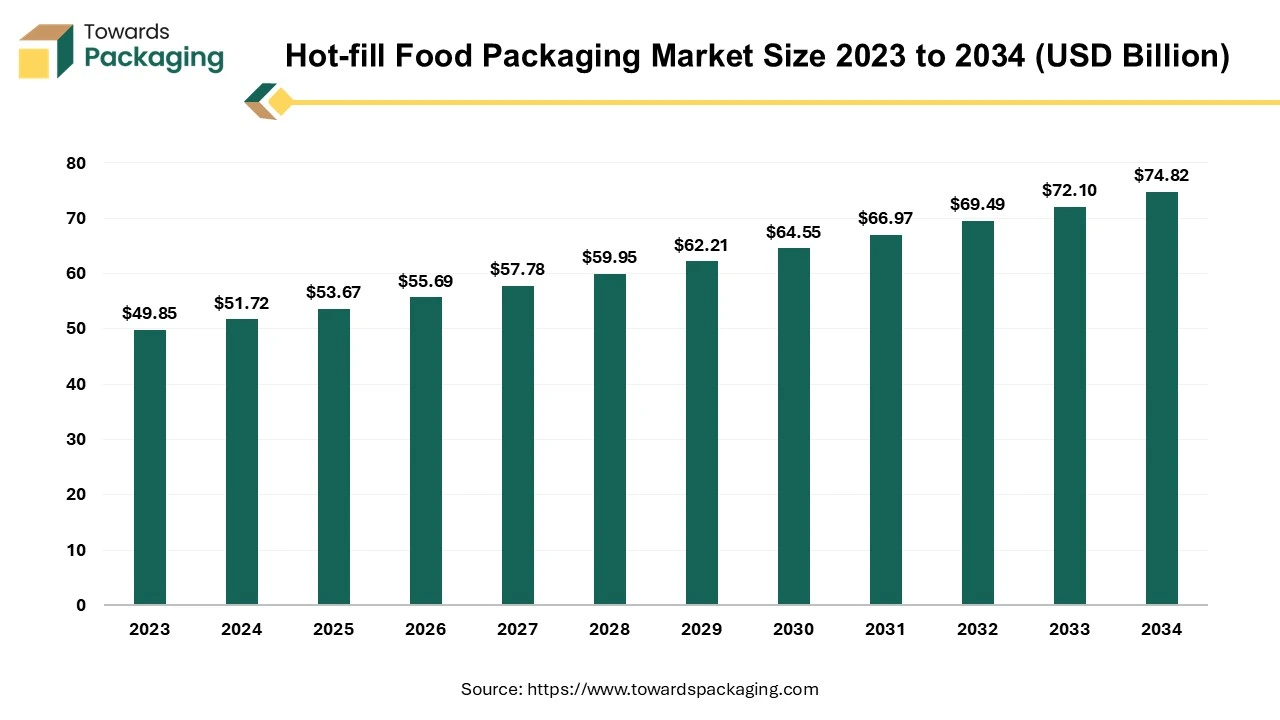
The hot-fill food packaging market is anticipated to augment with a considerable CAGR during the forecast period. A variety of packaging techniques are used by the food and beverages sector to maintain, preserve and increase the life span of the products that are consumed. Hot fill packing is among the most widely used methods for sterilizing the products like sauce, juice, or spread. With the use of heat and no preservatives, hot fill packaging extends the shelf life of the highly acidic foods and beverages under non-refrigerated environments. This aids in stopping the growth of the harmful bacteria that could ruin the products.
Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market Key Players

- Amcor
- Sealed Air Corporation
- Smurfit Kappa
- Mondi Group
- Berry Global, Inc.
- Huhtamaki Group
- Sonoco Products Company
- WestRock Company
- International Paper Company
- Tetra Pak
- Crown Holdings Inc.
- DS Smith
- RPC Group
- Plastipak Packaging, Inc.
- Uflex Limited
- Interpack
- Coveris Holdings S.A.
- Schur Flexibles Group
- Multivac Group
Industry Leader Announcement
- On 16 July 2025, LT Foods, a 70-year-old FMCG Company, revealed the expansion of its organic business arm, Nature Bio Foods Limited, into the Business-to-consumer segment in Europe. This growth follows the revelation of the new facility at Maasvlakte, Rotterdam, whose goal is to develop the organization's retail presence in the European organic food market.
Recent Developments
- On 15 January 2025, Cirkla, a sustainable packaging company, revealed the launch of its molded fibre Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) trays. As the primary and only company to serve this innovation, Cirkla's proprietary technology serves as a high-performance and sustainable alternative to MAP trays.
- On 9 April 2025, DS Smith and Primeale, which is a part of the agricultural and food processing group Agrial, partnered with plastic-free and fibre-based punnets for Primeale's vegetable kit range, crafted to protect the fresh produce during shipping, transportation, and on the supermarket shelf too.
- On 9 August 2024, in partnership with Swiss Cheese company Hardeggar Kse, Lidl Switzerland revealed the cellulose-based packaging created from leftover wood from different organic cheeses.
Europe Fresh Food Packaging Market Segments
By Packaging Type
- Flexible Packaging
- Bags
- Pouches
- Film
- Wrapping
- Other Flexible Formats
- Rigid Packaging
- Boxes
- Cartons
- Bottles
- Trays
- Containers
- Semi-Rigid Packaging
- Clamshells
- Cups
- Jars
- Other Semi-Rigid Formats
By Material Type
- Plastic
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Other Plastics
- Paper & Paperboard
- Kraft Paper
- Cardboard
- Coated Paper
- Other Paper-based Materials
- Glass
- Bottles
- Jars
- Metal
- Aluminum
- Tinplate
- Biodegradable/Compostable Materials
- Plant-based Plastics
- Edible Films
- Other Sustainable Materials
By Technology
- Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
- Vacuum Packaging
- Active Packaging
- Oxygen Absorbers
- Moisture Regulators
- Other Active Technologies
- Intelligent Packaging
- Sensors
- Indicators
By Functionality
- Shelf-Life Extension
- Tamper-Evidence
- Convenience & On-the-Go Packaging
- Portion Control
- Protection from Contamination
By End-Use Food Category
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Meat & Poultry
- Seafood
- Dairy Products
- Bakery Products
- Ready-to-Eat Meals
- Other Fresh Food Products








